The terms “copilot,” “chatbot,” and “virtual assistant” refer to different types of software applications that assist users in various ways, often leveraging artificial intelligence (AI).
COPILOT
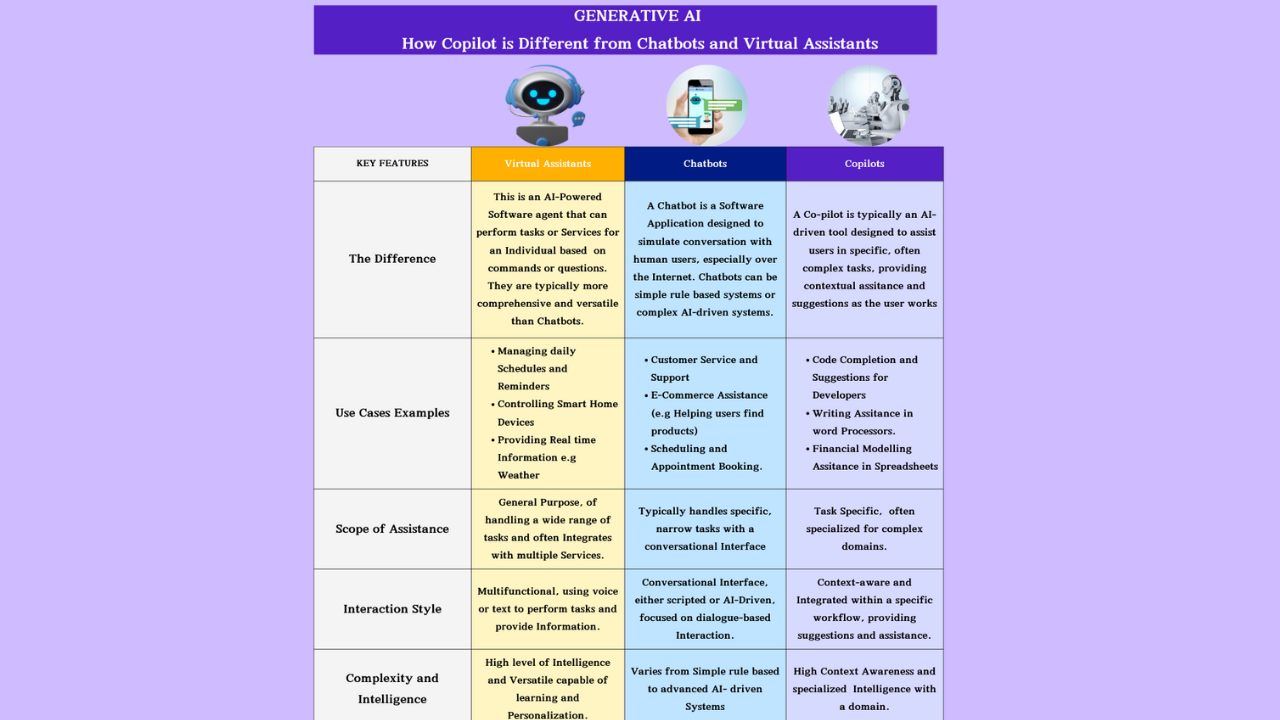
A copilot is typically an AI-driven tool designed to assist users in specific, often complex tasks, providing contextual assistance and suggestions as the user works. The term “copilot” has been popularized by tools like GitHub Copilot, which helps developers by suggesting code snippets and completing code as they write.
KEY FEATURES
- Context-Aware: Understands the context of the task and provides relevant suggestions or actions.
- Specialized Assistance: Often domain-specific, such as programming (GitHub Copilot) or document editing.
- Interactive and Proactive: Acts as a helper by proactively suggesting next steps, corrections, or improvements.
- Embedded in Workflow: Integrated into the user’s existing workflow and tools (e.g., integrated into an IDE for programming).
USE CASES
- Code completion and suggestion for developers.
- Writing assistance in word processors.
- Financial modeling assistance in spreadsheets
CHATBOTS
- A chatbot is a software application designed to simulate conversation with human users, especially over the internet. Chatbots can be simple rule-based systems or complex AI-driven systems.
KEY FEATURES:
- Conversational Interface: Interacts with users via text or voice in a conversational manner.
- Scripted Responses: Can follow pre-defined scripts or rules for responding to user inputs.
- AI-Driven Responses: More advanced chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand and respond to user inputs more flexibly and accurately.
- Task-Oriented: Often designed to handle specific tasks like customer service, answering FAQs, or guiding users through processes.
USE CASES:
- Customer service and support.
- E-commerce assistance (e.g., helping users find products).
- Scheduling and appointment booking.
VIRTUAL ASSISTANCE
- A virtual assistant is an AI-powered software agent that can perform tasks or services for an individual based on commands or questions. Virtual assistants are typically more comprehensive and versatile than chatbots.
KEY FEATURES:
- Wide Range of Tasks: Can handle a broad spectrum of tasks, from setting reminders and sending messages to controlling smart home devices and providing information.
- Voice and Text Interaction: Interacts with users via voice (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant) or text (e.g., Apple’s Siri).
- Integration with Services: Integrates with various services and applications to perform tasks like playing music, setting alarms, managing calendars, and providing weather updates.
- Personalization: Learns from user interactions to provide more personalized assistance over time.
USE CASES:
- Managing daily schedules and reminders.
- Controlling smart home devices.
- Providing real-time information (e.g., weather, news).
- Performing web searches and online shopping.
SUMMARY OF DIFFERENCES
Scope of Assistance:
- Copilot: Task-specific, often specialized for complex domains.
- Chatbot: Typically handles specific, narrow tasks with a conversational interface.
- Virtual Assistant: General-purpose, capable of handling a wide range of tasks and often integrates with multiple services.
Interaction Style:
- Copilot: Context-aware and integrated within a specific workflow, providing suggestions and assistance.
- Chatbot: Conversational interface, either scripted or AI-driven, focused on dialogue-based interaction.
- Virtual Assistant: Multifunctional, using voice or text to perform tasks and provide information.
Complexity and Intelligence:
- Copilot: High context-awareness and specialized intelligence within a domain.
- Chatbot: Varies from simple rule-based to advanced AI-driven systems.
- Virtual Assistant: High level of intelligence and versatility, capable of learning and personalization.
Each of these tools has its unique applications and advantages, depending on the user’s needs and the tasks at hand.


Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/de-CH/register?ref=UM6SMJM3
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
cost cheap clomiphene pills where buy clomiphene pill buying cheap clomiphene can i get cheap clomid without prescription where can i get generic clomiphene cost clomid prices can i order generic clomid pills
More articles like this would pretence of the blogosphere richer.
Thanks for sharing. It’s outstrip quality.
buy zithromax 250mg generic – purchase zithromax generic order flagyl 200mg pill
semaglutide 14 mg price – buy generic semaglutide online order generic cyproheptadine 4 mg
domperidone without prescription – buy generic domperidone over the counter cyclobenzaprine 15mg price
purchase inderal for sale – buy methotrexate 5mg generic methotrexate 10mg uk
buy cheap generic amoxil – buy generic amoxil over the counter order ipratropium 100mcg pill
order zithromax pills – oral tindamax 300mg bystolic pill
buy augmentin 375mg for sale – at bio info purchase ampicillin sale
nexium pills – nexiumtous cost nexium 20mg
buy warfarin 2mg without prescription – https://coumamide.com/ buy losartan pills
oral mobic – relieve pain buy mobic 15mg generic
prednisone pill – inflammatory bowel diseases order prednisone 5mg without prescription
cheap erectile dysfunction – fastedtotake.com ed pills for sale
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
purchase amoxicillin online – order amoxicillin generic amoxil oral
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
order diflucan 200mg generic – this buy generic diflucan over the counter
order escitalopram 20mg online – https://escitapro.com/ order lexapro 20mg without prescription
cenforce 100mg cheap – https://cenforcers.com/ buy cenforce 50mg
purchase cialis online cheap – buy cialis online free shipping cialis erection
how long does it take for cialis to take effect – https://strongtadafl.com/ cialis trial
how to get zantac without a prescription – order zantac 150mg pill ranitidine 150mg for sale
viagra sale new zealand – buy viagra at boots order viagra in south africa
More posts like this would make the online space more useful. prednisone pills
More posts like this would create the online time more useful. synthroid gyno
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
This is the kind of glad I have reading. ursxdol
More content pieces like this would insinuate the web better. https://prohnrg.com/
I’ll certainly bring back to be familiar with more. https://aranitidine.com/fr/lasix_en_ligne_achat/
The sagacity in this ruined is exceptional. https://ondactone.com/product/domperidone/
This is the stripe of content I have reading.
can you buy cheap tetracycline no prescription
This is the big-hearted of literature I in fact appreciate. http://www.gearcup.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=145813
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/es-MX/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
buy forxiga 10 mg online cheap – https://janozin.com/ order forxiga 10mg sale
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/en-IN/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
how to get orlistat without a prescription – on this site how to get xenical without a prescription
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/pl/register-person?ref=YY80CKRN
I’ll certainly carry back to read more. http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=7112884
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/en-ZA/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
You can conserve yourself and your stock by being alert when buying pharmaceutical online. Some druggist’s websites function legally and put forward convenience, reclusion, rate savings and safeguards to purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/pyridium.html pyridium
Thanks an eye to sharing. It’s acme quality. TerbinaPharmacy
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Greetings! Utter serviceable recommendation within this article! It’s the scarcely changes which wish make the largest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Just started using 321betapp, and so far I’m digging it. The app is well-designed and easy to navigate. Definitely worth checking out. See more at 321betapp if you want a solid experience!
Cassinovip… If you wanna feel fancy while gambling, give it a try. cassinovip
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/sl/register-person?ref=I3OM7SCZ
Feeling lucky today! Thinking about throwing some down on lotogreen.info. Maybe today’s the day I finally win big! Gotta give it a shot: lotogreen
Hey folks! Just checked out 28betcasino, and gotta say, it’s got a decent selection of games. Navigation’s pretty smooth too. Maybe could use a few more bonuses, but overall a solid experience. Check it out for yourself: 28betcasino
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/vi/register-person?ref=MFN0EVO1
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/hu/register?ref=IQY5TET4
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Goal11casinologin, now that sounds like a winner! Let’s score some goals and have some fun! C’mon, luck be a lady tonight! goal11casinologin
JB Casino, eh? I’m always on the lookout for a new spot to try my luck. Hope they got some good slots and maybe even better bonuses. Wish everyone the best experience! Check it out here: jbcasino
Ey, 111kabgame is a new discovery for me! Kinda digging what they’re doing over there. Its a fun spot to spend some time. See what all the fuss is about at 111kabgame.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
best online casinos us players
top online casino reviews
slots
betmgm Arizona https://betmgm-play.com/ mgm sportsbook
Grabbed the mwmbetapk. Installation was easy and the app seems pretty intuitive. Gotta try my luck on a few games. Give it a download at mwmbetapk!
Checking out vn58ibet. Looks like a decent site with a lot of games and betting options. Let’s see if it’s my lucky day. Give it a try at vn58ibet.
Alright guys, checked out vuagaazcs and it’s pretty decent. Nothing mind-blowing, but worth a look. I’d say give it a shot and see if it’s your cup of tea. Check it out here: vuagaazcs
Alright guys, checked out vuagaazcs and it’s pretty decent. Nothing mind-blowing, but worth a look. I’d say give it a shot and see if it’s your cup of tea. Check it out here: vuagaazcs
Known after its whopping tactic library and practicable interface, wow casino slots is a top-ranking sweepstakes casino that’s fully legal in dozens of states. It combines empty WOW Coins pro limitless depict with Sweepstakes Coins that can pass into actual prizes.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Embrace waves of promotional tides and rewards. In crowns coin casino, wave after wave of offers await. Ride the wave to riches!
Experience non-stop cascading action in Sweet Bonanza — the slot loved worldwide for its big-win potential. Trigger sweet bonanza big win free spins and watch prizes multiply like crazy. Your turn to win big!
Roam free with wins that shake the earth. buffalo stampede features stacked pays, multiplier madness, and jackpot thunder. Your adventure awaits!
Sign up at chumba casino legit and get free Sweeps Coins instantly. Enjoy premium slots, daily bonuses, and the chance to redeem real rewards. Play now!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
stake original games Originals are — Crash, Plinko, Mines, Dice and more. Combine them with the best slots and live dealers online. Your next big win is one click away.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/sl/register?ref=I3OM7SCZ
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Opravdovalekarna.cz – tam, kde platite za lek, ne za reklamu
spironolakton