The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that can collect, share, and analyze data without human intervention. These devices, often embedded with sensors and software, communicate over the internet, providing real-time information and automation.
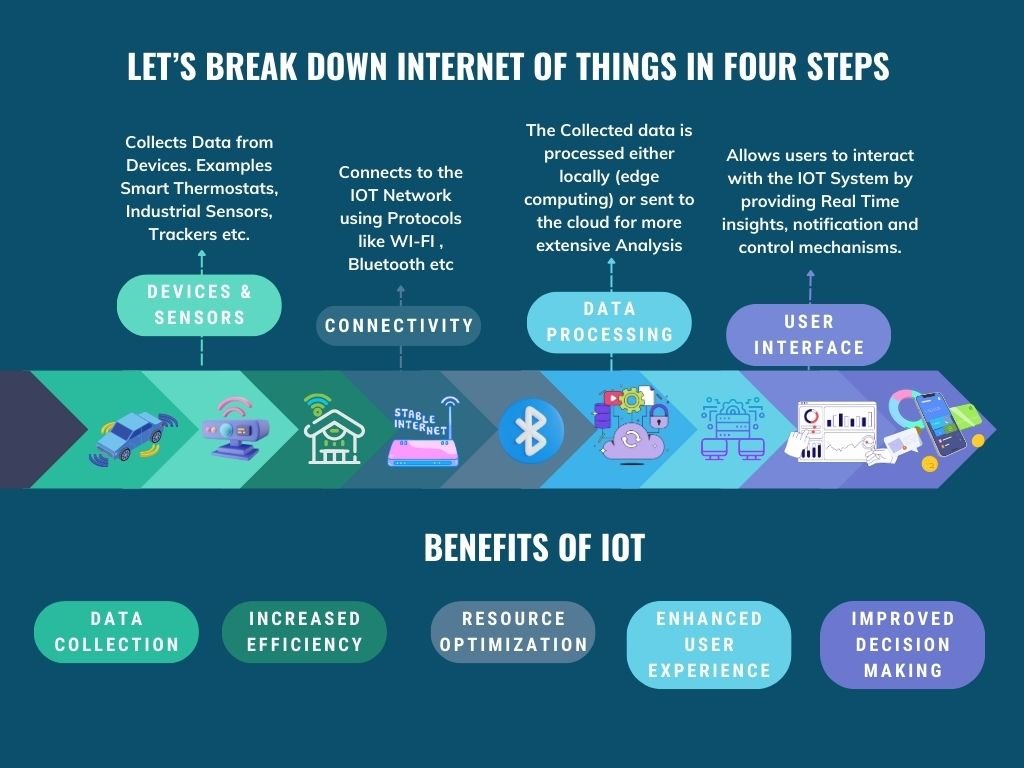
Key Components of IoT:
Devices and Sensors:
- These are physical objects like home appliances, wearables, industrial machines, vehicles, etc., equipped with sensors and actuators. Sensors collect data from the environment (temperature, humidity, motion, etc.).
Connectivity:
- Devices connect to an IoT gateway or directly to the internet using various communication protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks.
Data Processing:
- Once data is collected, it is processed either locally (edge computing) or sent to centralized servers (cloud computing). Processing can include real-time analytics, filtering, and actionable insights.
User Interface:
- The processed data is then made available to users through dashboards, apps, or other interfaces. Users can monitor, control, and interact with their IoT devices remotely.
Applications of IoT:
Smart Homes:
- IoT enables automation of home devices such as lighting, heating, and security systems, improving convenience, security, and energy efficiency.
Healthcare:
- Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems collect health data, enabling personalized healthcare, real-time monitoring, and improved patient outcomes.
Industrial IoT:
- In manufacturing, IoT sensors monitor equipment health, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
Smart Cities:
- IoT contributes to urban planning and management through smart traffic systems, waste management, environmental monitoring, and efficient energy use.
Agriculture:
- IoT devices monitor soil conditions, weather, and crop health, enabling precision farming and improving agricultural productivity.
Benefits of IoT:
- Efficiency and Automation: Automates routine tasks, reducing human effort and increasing productivity.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides real-time data for informed decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Optimizes resource use and reduces operational costs.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Improves service delivery and personalization.
Challenges:
- Security and Privacy: Ensuring data security and user privacy is a major concern.
- Interoperability: Integrating devices from different manufacturers can be challenging.
- Data Management: Handling large volumes of data effectively requires robust infrastructure.
The Internet of Things represents a significant shift in how we interact with technology, bringing more intelligence and connectivity to everyday objects and systems.


Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
canadian pharmacy in canada
https://expresscanadapharm.com/# canadian world pharmacy
canadian drug pharmacy
They have an extensive range of skincare products.
can you buy generic cipro without rx
Always up-to-date with international medical advancements.
Breaking down borders with every prescription.
get generic clomid without prescription
They take the hassle out of international prescription transfers.
Top 100 Searched Drugs.
can you get generic cipro
They have expertise in handling international shipping regulations.
Love their spacious and well-lit premises.
a cosa serve il farmaco gabapentin
Get warning information here.
Their global pharmacists’ network is commendable.
cost cheap cytotec online
I appreciate their late hours for those unexpected needs.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
where can i get cheap clomid price cost cheap clomid for sale cost of cheap clomid without insurance can i purchase cheap clomiphene without a prescription order generic clomiphene pills clomiphene contraindications clomiphene medication for women
I’ll certainly bring to review more.
The thoroughness in this draft is noteworthy.
buy zithromax for sale – flagyl where to buy buy flagyl generic
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
domperidone 10mg price – buy sumycin without prescription buy flexeril 15mg sale
buy inderal no prescription – order inderal 10mg online cheap methotrexate 2.5mg without prescription
purchase amoxil online cheap – buy ipratropium 100mcg pills ipratropium 100mcg uk
azithromycin 500mg tablet – buy bystolic 20mg pills nebivolol 5mg generic
order augmentin 625mg sale – atbio info buy acillin online
cost nexium – anexa mate buy esomeprazole 20mg generic
warfarin price – https://coumamide.com/ buy losartan 50mg sale
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
buy mobic pills for sale – https://moboxsin.com/ meloxicam for sale
deltasone 40mg cost – adrenal order deltasone generic
best ed pills online – site over the counter ed pills
buy amoxicillin tablets – buy amoxicillin without prescription cheap amoxil for sale
diflucan 200mg ca – https://gpdifluca.com/# buy cheap forcan
cenforce 100mg cheap – https://cenforcers.com/ cost cenforce 50mg
when should you take cialis – https://ciltadgn.com/ buying cheap cialis online
tadalafil and sildenafil taken together – generic cialis 5mg cialis overnight shipping
buy zantac 300mg online – https://aranitidine.com/# buy zantac generic
50 or 100mg viagra – https://strongvpls.com/ where can i buy cialis or viagra on line
More content pieces like this would create the web better. https://gnolvade.com/
I’ll certainly bring back to review more. amoxil without prescription
This is the kind of advise I turn up helpful. https://ursxdol.com/amoxicillin-antibiotic/
More posts like this would force the blogosphere more useful. https://prohnrg.com/product/metoprolol-25-mg-tablets/
I couldn’t weather commenting. Profoundly written! https://aranitidine.com/fr/en_france_xenical/
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
More posts like this would prosper the blogosphere more useful. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
With thanks. Loads of knowledge! where to buy generic motilium no prescription
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/en-NG/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/en-IN/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
The depth in this ruined is exceptional. http://furiouslyeclectic.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=24634
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
purchase dapagliflozin pills – https://janozin.com/# forxiga 10mg over the counter
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
xenical cost – janozin.com purchase xenical online
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
With thanks. Loads of erudition! http://iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=916843
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! sign up binance
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! binance
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! create a binance account
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. create binance account
Reading your article has greatly helped me, and I agree with you. But I still have some questions. Can you help me? I will pay attention to your answer. thank you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
You can keep yourself and your dearest close being wary when buying prescription online. Some druggist’s websites operate legally and sell convenience, privacy, sell for savings and safeguards as a replacement for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/kamagra.html kamagra
More posts like this would bring about the blogosphere more useful. TerbinaPharmacy
The vividness in this piece is exceptional.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for another informative site. Where else could I get that type of information written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/ka-GE/register?ref=ILE8IH9H
Just signed up on b66club.net! So far, so good. If you are looking for a new place, give it a try with this link: b66club
I tried to find something intresting, Goperyalogin is not bad choice. Website is easy to see, and have many game. Try it here: goperyalogin
Hello, Neat post. There’s a problem with your web site in web explorer, might test this… IE nonetheless is the marketplace leader and a good part of people will leave out your magnificent writing due to this problem.
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Whoa! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Superb choice of colors!
Really clear internet site, regards for this post.
Just signed into 789betmpls to place my bets. Feeling good, hoping to score some big wins! Good luck to all the serious betters out there! Find out more 789betmpls.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/register-person?ref=IXBIAFVY
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
Oi, judibola828bet, eh? A bit of a gamble, innit? But hey, if you fancy a punt, give it a go! Just remember, gamble responsibly! judibola828bet
There is perceptibly a bunch to identify about this. I assume you made some good points in features also.
люстра в комнату деревянная люстра
Играешь в казино? апх Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
заклепка вытяжная 4 8 заклепка вытяжная
За год использования кракен маркет даркнет ни разу не подвёл с доступом
дизайн окон дома дизайн коттеджа
дизайн прихожей в квартире дизайн двухкомнатной квартиры
теплый полотенцесушитель полотенцесушитель сталь купить
накрутка подписчиков тик ток накрутка подписчиков инстаграм
Занимаешься спортом? блины на штангу на заказ диски для пауэрлифтинга, бодибилдинга и фитнеса. Прочные покрытия, стандартные размеры и широкий выбор весов.
Wonderful work! This is the type of information that are meant to be shared across the internet. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this publish higher! Come on over and talk over with my site . Thank you =)
Осваиваешь арбитраж? https://corsairmedia.ru поможет разобраться в инструментах, выбрать первую партнерку и избежать типичных ошибок новичков. Подробные обзоры от практиков: плюсы, минусы и реальные цифры заработка без воды.
online casino real money no deposit
best real money online casinos
online blackjack olga
Лучшее онлайн казино? https://pokerinfo.ru/download/index.html онлайн-покер, турниры и кэш-игры для игроков разного уровня. Удобный интерфейс, доступ с ПК и мобильных устройств, регулярные события и акции.
Нужен стим аккаунт? общий аккаунты стим доступ к библиотеке игр по выгодной цене. Совместное использование, подробные условия, инструкции по входу и рекомендации для комфортной игры.
Здарова народ!
Наткнулся на годную тему.
Может кому пригодится.
Подробности здесь:
[url=https://eb-bayer.de/]блэкспрут тор[/url]
Всем удачи!
врачебная косметология услуги клиники косметологии
Всем привет!
Увидел любопытную статью.
Решил поделиться.
Линк:
[url=https://eb-bayer.de/]рулетка блэкспрут[/url]
Как вам?
betmgm РћРќ betmgm-play mgm 200 free bet
Всем привет!
Увидел годную информацию.
Решил поделиться.
Подробности здесь:
[url=https://gccassociation.org/]кракен ссылка onion[/url]
Пользуйтесь на здоровье.
Всем привет!
Наткнулся на полезную статью.
Думаю, многим будет полезно.
Смотрите тут:
[url=https://fieldmore.dk]Mega ссылка[/url]
Всем удачи!