In AI, RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) and Sequential (sequential models) refer to two different paradigms for processing and generating information:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG):
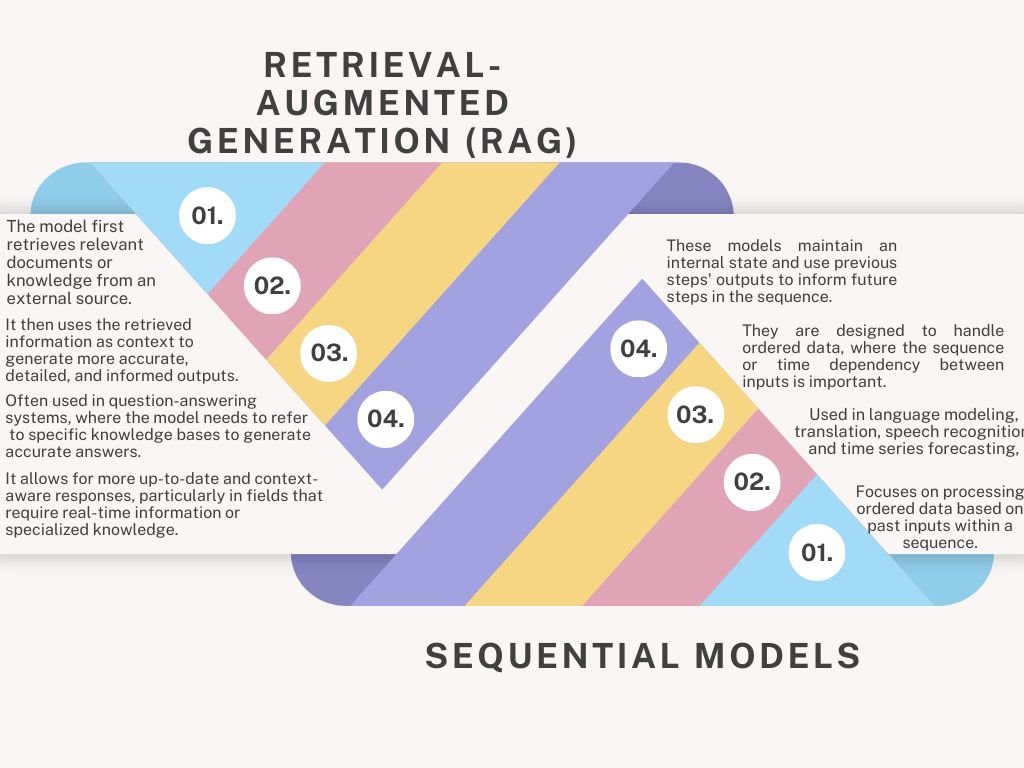
- Definition: RAG is a hybrid AI model that combines information retrieval and generation. It leverages external knowledge by retrieving relevant documents or data from a large corpus (such as databases or the web) and then uses a generative model (like GPT) to generate responses based on the retrieved information.
- Process:
- The model first retrieves relevant documents or knowledge from an external source.
- It then uses the retrieved information as context to generate more accurate, detailed, and informed outputs.
- Use Cases: Often used in question-answering systems, chatbots, and applications where the AI needs to refer to specific knowledge bases to generate accurate answers.
- Advantages: It allows for more up-to-date and context-aware responses, particularly in fields that require real-time information or specialized knowledge.
Sequential Models:
- Definition: Sequential models are models that process data in a sequence, step by step, typically used for tasks like time series prediction, natural language processing, and speech recognition. Examples include RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks), LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory networks), and GRUs (Gated Recurrent Units).
- Process:
- These models maintain an internal state and use previous steps’ outputs to inform future steps in the sequence.
- They are designed to handle ordered data, where the sequence or time dependency between inputs is important.
- Use Cases: Used in language modeling, translation, speech recognition, and time series forecasting, where maintaining context over time is crucial.
- Advantages: Ideal for capturing temporal dependencies, handling sequential data like audio, text, or time-series information.
Key Differences:
- RAG focuses on combining retrieval with generation to enhance responses using external knowledge, whereas sequential models focus on processing ordered data based on past inputs within a sequence.
- RAG is more useful for dynamic knowledge-based tasks, while sequential models are better suited for tasks requiring an understanding of sequence or temporal patterns.



Mobil bahis SEO çalışmaları, web sitemizin performansını iyileştirdi. http://www.royalelektrik.com/
Keep up the fantastic work! Kalorifer Sobası odun, kömür, pelet gibi yakıtlarla çalışan ve ısıtma işlevi gören bir soba türüdür. Kalorifer Sobası içindeki yakıtın yanmasıyla oluşan ısıyı doğrudan çevresine yayar ve aynı zamanda suyun ısınmasını sağlar.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Reading your work feels like stepping into a quiet space where everything makes sense, even the things that were once unclear.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
clomiphene medication where to get clomiphene without dr prescription how to get cheap clomid price clomid chart clomid uses can you buy generic clomid pills where to buy clomid without prescription
More delight pieces like this would make the интернет better.
This is the tolerant of post I unearth helpful.
order generic azithromycin 250mg – order ofloxacin 400mg online order flagyl 400mg for sale
rybelsus 14 mg sale – rybelsus 14mg pills cyproheptadine 4mg cheap
motilium 10mg ca – purchase sumycin online cheap buy cyclobenzaprine generic
inderal ca – buy clopidogrel pills for sale cost methotrexate 2.5mg
purchase amoxil sale – order valsartan 160mg pill ipratropium without prescription
order generic azithromycin 250mg – buy bystolic tablets buy bystolic 20mg generic
clavulanate tablet – atbioinfo.com brand acillin
esomeprazole 20mg cost – https://anexamate.com/ cheap esomeprazole
warfarin online buy – anticoagulant order losartan 25mg online cheap
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
order mobic online – moboxsin meloxicam sale
order deltasone without prescription – https://apreplson.com/ order deltasone 10mg pill
otc ed pills – erection pills viagra online buy ed pills cheap
amoxicillin pill – buy amoxicillin generic amoxicillin for sale
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
purchase forcan online cheap – https://gpdifluca.com/ fluconazole 200mg cost
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/pt-PT/join?ref=PORL8W0Z
cenforce us – order cenforce 100mg pills cenforce 50mg cheap
cialis super active real online store – https://ciltadgn.com/# how long does cialis take to work
buy ranitidine 300mg sale – https://aranitidine.com/# zantac for sale
what is the generic name for cialis – https://strongtadafl.com/ maximpeptide tadalafil review
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
With thanks. Loads of erudition! viagra espaГ±a
buy viagra super active – this viagra 50 off coupon
More text pieces like this would insinuate the интернет better. https://ursxdol.com/doxycycline-antibiotic/
This website absolutely has all of the tidings and facts I needed there this subject and didn’t identify who to ask. https://buyfastonl.com/isotretinoin.html
Greetings! Extremely useful suggestion within this article! It’s the crumb changes which choice turn the largest changes. Thanks a a quantity in the direction of sharing! https://prohnrg.com/product/omeprazole-20-mg/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
You consistently make complex subjects accessible—thank you! Additional resources worth visiting include https://medimexicorx.com/.
cost of amoxicillin 875 mg: amoxicillin 500mg capsules uk – order amoxicillin without prescription
order amoxicillin without prescription: ClearMeds Direct – low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
Clomid Hub Pharmacy: how to get cheap clomid tablets – Clomid Hub Pharmacy
Clomid Hub: Clomid Hub – buying clomid without prescription
affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement: safe Provigil online delivery service – affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement
WakeMedsRX: nootropic Modafinil shipped to USA – Wake Meds RX
legitimate canadian pharmacies: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
MexiCare Rx Hub: mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
MexiCare Rx Hub: best mexican online pharmacies – reputable mexican pharmacies online
cheapest online pharmacy india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – mail order pharmacy india
canadian drugstore online: best rated canadian pharmacy – CanadRx Nexus
IndiGenix Pharmacy: top 10 pharmacies in india – cheapest online pharmacy india
reputable indian online pharmacy: indianpharmacy com – IndiGenix Pharmacy
canadian pharmacy world: canadian online pharmacy reviews – ed drugs online from canada
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – world pharmacy india
reputable indian online pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – Online medicine order
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: does semaglutide cause cancer – maximum dose of rybelsus
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: ventolin uk price – ventolin tabs
when should you take rybelsus: rybelsus medication class – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
lasix furosemide: lasix online – buy furosemide online
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
More posts like this would bring about the blogosphere more useful. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
how to take rybelsus for weight loss: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – what to eat while on semaglutide
Khuy?n mai GK88: Dang ky GK88 – Khuy?n mai GK88
More posts like this would make the blogosphere more useful.
zantac 300mg without prescription
Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan: Onlayn kazino Az?rbaycan – Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan
Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88 [url=https://gkwinviet.company/#]Casino online GK88[/url] Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88
https://mandiwinindo.site/# Mandiribet
Jackpot togel hari ini: Abutogel – Bandar togel resmi Indonesia
Swerte99 login: Swerte99 bonus – Swerte99
Link alternatif Abutogel: Bandar togel resmi Indonesia – Abutogel
Bonus new member 100% Beta138 [url=https://betawinindo.top/#]Slot gacor Beta138[/url] Bandar bola resmi
Live casino Indonesia: Bandar bola resmi – Promo slot gacor hari ini
GK88: GK88 – Khuy?n mai GK88
https://1winphili.company/# Jollibet online sabong
Jackpot togel hari ini: Situs togel online terpercaya – Bandar togel resmi Indonesia
Yuks?k RTP slotlar: Pinco r?smi sayt – Pinco r?smi sayt
jollibet login [url=https://1winphili.company/#]1winphili[/url] Online casino Jollibet Philippines
Situs judi resmi berlisensi: Mandiribet – Link alternatif Mandiribet
Situs judi resmi berlisensi: Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia – Slot gacor hari ini
https://jilwin.pro/# Jiliko casino
Online betting Philippines [url=https://1winphili.company/#]jollibet[/url] jollibet casino
Bonus new member 100% Beta138: Live casino Indonesia – Slot gacor Beta138
Link vao GK88 m?i nh?t: Dang ky GK88 – Link vao GK88 m?i nh?t
Jiliko casino: maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas – Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
Judi online deposit pulsa [url=https://mandiwinindo.site/#]Mandiribet login[/url] Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet
jollibet: jollibet – jollibet casino
Jiliko: Jiliko casino – Jiliko
https://mandiwinindo.site/# Mandiribet
Abutogel login [url=https://abutowin.icu/#]Bandar togel resmi Indonesia[/url] Situs togel online terpercaya
Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan – Qeydiyyat bonusu Pinco casino
Swerte99 slots: Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas – Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas
Slot gacor hari ini [url=https://mandiwinindo.site/#]Link alternatif Mandiribet[/url] Slot gacor hari ini
Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia: Situs judi resmi berlisensi – Slot jackpot terbesar Indonesia
Tro choi n? hu GK88: Link vao GK88 m?i nh?t – Tro choi n? hu GK88
https://betawinindo.top/# Beta138
Online casino Jollibet Philippines: jollibet login – jollibet app
Slot jackpot terbesar Indonesia: Live casino Mandiribet – Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet
medical pharmacy south: best retail pharmacy viagra price – viagra certified pharmacy online
Indian Meds One [url=https://indianmedsone.com/#]Indian Meds One[/url] Indian Meds One
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – reputable indian online pharmacy
http://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# mexican rx online
MediDirect USA: lortab online pharmacy no prescription – MediDirect USA
cheap cialis mexico: buy neurontin in mexico – legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills
amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy [url=https://mexicanpharmacyhub.shop/#]Mexican Pharmacy Hub[/url] buy cheap meds from a mexican pharmacy
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
Indian Meds One: best india pharmacy – Indian Meds One
https://indianmedsone.com/# india online pharmacy
does rx pharmacy coupons work: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
best online pharmacy india [url=https://indianmedsone.com/#]Indian Meds One[/url] online pharmacy india
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: buy propecia mexico – modafinil mexico online
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – online pharmacy propecia no prescription
MediDirect USA [url=http://medidirectusa.com/#]MediDirect USA[/url] MediDirect USA
http://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# Mexican Pharmacy Hub
MediDirect USA [url=http://medidirectusa.com/#]MediDirect USA[/url] MediDirect USA
http://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# Mexican Pharmacy Hub
MediDirect USA [url=https://medidirectusa.com/#]MediDirect USA[/url] Claritin
https://medidirectusa.com/# how much does viagra cost at pharmacy
pharmacy website india [url=http://indianmedsone.com/#]india online pharmacy[/url] Indian Meds One
ED treatment without doctor visits: Online sources for Kamagra in the United States – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
http://sildenapeak.com/# where to buy cheap viagra uk
where to buy tadalafil in singapore: Tadalify – cialis price per pill
cheapest sildenafil 100mg uk: generic viagra 2018 – buy online viagra tablets in india
https://sildenapeak.com/# canada viagra online
Tadalify: Tadalify – order generic cialis
SildenaPeak: viagra for sale in united states – sildenafil 50mg canada
https://tadalify.com/# cialis insurance coverage blue cross
generic sildenafil cost usa: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
This is the type of delivery I unearth helpful. http://web.symbol.rs/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1171357
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
https://kamameds.shop/# Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
online cialis no prescription: cialis 20mg – cialis coupon code
viagra generic 100mg: SildenaPeak – where to buy female viagra canada
https://kamameds.com/# ED treatment without doctor visits
uptown pokies australia review, mini slot machine
united states and united statesn gambling legislation, or new zealandn casino guide app
Here is my page … goplayslots.net
where can i get viagra tablets: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
https://tadalify.shop/# Tadalify
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
https://tadalify.com/# what is cialis good for
https://tadalify.shop/# when to take cialis 20mg
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
https://kamameds.com/# Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
order dapagliflozin 10 mg – click buy generic dapagliflozin 10mg
cheap generic prednisone: prednisone 5 mg brand name – SteroidCare Pharmacy
FertiCare Online: where to buy generic clomid without dr prescription – FertiCare Online
https://trustedmedsdirect.com/# TrustedMeds Direct
generic for amoxicillin: TrustedMeds Direct – generic amoxicillin
FertiCare Online: can i order clomid for sale – where buy generic clomid pill
ivermectin pour-on tractor supply: ivermectin in canada – stromectol and herbs
lasix 100mg: CardioMeds Express – lasix side effects
non prescription prednisone 20mg [url=http://steroidcarepharmacy.com/#]SteroidCare Pharmacy[/url] generic prednisone tablets
https://cardiomedsexpress.com/# CardioMeds Express
lasix medication: CardioMeds Express – lasix generic
FertiCare Online [url=https://ferticareonline.com/#]FertiCare Online[/url] FertiCare Online
ivermectin.: how long is ivermectin effective – ivermectin cream 1
Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente [url=https://pillolesubito.shop/#]medicinali senza prescrizione medica[/url] migliori farmacie online 2024
https://farmacidiretti.shop/# acquistare farmaci senza ricetta
buy xenical generic – xenical online buy orlistat 60mg us
https://forzaintima.com/# soluzioni rapide per la potenza maschile
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
https://farmacidiretti.shop/# farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff
previous to and you are just extremely wonderful. I actually like what you
have acquired here, certainly like what you are saying and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and yoou still care for to keep
it smart. I cant wait to read much more from you.
This is really a great website. https://U7Bm8.mssg.me/
https://maplemedsdirect.com/# target pharmacy pantoprazole
https://bordermedsexpress.shop/# mexican rx online
top 10 online pharmacy in india: buy medicines online in india – BharatMeds Direct
BharatMeds Direct: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
http://bharatmedsdirect.com/# BharatMeds Direct
BorderMeds Express: BorderMeds Express – BorderMeds Express
reputable mexican pharmacies online: medicine in mexico pharmacies – BorderMeds Express
https://maplemedsdirect.com/# price chopper pharmacy
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/en-NG/register-person?ref=JHQQKNKN
BorderMeds Express: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – BorderMeds Express
preman69 login tanpa ribet: slot gacor hari ini preman69 – preman69 login
https://1wstarburst.com/# migliori casino online con Starburst
giocare da mobile a Starburst: starburst – migliori casino online con Starburst
https://1wstarburst.shop/# Starburst giri gratis senza deposito
Starburst giri gratis senza deposito: casino online sicuri con Starburst – starburst
http://1wbona.com/# bonaslot link resmi mudah diakses
The reconditeness in this piece is exceptional. http://pokemonforever.com/User-Zpigdz
https://1wbona.com/# bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah
kratonbet: kratonbet login – kratonbet
batara vip [url=https://mez.ink/batarabet#]situs slot batara88[/url] situs slot batara88
kratonbet alternatif: kratonbet – kratonbet
mawartoto slot [url=https://linktr.ee/mawartotol#]mawartoto login[/url] mawartoto
bataraslot 88: slot online – bataraslot 88
betawi77 net [url=https://linkr.bio/betawi777#]betawi77 net[/url] betawi77 login
mawartoto login: mawartoto login – mawartoto login
situs slot batara88: batara88 – bataraslot 88
bataraslot alternatif: bataraslot 88 – bataraslot login
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# great white peptides tadalafil
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – what is cialis taken for
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
cialis before and after: buy tadalafil no prescription – tadalafil vs cialis
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – purchasing cialis online
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# cialis daily vs regular cialis
how long does it take for cialis to start working: cialis no perscription overnight delivery – EverGreenRx USA
order viagra online safely UK https://bluepilluk.shop/# generic sildenafil UK pharmacy
http://meditrustuk.com/# MediTrustUK
pharmacy online fast delivery UK: MediQuick – online pharmacy UK no prescription
BluePill UK https://meditrustuk.com/# ivermectin cheap price online UK
http://meditrustuk.com/# ivermectin cheap price online UK
fast delivery viagra UK online: viagra online UK no prescription – fast delivery viagra UK online
BluePillUK https://meditrustuk.shop/# trusted online pharmacy ivermectin UK
https://intimacareuk.com/# buy ED pills online discreetly UK
sildenafil tablets online order UK http://mediquickuk.com/# MediQuick
branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy: confidential delivery cialis UK – cialis cheap price UK delivery
IntimaCare UK: IntimaCareUK – IntimaCare UK
order viagra online safely UK: generic sildenafil UK pharmacy – sildenafil tablets online order UK
cialis online UK no prescription: IntimaCareUK – cialis cheap price UK delivery
ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy: MediTrust UK – safe ivermectin pharmacy UK
order medicines online discreetly: online pharmacy UK no prescription – MediQuick
CuraBharat USA: CuraBharat USA – medicine online order
mexican pharmacy that ships to the us: tijuana pharmacy online – SaludFrontera
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! Създаване на личен профил
https://curabharatusa.shop/# CuraBharat USA
pharmacy india: CuraBharat USA – CuraBharat USA
SaludFrontera [url=https://saludfrontera.shop/#]mexico farmacia[/url] purple pharmacy mexico
https://truenorthpharm.com/# TrueNorth Pharm
https://truenorthpharm.shop/# TrueNorth Pharm
best online pharmacy in india: CuraBharat USA – CuraBharat USA
CuraBharat USA [url=https://curabharatusa.com/#]CuraBharat USA[/url] online medicine website
https://curabharatusa.shop/# CuraBharat USA
canadian pharmacy tampa: TrueNorth Pharm – buying drugs from canada
https://mannerkraft.com/# online apotheke versandkostenfrei
http://intimgesund.com/# kamagra oral jelly deutschland bestellen
http://gesunddirekt24.com/# europa apotheke
https://evertrustmeds.shop/# Ever Trust Meds
EverTrustMeds: EverTrustMeds – Ever Trust Meds
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# VitalEdge Pharma
EverTrustMeds: EverTrustMeds – Cialis without a doctor prescription
https://vitaledgepharma.com/# VitalEdge Pharma
Clear Meds Hub: Clear Meds Hub – ClearMedsHub
http://clearmedshub.com/# Clear Meds Hub
VitalEdgePharma: cheap ed pills online – buy ed medication online
http://vitaledgepharma.com/# VitalEdgePharma
https://evertrustmeds.com/# Ever Trust Meds
ClearMedsHub: ClearMedsHub –
https://clearmedshub.shop/# Clear Meds Hub
EverTrustMeds: EverTrustMeds – Ever Trust Meds
https://clearmedshub.shop/# Clear Meds Hub
Clear Meds Hub: ClearMedsHub –
Canadian pharmacy online: Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US – canadian pharmacy
CuraMedsIndia: CuraMedsIndia – Best Indian pharmacy
http://bajamedsdirect.com/# Best Mexican pharmacy online
Indian pharmacy ship to USA: Indian pharmacy to USA – buy medicine online in india
Mexican pharmacy ship to USA: mexican pharmacy – mexico pharmacy
https://maplecarerx.com/# MapleCareRx
https://maplecarerx.com/# canadian pharmacy
bonus Plinko slot Italia: scommesse Plinko online – Plinko demo gratis
Plinko [url=http://plinkoslotitalia.com/#]giocare Plinko con soldi veri[/url] migliori casinò italiani con Plinko
MedicExpress MX: mexican pharmacy – mexican pharmacy
Buy sildenafil online usa [url=https://truevitalmeds.shop/#]true vital meds[/url] 140 mg sildenafil
Legit online Mexican pharmacy: purple pharmacy mexico price list – Online Mexican pharmacy
Legit online Mexican pharmacy [url=https://medicexpressmx.shop/#]Legit online Mexican pharmacy[/url] Best online Mexican pharmacy
MedicExpress MX: Mexican pharmacy price list – Online Mexican pharmacy
mexican pharmacy [url=http://medicexpressmx.com/#]Legit online Mexican pharmacy[/url] Online Mexican pharmacy
Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription: Buy Tadalafil 20mg – Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Mexican pharmacy price list [url=http://medicexpressmx.com/#]Best online Mexican pharmacy[/url] Best online Mexican pharmacy
Best online Mexican pharmacy: mexican pharmacy – mexican pharmacy
Buy sildenafil online usa [url=https://truevitalmeds.shop/#]Sildenafil 100mg[/url] true vital meds
tadalafil: Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription – Generic tadalafil 20mg price
true vital meds [url=https://truevitalmeds.com/#]sildenafil[/url] sildenafil
MedicExpress MX: Online Mexican pharmacy – mexican pharmacy
Sildenafil 100mg [url=http://truevitalmeds.com/#]sildenafil buy usa[/url] Sildenafil 100mg
buy zithromax: buy zithromax – zithromax online no prescription
buy finasteride [url=https://regrowrxonline.com/#]Propecia prescription[/url] Best place to buy propecia
Buy Clomid online: buy clomid – ClomiCare USA
Buy Clomid online [url=http://clomicareusa.com/#]buy clomid[/url] ClomiCare USA
AmoxDirect USA: amoxicillin 500 mg capsule – buy amoxil
AmoxDirect USA [url=https://amoxdirectusa.shop/#]Amoxicillin 500mg buy online[/url] Amoxicillin 500mg buy online
You can conserve yourself and your family close being cautious when buying medicine online. Some pharmaceutics websites operate legally and put forward convenience, secretiveness, sell for savings and safeguards for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/tamoxifen.html tamoxifen
discreet delivery for ED medication: discreet delivery for ED medication – discreet delivery for ED medication
neuropathic pain relief treatment online: FDA-approved gabapentin alternative – generic gabapentin pharmacy USA
https://predniwellonline.com/# Prednisone tablets online USA
This is a keynote which is virtually to my callousness… Many thanks! Unerringly where can I lay one’s hands on the phone details an eye to questions? TerbinaPharmacy
discreet delivery for ED medication: EverLastRx – discreet delivery for ED medication
https://everlastrx.shop/# discreet delivery for ED medication
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK: best UK online chemist for Prednisolone – cheap prednisolone in UK
https://medreliefuk.com/# UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
https://britpharmonline.shop/# BritPharm Online
BritPharm Online: Viagra online UK – buy sildenafil tablets UK
generic amoxicillin: cheap amoxicillin – generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK
https://amoxicareonline.com/# Amoxicillin online UK
https://britpharmonline.shop/# viagra uk
Prednisolone tablets UK online: buy prednisolone – UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
http://medreliefuk.com/# Prednisolone tablets UK online
pharmacy online UK: private online pharmacy UK – BritMeds Direct
https://medreliefuk.com/# UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
https://amoxicareonline.shop/# generic amoxicillin
[url=https://detikoptevo.ru/]здесь[/url]
[url=https://muzikalnie-pozdravlenia.ru/]шарики на день рождения круглосуточно[/url]
[url=https://stellag-belgorod.ru/]тут[/url]
https://valeriakarat.ru/
[url=newmexicojeepgroup.com]here[/url]
[url=https://magicampat.ru/]ссылка[/url]
[url=newmexicojeepgroup.com]????? ??? ??? ????[/url]
[url=https://muzikalnie-pozdravlenia.ru/]muzikalnie-pozdravlenia.ru[/url]
[url=https://earnforexrebates.com/]Highest Forex Bonuses[/url]
[url=newmexicojeepgroup.com]newmexicojeepgroup.com[/url]
[url=https://detikoptevo.ru/]сюда[/url]
The thoroughness in this section is noteworthy.
viagra: viagra uk – Viagra online UK
Prednisolone tablets UK online: cheap prednisolone in UK – UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
http://medreliefuk.com/# order steroid medication safely online
buy sildenafil tablets UK: buy viagra online – BritPharm Online
https://britpharmonline.shop/# order ED pills online UK
generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK: UK online antibiotic service – UK online antibiotic service
https://medreliefuk.com/# buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
BritPharm Online: order ED pills online UK – British online pharmacy Viagra
https://medreliefuk.com/# Prednisolone tablets UK online
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
https://zencaremeds.shop/# safe online medication store
MedicoSur: MedicoSur – medicine mexico
MedicoSur [url=https://medicosur.com/#]mexican pharmacy[/url] mexico pharmacy
online pharmacy [url=http://zencaremeds.com/#]buy Doxycycline[/url] my canadian pharmacy rx
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
mexican pharmacies that ship to us [url=http://medicosur.com/#]mexico pharmacy[/url] mexican pharmacy
generic Cialis online pharmacy: generic Cialis online pharmacy – safe online pharmacy for Cialis
trusted online pharmacy USA: trusted online pharmacy USA – buy Doxycycline
mexico pharmacy [url=http://medicosur.com/#]mexico pharmacy[/url] MedicoSur
cialis generika: PotenzVital – Potenz Vital
Tadalafilo Express: farmacia online madrid – cialis generico
medikament ohne rezept notfall: Cialis Preisvergleich Deutschland – Potenz Vital
cialis: compresse per disfunzione erettile – cialis
PilloleVerdi: compresse per disfunzione erettile – acquistare Cialis online Italia
comprar cialis: cialis generico – cialis generico
cialis generico: farmacia online italiana Cialis – tadalafil senza ricetta
cialis 20 mg achat en ligne: cialis prix – Intimi Santé
farmacia online madrid: farmacia online españa envÃo internacional – cialis precio
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Школьные и офисные принадлежности[/url] — это неотъемлемая часть повседневной жизни. Качественные канцелярские товары помогают сделать процесс обучения и работы проще. В нашем ассортименте вы найдете всё необходимое, чтобы собрать школьный рюкзак. Письменные принадлежности, бумажная продукция, органайзеры и скоросшиватели — всё это отличается высоким качеством и надежностью. Продукция ведущих брендов гарантирует комфорт и эффективность. Школьникам, офисным сотрудникам и тем, кто заботится о комфорте рабочего пространства будет легко выбрать подходящие решения для своих задач. Мы тщательно подбираем ассортимент, чтобы работа и учеба стали приятнее. С учетом современных требований и стандартов, наша коллекция товаров всегда предлагает новинки. Выбирайте и заказывайте прямо на сайте — мы заботимся о клиентах и ценим ваше время. Каждый предмет — часть вашего успеха. Пусть каждое утро начинается с порядка и вдохновения. Доверьтесь нашему опыту и надежности — именно из них складывается продуктивность и успех.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Принадлежности для школы и офиса[/url] — это неотъемлемая часть повседневной жизни. Качественные канцелярские товары помогают создать порядок. Наш каталог включает десятки полезных товаров, чтобы организовать рабочее место. Ручки, карандаши, маркеры, папки и блокноты — всё это отличается высоким качеством и надежностью. Каждый предмет создается с учетом удобства и долговечности. Студентам, руководителям и всем, кто ценит порядок и удобство будет легко выбрать необходимые предметы для своих задач. Каждый товар проходит проверку на практичность и надежность, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на делах, не отвлекаясь на мелочи. Опираясь на опыт пользователей и тенденции рынка, наш магазин всегда предлагает новинки. Выбирайте и заказывайте прямо на сайте — гарантия быстрой доставки и вежливого обслуживания. Каждый предмет — часть вашего успеха. Создайте комфортную среду для работы и учебы уже сегодня. Делайте выбор в пользу качества — именно из них складывается продуктивность и успех.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Принадлежности для школы и офиса[/url] — это важная составляющая учебы и работы. Удобные инструменты для письма и хранения документов помогают создать порядок. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор канцелярии и аксессуаров, чтобы собрать школьный рюкзак. Письменные принадлежности, бумажная продукция, органайзеры и скоросшиватели — всё это отличается высоким качеством и надежностью. Каждый предмет создается с учетом удобства и долговечности. Школьникам, офисным сотрудникам и всем, кто ценит порядок и удобство будет легко выбрать подходящие решения для своих задач. Мы тщательно подбираем ассортимент, чтобы каждая покупка приносила удовольствие. С учетом современных требований и стандартов, наша коллекция товаров всегда предлагает новинки. Выбирайте и заказывайте прямо на сайте — гарантия быстрой доставки и вежливого обслуживания. Каждый предмет — часть вашего успеха. Пусть каждое утро начинается с порядка и вдохновения. Делайте выбор в пользу качества — именно из них складывается продуктивность и успех.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Школьные и офисные принадлежности[/url] — это неотъемлемая часть повседневной жизни. Качественные канцелярские товары помогают сделать процесс обучения и работы проще. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор канцелярии и аксессуаров, чтобы оснастить офис всем нужным. Письменные принадлежности, бумажная продукция, органайзеры и скоросшиватели — всё это представлено в разных ценовых категориях. Современные канцелярские товары сочетают стильный дизайн и функциональность. Школьникам, офисным сотрудникам и тем, кто заботится о комфорте рабочего пространства будет легко выбрать лучшие варианты для своих задач. Каждый товар проходит проверку на практичность и надежность, чтобы каждая покупка приносила удовольствие. С учетом современных требований и стандартов, наша платформа постоянно обновляется. Оцените удобство онлайн-покупок — гарантия быстрой доставки и вежливого обслуживания. Канцелярия — это помощник в каждом дне. Выберите то, что поможет вам достигать целей. Покупайте с удовольствием — каждая деталь имеет значение.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Товары для школы и офиса[/url] — это неотъемлемая часть повседневной жизни. Удобные инструменты для письма и хранения документов помогают сделать процесс обучения и работы проще. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор канцелярии и аксессуаров, чтобы организовать рабочее место. Письменные принадлежности, бумажная продукция, органайзеры и скоросшиватели — всё это отличается высоким качеством и надежностью. Каждый предмет создается с учетом удобства и долговечности. Учителям, офисным сотрудникам и всем, кто ценит порядок и удобство будет легко выбрать лучшие варианты для своих задач. Каждый товар проходит проверку на практичность и надежность, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на делах, не отвлекаясь на мелочи. С учетом современных требований и стандартов, наша платформа всегда предлагает новинки. Сделайте заказ всего за пару кликов — быстрая доставка, честные цены и качественный сервис. Каждый предмет — часть вашего успеха. Выберите то, что поможет вам достигать целей. Покупайте с удовольствием — именно из них складывается продуктивность и успех.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Принадлежности для школы и офиса[/url] — это основа комфорта и продуктивности. Правильно подобранные аксессуары помогают сделать процесс обучения и работы проще. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор канцелярии и аксессуаров, чтобы оснастить офис всем нужным. Ручки, карандаши, маркеры, папки и блокноты — всё это отличается высоким качеством и надежностью. Каждый предмет создается с учетом удобства и долговечности. Учителям, фрилансерам и творческим людям и организаторам будет легко выбрать необходимые предметы для своих задач. Наша цель — предложить максимум качества и удобства, чтобы каждая покупка приносила удовольствие. С учетом современных требований и стандартов, наша коллекция товаров всегда предлагает новинки. Сделайте заказ всего за пару кликов — гарантия быстрой доставки и вежливого обслуживания. Принадлежности для школы и офиса — это не просто вещи. Создайте комфортную среду для работы и учебы уже сегодня. Покупайте с удовольствием — именно из них складывается продуктивность и успех.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Принадлежности для школы и офиса[/url] — это основа комфорта и продуктивности. Правильно подобранные аксессуары помогают повысить эффективность труда. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор канцелярии и аксессуаров, чтобы собрать школьный рюкзак. Письменные принадлежности, бумажная продукция, органайзеры и скоросшиватели — всё это отличается высоким качеством и надежностью. Современные канцелярские товары сочетают стильный дизайн и функциональность. Учителям, офисным сотрудникам и тем, кто заботится о комфорте рабочего пространства будет легко выбрать необходимые предметы для своих задач. Мы тщательно подбираем ассортимент, чтобы каждая покупка приносила удовольствие. С учетом современных требований и стандартов, наша платформа всегда предлагает новинки. Сделайте заказ всего за пару кликов — быстрая доставка, честные цены и качественный сервис. Каждый предмет — часть вашего успеха. Выберите то, что поможет вам достигать целей. Доверьтесь нашему опыту и надежности — именно из них складывается продуктивность и успех.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://frnt.su/]Рациональное распределение времени и дел[/url] — основа успешной работы и личного развития. Множество людей жалуется на то, что день пролетает, а дела стоят на месте, но правильно выстроенная система планирования помогает изменить ситуацию. Главное — расставить приоритеты по важности. Многие используют матрицу Эйзенхауэра, которая наглядно показывает, на что стоит тратить время, а что можно отложить. Следующий шаг — составление чёткого расписания. Современные инструменты управления временем делают процесс планирования удобным и наглядным. Популярные варианты — Trello, Notion, Todoist делают управление делами более системным. Главное — придерживаться расписания и избегать отклонений. Многие успешные люди начинают утро с планирования дня. Регулярное планирование превращается в естественную часть жизни. Этот подход полезен не только профессионалам, но и каждому человеку. Организованность придаёт уверенность и внутренний баланс. Контроль прогресса позволяет увидеть реальные результаты вдохновляет и помогает скорректировать цели. Начните с простого — записывать три главные задачи на день. Через пару недель вы заметите, что стали успевать больше. Эффективное планирование задач — это не ограничение свободы, а инструмент для её расширения. Создавайте систему, которая работает именно под вас. Любой план требует последовательности и движения вперёд. Пусть планирование станет вашим союзником на пути к целям и внутреннему комфорту.
https://frnt.su/
[url=https://prilozhenie-napominanie.ru/]Способы эффективного планирования задач[/url] — ключ к успеху в работе и личной жизни. Грамотное распределение задач помогает достигать целей быстрее. Отсутствие структуры делает день менее результативным, но всего несколько простых приёмов могут полностью изменить ситуацию. Начать стоит с расстановки приоритетов. Техника матрицы важности и срочности помогает разделить задачи по уровням значимости. Далее стоит зафиксировать план на день или неделю. Сегодня существует множество инструментов для планирования. Современные планировщики задач и календарные системы позволяют контролировать прогресс и анализировать результаты. Главное в планировании — постоянство и самоконтроль. Секрет успеха не в количестве задач, а в их осознанности. Хорошее правило — начинать день с трёх главных задач. Такой подход создаёт ощущение прогресса и уверенности. Чрезмерное планирование часто приводит к выгоранию. План должен быть гибким, чтобы адаптироваться к изменениям. Проверяйте, какие задачи действительно приближают к целям. Планирование — это живой процесс, а не одноразовое действие. Когда вы научитесь управлять своим временем, изменится качество жизни. Начните день с определения приоритетов и посмотрите, как это изменит результат. Планирование задач — ваш главный инструмент для уверенного движения к целям.
https://prilozhenie-napominanie.ru/
[url=https://garantia-uyta.ru/]Комплексное управление задачами и проектами[/url] — важнейшая часть эффективной работы любой команды. Каждая команда нуждается в чётком подходе к распределению обязанностей, ведь правильная организация проектов позволяет достигать целей быстрее и с меньшими затратами. Начинать стоит с постановки конкретных целей и приоритетов. Формирование структуры задач даёт возможность эффективно распределить ресурсы. Современные инструменты вроде Trello, Asana, ClickUp или Notion обеспечивают удобство взаимодействия между участниками. Такие платформы упрощают совместную работу и коммуникацию. Важно учитывать не только задачи, но и возможности команды. Для сложных проектов применяется методология Agile, обеспечивая высокую скорость и качество реализации. Командное взаимодействие — один из важнейших факторов успеха. Анализ выполненных задач позволяет улучшать будущие проекты. Системный подход делает даже сложные проекты понятными. Контроль прогресса позволяет находить слабые места и улучшать систему. Эффективная система управления требует постоянного совершенствования. Лучшие компании создают культуру ответственности и прозрачности. Чтобы повысить результативность, внедрите принципы проектного управления. Сильная система организации проектов — это инвестиция в стабильность и успех.
https://garantia-uyta.ru/
[url=https://superiortds.ru/]Организация работы и контроль задач[/url] — неотъемлемая часть современного бизнеса. Эффективная координация задач и участников помогает достигать целей быстрее. Современные методы управления проектами создают единую экосистему для совместной работы. Любое управление проектом начинается с чёткого плана. Стоит сразу установить контрольные точки для отслеживания прогресса. Популярные инструменты вроде Trello, Asana или Jira помогают визуализировать процессы и улучшить коммуникацию. На практике часто применяются гибкие методологии, чтобы проект развивался в соответствии с реальными потребностями. Смысл проектного менеджмента — в управлении временем, качеством и ресурсами. При этом важно выстроить чёткую коммуникацию. Успех зависит от умения вдохновлять команду и управлять ресурсами. Контрольные точки и анализ хода проекта повышают прозрачность. Оценка результатов помогает скорректировать действия вовремя. Современные организации автоматизируют управление проектами, чтобы сократить человеческий фактор и ускорить реализацию идей. Даже лучшие инструменты не сработают без вовлечённых людей. Эффективное управление проектами и задачами помогает объединить всех участников процесса. Настоящая эффективность достигается при сочетании дисциплины и адаптивности. Если каждый знает свою роль, проект становится предсказуемым и успешным. Понимание основ проектного менеджмента полезно даже вне бизнеса. Попробуйте внедрить методы управления проектами в своей работе. Управление проектами и задачами — это путь к стабильности, росту и уверенности в будущем.
https://superiortds.ru/
[url=https://4domains.su/]Как эффективно распределять время в течение дня[/url] — вопрос, который задают себе люди, стремящиеся достигать целей без стресса. Планирование — это не просто ежедневник с заметками, а способ организовать жизнь так, чтобы оставалось время на всё важное. Первое, что нужно — понять, что для вас главное. Разделите день на смысловые блоки. Не стоит загружать день без перерывов. Не переоценивайте силы, чтобы избежать выгорания. Составляйте список из ключевых пунктов, которые приближают вас к цели. После основных дел займитесь второстепенными. У каждого есть время, когда концентрация выше — используйте это. Оптимизация по биоритмам повышает эффективность. Используйте инструменты — ежедневники, приложения, календари. Главное — не приложение, а ваше намерение. Анализируйте, что удалось, а что нет. Планирование со временем становится естественным процессом. Перерывы помогают восстанавливать энергию и сохранять мотивацию. Просто составьте план на завтра и выполните половину — это уже шаг вперёд. Планирование станет вашим союзником в достижении целей. Тот, кто управляет своим днём, управляет жизнью
https://4domains.su/
[url=https://frnt.su/]Рациональное распределение времени и дел[/url] — ключ к высокой продуктивности и внутреннему равновесию. Множество людей жалуется на то, что день пролетает, а дела стоят на месте, но правильно выстроенная система планирования способно кардинально улучшить жизнь. Первое, с чего стоит начать — определить приоритеты. Популярным инструментом является матрица Эйзенхауэра, которая позволяет понять, что действительно требует внимания. Следующий шаг — составление чёткого расписания. Современные инструменты управления временем позволяют видеть всю картину задач и сроков. Популярные варианты — Trello, Notion, Todoist создают порядок в делах и избавляют от хаоса. Без самоконтроля даже лучший план не будет работать. Многие успешные люди начинают утро с планирования дня. Постепенно вырабатывается привычка осознанного управления временем. Грамотное распределение времени делает повседневность более гармоничной. Когда вы знаете, что и зачем делаете, пропадает тревожность. Кроме того, регулярный анализ выполненных задач вдохновляет и помогает скорректировать цели. Начните с простого — записывать три главные задачи на день. Через пару недель вы заметите, что стали успевать больше. Планирование — это не про жёсткие рамки, а про осознанное использование времени. Создавайте систему, которая работает именно под вас. И помните: план без действия остаётся лишь мечтой. Осознанное планирование — ключ к уверенности, результатам и гармонии.
https://frnt.su/
[url=https://frnt.su/]Рациональное распределение времени и дел[/url] — основа успешной работы и личного развития. Множество людей жалуется на то, что день пролетает, а дела стоят на месте, но правильно выстроенная система планирования помогает изменить ситуацию. Главное — расставить приоритеты по важности. Многие используют матрицу Эйзенхауэра, которая наглядно показывает, на что стоит тратить время, а что можно отложить. Когда цели ясны, важно создать структурированный список дел. Современные инструменты управления временем делают процесс планирования удобным и наглядным. Для визуализации подойдут Trello и Kanban-доски дают возможность организовать задачи в удобной форме. Без самоконтроля даже лучший план не будет работать. Практика показывает, что утреннее планирование повышает продуктивность. Со временем формируется внутренняя структура продуктивности. Планирование задач помогает не только в работе, но и в личной жизни. Организованность придаёт уверенность и внутренний баланс. Кроме того, регулярный анализ выполненных задач вдохновляет и помогает скорректировать цели. Попробуйте внедрить планирование в повседневную практику. Результаты не заставят себя ждать — продуктивность возрастёт. Планирование — это не про жёсткие рамки, а про осознанное использование времени. Не копируйте чужие методы, адаптируйте под свой стиль жизни. Любой план требует последовательности и движения вперёд. Развивайте навык планирования, совершенствуйте подходы и наблюдайте, как ваша жизнь становится более осознанной, сбалансированной и успешной.
https://frnt.su/
[url=https://garantia-uyta.ru/]Организация проектов и задач[/url] — фундамент успешного бизнеса и личной эффективности. Каждая команда нуждается в чётком подходе к распределению обязанностей, ведь ясная система работы делает коллективную работу слаженной и понятной. Базой для любой организации является план действий. Формирование структуры задач создаёт основу для дальнейшего управления проектом. Онлайн-платформы для организации задач, такие как Jira, Monday или Wrike позволяют отслеживать прогресс и соблюдать сроки. С их помощью дистанционные сотрудники чувствуют себя частью общего процесса. Важно учитывать не только задачи, но и возможности команды. Гибкие методы управления позволяют быстрее адаптироваться к изменениям, что делает работу более динамичной и результативной. Без открытого общения организация проектов теряет эффективность. Регулярные совещания и отчёты помогают контролировать прогресс. Хорошо выстроенная организация задач снижает стресс и хаос. Важно не просто планировать, но и анализировать результаты. Управление задачами должно адаптироваться к изменениям и целям. Лучшие компании создают культуру ответственности и прозрачности. Первый шаг к росту компании — создание чёткой структуры проектов. Сильная система организации проектов — это инвестиция в стабильность и успех.
https://garantia-uyta.ru/
https://mediuomo.com/# Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro
Sildenafil-tabletter pris: köp receptfria potensmedel online – mannens apotek
trattamento ED online Italia [url=http://mediuomo.com/#]comprare Sildenafil senza ricetta[/url] trattamento ED online Italia
https://herengezondheid.com/# goedkope Viagra tabletten online
goedkope Viagra tabletten online: Sildenafil zonder recept bestellen – betrouwbare online apotheek
HerenGezondheid [url=http://herengezondheid.com/#]officiële Sildenafil webshop[/url] ED-medicatie zonder voorschrift
https://confiafarmacia.shop/# Viagra generico online Espana
https://mannensapotek.shop/# diskret leverans i Sverige
farmacia online para hombres: pastillas de potencia masculinas – Viagra sin prescripción médica
farmacia online para hombres: Viagra sin prescripción médica – ConfiaFarmacia
pillole per disfunzione erettile: Medi Uomo – pillole per disfunzione erettile
https://confiafarmacia.shop/# farmacia online para hombres
[url=https://pg13.ru/shary-na-den-rozhdeniya-yarkaya-detal-prazdnika]Заказ шаров с доставкой по Москве[/url] — это идеальный вариант оформления день рождения. Мы предлагаем красивые букеты из шаров для любого возраста. Праздничные шары добавляют волшебства. Вы можете оформить заказ в любой район Москвы. Мы работаем круглосуточно, поэтому всегда доставим вовремя. В нашем каталоге огромный выбор фольгированных и латексных шаров. Можно выбрать любые формы и цвета. Мы предлагаем украшение дома под ключ — всё включено. Опытные флористы и декораторы помогут подобрать шары под ваш вкус и бюджет. Цены доступны, а гелий и латекс гарантирует длительный эффект праздника. Для организаций доступны специальные предложения. Позвоните нам и оформите заказ прямо сейчас. Гелиевые шарики с доставкой — это идеальное оформление вашего праздника!
[url=https://progorod35.ru/kruglosutochnaya-dostavka-vozdushnykh-sharov-radost-v-lyuboye-vremya]Шары на др в Москве и области[/url] — это идеальный вариант оформления вечеринку. Мы предлагаем оригинальные варианты украшений для детских и взрослых праздников. Гелиевые шары делают праздник незабываемым. Вы можете купить онлайн по всей Москве и области. Доставка возможна 24/7, поэтому гарантируем своевременную доставку. В нашем каталоге десятки вариантов гелиевых шаров. Можно выбрать тематические наборы для дня рождения. Мы предлагаем украшение дома под ключ — с установкой и доставкой. Команда профессионалов помогут подобрать шары под ваш вкус и бюджет. Стоимость приятно удивит, а прочность и стойкость шаров гарантирует долгое удержание формы. Для организаций доступны скидки и персональные условия. Позвоните нам и оформите заказ прямо сейчас. Шары на день рождения в Москве и области — это радость и улыбки для всех!
[url=https://volga.news/article/764763.html]Шарики на день рождения с доставкой[/url] — это идеальный вариант оформления день рождения. Мы предлагаем оригинальные варианты украшений для детских и взрослых праздников. Гелиевые шары делают праздник незабываемым. Вы можете оформить заказ в любой район Москвы. Принимаем заказы в любое время, поэтому всегда доставим вовремя. В нашем каталоге огромный выбор гелиевых шаров. Можно выбрать тематические наборы для дня рождения. Мы предлагаем декор помещения под ключ — от идеи до монтажа. Опытные флористы и декораторы помогут создать уникальную атмосферу. Мы предлагаем выгодные цены и акции, а качество материалов гарантирует длительный эффект праздника. Для организаций доступны специальные предложения. Оставьте заявку и уточните стоимость. Праздничные шары от нашей компании — это эмоции, которые запомнятся надолго!
[url=https://vladnews.ru/post/256675/dostavka_sharov]Гелиевые воздушные шары для праздника[/url] — это лучший способ украсить праздник. Мы предлагаем красивые букеты из шаров для взрослых и детей. Гелиевые шары делают праздник незабываемым. Вы можете оформить заказ по всей Москве и области. Доставка возможна 24/7, поэтому всегда доставим вовремя. В нашем каталоге десятки вариантов шаров с надписями. Можно выбрать сердца, цифры, буквы. Мы предлагаем декор помещения под ключ — с установкой и доставкой. Опытные флористы и декораторы помогут создать уникальную атмосферу. Мы предлагаем выгодные цены и акции, а качество материалов гарантирует долговечность. Для корпоративных клиентов доступны скидки и персональные условия. Позвоните нам и получите консультацию. Праздничные шары от нашей компании — это идеальное оформление вашего праздника!
[url=https://progorod35.ru/kruglosutochnaya-dostavka-vozdushnykh-sharov-radost-v-lyuboye-vremya]Гелиевые воздушные шары для праздника[/url] — это простой способ добавить радости на вечеринку. Мы предлагаем яркие композиции для взрослых и детей. Праздничные шары создают атмосферу веселья. Вы можете оформить заказ в любой район Москвы. Доставка возможна 24/7, поэтому всегда доставим вовремя. В нашем каталоге большой ассортимент шаров с надписями. Можно выбрать сердца, цифры, буквы. Мы предлагаем декор помещения под ключ — с установкой и доставкой. Наши специалисты по оформлению помогут оформить праздник в любом стиле. Мы предлагаем выгодные цены и акции, а прочность и стойкость шаров гарантирует долгое удержание формы. Для корпоративных клиентов доступны специальные предложения. Оставьте заявку и оформите заказ прямо сейчас. Праздничные шары от нашей компании — это радость и улыбки для всех!
[url=https://pg13.ru/shary-na-den-rozhdeniya-yarkaya-detal-prazdnika]Шары для дня рождения недорого[/url] — это лучший способ украсить день рождения. Мы предлагаем яркие композиции для взрослых и детей. Праздничные шары добавляют волшебства. Вы можете оформить заказ в любой район Москвы. Доставка возможна 24/7, поэтому вы получите шары точно к началу праздника. В нашем каталоге огромный выбор гелиевых шаров. Можно выбрать сердца, цифры, буквы. Мы предлагаем декор помещения под ключ — от идеи до монтажа. Наши специалисты по оформлению помогут создать уникальную атмосферу. Цены доступны, а качество материалов гарантирует долговечность. Для организаций доступны оптовые заказы. Позвоните нам и оформите заказ прямо сейчас. Шары на день рождения в Москве и области — это идеальное оформление вашего праздника!
[url=https://vladnews.ru/post/256675/dostavka_sharov]Шары для дня рождения недорого[/url] — это лучший способ украсить день рождения. Мы предлагаем красивые букеты из шаров для детских и взрослых праздников. Гелиевые шары делают праздник незабываемым. Вы можете оформить заказ в любой район Москвы. Принимаем заказы в любое время, поэтому гарантируем своевременную доставку. В нашем каталоге огромный выбор гелиевых шаров. Можно выбрать тематические наборы для дня рождения. Мы предлагаем украшение дома под ключ — с установкой и доставкой. Команда профессионалов помогут оформить праздник в любом стиле. Цены доступны, а гелий и латекс гарантирует долгое удержание формы. Для агентств и компаний доступны оптовые заказы. Оставьте заявку и уточните стоимость. Шары на день рождения в Москве и области — это радость и улыбки для всех!
[url=https://pg13.ru/shary-na-den-rozhdeniya-yarkaya-detal-prazdnika]Шары на др в Москве и области[/url] — это идеальный вариант оформления вечеринку. Мы предлагаем красивые букеты из шаров для любого возраста. Воздушные шары создают атмосферу веселья. Вы можете оформить заказ с доставкой на дом или в офис. Мы работаем круглосуточно, поэтому вы получите шары точно к началу праздника. В нашем каталоге десятки вариантов шаров с надписями. Можно выбрать тематические наборы для дня рождения. Мы предлагаем украшение дома под ключ — всё включено. Опытные флористы и декораторы помогут создать уникальную атмосферу. Мы предлагаем выгодные цены и акции, а гелий и латекс гарантирует длительный эффект праздника. Для корпоративных клиентов доступны оптовые заказы. Оставьте заявку и получите консультацию. Гелиевые шарики с доставкой — это эмоции, которые запомнятся надолго!
[url=https://progorod35.ru/kruglosutochnaya-dostavka-vozdushnykh-sharov-radost-v-lyuboye-vremya]Шарики на день рождения с доставкой[/url] — это лучший способ украсить вечеринку. Мы предлагаем яркие композиции для детских и взрослых праздников. Праздничные шары добавляют волшебства. Вы можете купить онлайн в любой район Москвы. Мы работаем круглосуточно, поэтому гарантируем своевременную доставку. В нашем каталоге большой ассортимент фольгированных и латексных шаров. Можно выбрать тематические наборы для дня рождения. Мы предлагаем декор помещения под ключ — всё включено. Наши специалисты по оформлению помогут подобрать шары под ваш вкус и бюджет. Стоимость приятно удивит, а качество материалов гарантирует долговечность. Для агентств и компаний доступны специальные предложения. Позвоните нам и получите консультацию. Гелиевые шарики с доставкой — это идеальное оформление вашего праздника!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
A lot of thanks for all of your work on this site. Gloria delights in getting into research and it’s really easy to see why. We all learn all relating to the compelling method you offer useful tips and hints on this web blog and as well encourage response from people on this idea then our favorite girl is studying so much. Enjoy the remaining portion of the new year. You’re doing a remarkable job.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback, forex rebate is a financial tool intended to refund part of transaction expenses that traders normally pay to brokers. This model helps reduce overall trading expenses, making each trade more cost-efficient, which is extremely beneficial for active traders. Rebates are generally credited automatically on a daily or weekly basis, ensuring a consistent monetary return. Through participating in forex rebate programs, market participants can enhance their investment efficiency without altering their existing trading approach. The main step is picking a proven cashback partner, connecting the account and operating normally. Many brokers cooperate with cashback services, enabling users to trade on their chosen terminal while still getting valuable cashback credits. Cashback structures support transparency, allowing users to monitor each refunded value, making personal financial planning easier. An added benefit is accumulation of rebates even with smaller trade frequency, building an extra layer of measurable income. Because cashback does not require changes in strategy, both beginners and professionals can benefit equally. Active traders may see notable accumulated payouts, enhancing stability and growth potential over time. Within the dynamic forex landscape, each decrease in trading expense is valuable, with rebate systems being one of the easiest cost-optimization tools. Working with a credible cashback platform guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, positioning rebates as an important feature of profitable long-term trading.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback bonus, forex rebate system represents a useful trading feature designed to return part of the trading costs commonly deducted by broker platforms. This model helps reduce overall trading expenses, helping traders maintain a more profitable cost structure, which is extremely beneficial for active traders. The rebate is typically issued automatically per executed transaction or for a set timeframe, offering a stable added value. By using forex cashback services, market participants can enhance their investment efficiency without altering their existing trading approach. All that is required is selecting a reputable provider, connecting the account and operating normally. A wide range of brokers support cashback partnerships, letting traders stay with the platform they prefer while still getting valuable cashback credits. Cashback structures support transparency, allowing users to monitor each refunded value, making budget management more predictable. An added benefit is accumulation of rebates even with smaller trade frequency, building an extra layer of measurable income. Because cashback does not require changes in strategy, both beginners and professionals can benefit equally. Active traders may see notable accumulated payouts, strengthening the long-term robustness of their method. Within the dynamic forex landscape, any reduction in commissions becomes meaningful, making rebate services an approachable method to reduce costs. Working with a credible cashback platform guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, turning cashback into a vital part of an efficient trading environment.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback bonus, forex rebate system serves as an effective instrument designed to return part of the trading costs commonly deducted by broker platforms. Such a model cuts down the total cost of trading, making each trade more cost-efficient, particularly for high-volume traders. The rebate is typically issued automatically per executed transaction or for a set timeframe, offering a stable added value. By using forex cashback services, market participants can enhance their investment efficiency all while keeping their strategies unchanged. All that is required is selecting a reputable provider, connecting the account and operating normally. A wide range of brokers support cashback partnerships, allowing traders to maintain their preferred platform yet benefiting from important cashback returns. Forex cashback also provides transparency, as traders can track every refunded amount, making personal financial planning easier. An added benefit is accumulation of rebates even with smaller trade frequency, building an extra layer of measurable income. Since cashback works independently of strategy, both beginners and professionals can benefit equally. High-frequency traders may generate sizeable monthly returns, strengthening the long-term robustness of their method. Within the dynamic forex landscape, any reduction in commissions becomes meaningful, with rebate systems being one of the easiest cost-optimization tools. Working with a credible cashback platform guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, turning cashback into a vital part of an efficient trading environment.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback bonus, forex rebate system represents a useful trading feature designed to return part of the trading costs commonly deducted by broker platforms. This approach minimizes cumulative trading costs, helping traders maintain a more profitable cost structure, which is extremely beneficial for active traders. The rebate is typically issued automatically on a daily or weekly basis, ensuring a consistent monetary return. Through participating in forex rebate programs, users can strengthen their long-term profitability without modifying their trading strategy. The main step is picking a proven cashback partner, linking the trading account, and continuing to trade as usual. A wide range of brokers support cashback partnerships, allowing traders to maintain their preferred platform while still receiving substantial rebate payouts. Cashback structures support transparency, as traders can track every refunded amount, making personal financial planning easier. An added benefit is accumulation of rebates even with smaller trade frequency, forming a steady supplementary return. Since cashback works independently of strategy, both beginners and professionals can benefit equally. Those who trade intensively may receive significant monthly rebates, further improving the long-term sustainability of their trading approach. In the competitive forex environment, any reduction in commissions becomes meaningful, making rebate services an approachable method to reduce costs. Working with a credible cashback platform ensures transparent conditions, timely payments, and steady benefits, positioning rebates as an important feature of profitable long-term trading.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback, forex rebate is a financial tool created to give back a portion of spreads or commissions commonly deducted by broker platforms. This approach minimizes cumulative trading costs, increasing the cost-efficiency of every trading action, especially for those working with high volumes. Rebates are generally credited automatically per executed transaction or for a set timeframe, providing a predictable financial benefit. With the adoption of reliable cashback solutions, market participants can enhance their investment efficiency without altering their existing trading approach. The key factor is choosing a trustworthy service, attaching the account and following the standard routine. A wide range of brokers support cashback partnerships, enabling users to trade on their chosen terminal while still getting valuable cashback credits. Forex cashback also provides transparency, as traders can track every refunded amount, making budget management more predictable. A further advantage is that earnings accumulate regardless of market intensity, creating a passive addition to the trading balance. Because cashback does not require changes in strategy, it suits both novice and experienced traders. Active traders may see notable accumulated payouts, enhancing stability and growth potential over time. In the competitive forex environment, each decrease in trading expense is valuable, and cashback programs stand out as one of the most accessible ways to optimize expenses. Choosing a reliable cashback provider secures stable payouts, accurate tracking, and dependable performance, turning cashback into a vital part of an efficient trading environment.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex rebate, forex cashback represents a useful trading feature created to give back a portion of spreads or commissions usually charged by brokers. This approach minimizes cumulative trading costs, increasing the cost-efficiency of every trading action, which is extremely beneficial for active traders. Rebates are generally credited automatically on a daily or weekly basis, ensuring a consistent monetary return. With the adoption of reliable cashback solutions, traders can improve their ROI all while keeping their strategies unchanged. The key factor is choosing a trustworthy service, connecting the account and operating normally. Numerous brokers work with rebate platforms, letting traders stay with the platform they prefer while still getting valuable cashback credits. Forex rebates likewise offer clarity, as traders can track every refunded amount, helping maintain a clear picture of expenses. An added benefit is accumulation of rebates even with smaller trade frequency, forming a steady supplementary return. Since cashback works independently of strategy, it suits both novice and experienced traders. Those who trade intensively may receive significant monthly rebates, enhancing stability and growth potential over time. Across today’s global forex market, each decrease in trading expense is valuable, and cashback programs stand out as one of the most accessible ways to optimize expenses. Selecting a trustworthy rebate partner ensures transparent conditions, timely payments, and steady benefits, making forex cashback an essential component of a modern trading setup.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex rebate, forex cashback is a financial tool designed to return part of the trading costs commonly deducted by broker platforms. This approach minimizes cumulative trading costs, increasing the cost-efficiency of every trading action, particularly for high-volume traders. Such cashback is usually delivered without additional actions either per trade or by period, providing a predictable financial benefit. With the adoption of reliable cashback solutions, market participants can enhance their investment efficiency without altering their existing trading approach. The key factor is choosing a trustworthy service, attaching the account and following the standard routine. Many brokers cooperate with cashback services, enabling users to trade on their chosen terminal yet benefiting from important cashback returns. Forex cashback also provides transparency, allowing users to monitor each refunded value, helping maintain a clear picture of expenses. An added benefit is accumulation of rebates even with smaller trade frequency, building an extra layer of measurable income. Because cashback does not require changes in strategy, it suits both novice and experienced traders. Those who trade intensively may receive significant monthly rebates, further improving the long-term sustainability of their trading approach. In the competitive forex environment, any reduction in commissions becomes meaningful, and cashback programs stand out as one of the most accessible ways to optimize expenses. Selecting a trustworthy rebate partner guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, positioning rebates as an important feature of profitable long-term trading.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback bonus, forex rebate system serves as an effective instrument intended to refund part of transaction expenses usually charged by brokers. This approach minimizes cumulative trading costs, increasing the cost-efficiency of every trading action, particularly for high-volume traders. Such cashback is usually delivered without additional actions per executed transaction or for a set timeframe, offering a stable added value. Through participating in forex rebate programs, traders can improve their ROI without altering their existing trading approach. The main step is picking a proven cashback partner, connecting the account and operating normally. Numerous brokers work with rebate platforms, letting traders stay with the platform they prefer yet benefiting from important cashback returns. Forex cashback also provides transparency, as traders can track every refunded amount, making budget management more predictable. A further advantage is that earnings accumulate regardless of market intensity, creating a passive addition to the trading balance. Since cashback works independently of strategy, traders of all skill levels can utilize it effectively. Active traders may see notable accumulated payouts, strengthening the long-term robustness of their method. Within the dynamic forex landscape, every reduction of cost matters, making rebate services an approachable method to reduce costs. Choosing a reliable cashback provider guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, making forex cashback an essential component of a modern trading setup.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback, forex rebate represents a useful trading feature intended to refund part of transaction expenses commonly deducted by broker platforms. This model helps reduce overall trading expenses, increasing the cost-efficiency of every trading action, particularly for high-volume traders. Such cashback is usually delivered without additional actions on a daily or weekly basis, ensuring a consistent monetary return. Through participating in forex rebate programs, market participants can enhance their investment efficiency without altering their existing trading approach. The key factor is choosing a trustworthy service, connecting the account and operating normally. A wide range of brokers support cashback partnerships, enabling users to trade on their chosen terminal while still receiving substantial rebate payouts. Forex cashback also provides transparency, giving access to detailed rebate history, helping maintain a clear picture of expenses. A further advantage is that earnings accumulate regardless of market intensity, creating a passive addition to the trading balance. As cashback functions parallel to strategy, it suits both novice and experienced traders. High-frequency traders may generate sizeable monthly returns, enhancing stability and growth potential over time. In the competitive forex environment, any reduction in commissions becomes meaningful, with rebate systems being one of the easiest cost-optimization tools. Working with a credible cashback platform guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, turning cashback into a vital part of an efficient trading environment.
[url=https://myforexcashback.com/]https://myforexcashback.com/[/url]forex cashback, forex rebate serves as an effective instrument created to give back a portion of spreads or commissions usually charged by brokers. Such a model cuts down the total cost of trading, increasing the cost-efficiency of every trading action, which is extremely beneficial for active traders. Such cashback is usually delivered without additional actions either per trade or by period, offering a stable added value. Through participating in forex rebate programs, traders can improve their ROI all while keeping their strategies unchanged. The main step is picking a proven cashback partner, connecting the account and operating normally. A wide range of brokers support cashback partnerships, allowing traders to maintain their preferred platform yet benefiting from important cashback returns. Forex cashback also provides transparency, as traders can track every refunded amount, helping maintain a clear picture of expenses. Another advantage is that rebates accumulate even during minor market activity, building an extra layer of measurable income. Since cashback works independently of strategy, it suits both novice and experienced traders. High-frequency traders may generate sizeable monthly returns, enhancing stability and growth potential over time. In the competitive forex environment, every reduction of cost matters, making rebate services an approachable method to reduce costs. Selecting a trustworthy rebate partner guarantees clear terms, punctual credits, and consistent advantages, making forex cashback an essential component of a modern trading setup.
[url=https://fxreversemoney.com/]forex rebate[/url] represents a specialized system designed to refund a portion of spreads or commissions to traders without requiring additional actions. The concept decreases total trading costs, helping investors minimize their operational expenses, which becomes especially beneficial for long-term strategies. Rebate programs for forex work automatically, meaning traders do not need to change their strategy, but continue earning steady cashback payouts. Depending on the provider, payouts can occur per trade or by period, ensuring smooth and reliable compensation. A large number of traders adopt these systems to increase their economic efficiency, especially when operating with higher trading volumes. The rebate does not interfere with trading execution, allowing the process to stay smooth, and making it easy to incorporate into any routine. A key positive aspect of cashback models is the ability to view detailed payout records, assisting in forming a clear long-term cost picture. Even during periods of low activity, returns keep adding to the balance, adding a measurable extra layer of value. Selecting a reliable rebate service ensures accurate reporting, timely payments, and stable cooperation, turning rebates into a valuable part of any sustainable trading plan.
[url=https://moneycomeback.ru]кэшбэк от Moneycomeback[/url]Moneycomeback платформа для возврата комиссий и спреда у брокеров
[url=https://moneycomeback.ru]кэшбэк от Moneycomeback[/url]Получайте кэшбек от брокеров Forex и фьючерсов легко
[url=https://moneycomeback.ru]кэшбэк от Moneycomeback[/url]Кэшбек от брокеров Forex с возвратом спреда и комиссий
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, и наша компания предоставляет качественную продукцию любого формата. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, включая разработку дизайна, печать и постпечатную обработку, до изготовления рекламных конструкций и наружных решений. Наши дизайнеры и технические специалисты создают визуальные решения под конкретные задачи, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Печатные материалы создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы создаем визитки, листовки, журналы, что дает возможность выполнить заказ любой сложности. Кроме печатной продукции изготовление рекламной продукции, которые помогают привлекать внимание аудитории, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Наружная реклама производятся с учетом климатических нагрузок, и позволяет сохранять привлекательный вид в течение долгого времени. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, начиная от разработки концепции, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждый клиент получает индивидуальный подход, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. В работе применяются инновационные методы, которые обеспечивают высокую скорость выполнения, не снижая качества продукции. Обращаясь к нам, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, который помогает реализовать любые рекламные задачи.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]листы картонные[/url] используются для упаковки, складирования и производства, и у нас можно заказать качественную продукцию любого формата. Наша компания оказывает комплекс услуг, которые охватывают создание макетов, печать и производство продукции, до изготовления рекламных конструкций и наружных решений. Команда специалистов подготавливают дизайн, соответствующий вашему бренду, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Полиграфия различных форматов создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, обеспечивая безупречный внешний вид материалов. Мы работаем с визитками, буклетами, каталогами, и можем выполнить как небольшие партии, так и крупные тиражи. Кроме печатной продукции разработка рекламных носителей, которые помогают привлекать внимание аудитории, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Рекламные конструкции производятся с учетом климатических нагрузок, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, включая создание визуального решения, и до полного производства и установки. Мы работаем с каждым проектом персонально, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. В работе применяются инновационные методы, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, при неизменно высоком уровне исполнения. Обращаясь к нам, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, позволяющий закрыть все потребности в дизайне и рекламе.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, а мы предлагаем разнообразные варианты под любые задачи. Наша компания оказывает комплекс услуг, которые охватывают создание макетов, печать и производство продукции, до изготовления рекламных конструкций и наружных решений. Профессиональные сотрудники компании разрабатывают макеты любой сложности, делая акцент на привлекательности и функциональности. Полиграфическая продукция изготавливается с использованием профессиональной техники, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, и можем выполнить как небольшие партии, так и крупные тиражи. Кроме печатной продукции изготовление рекламной продукции, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, которые эффективно работают в различных условиях. Внешние рекламные решения создаются с применением устойчивых материалов, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы сопровождаем проект на всех этапах, от продумывания дизайна, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждому заказчику уделяется особое внимание, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы используем современные технологии, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Сотрудничая с нашей компанией, вы получаете профессиональный подход, который помогает реализовать любые рекламные задачи.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] используются для упаковки, складирования и производства, а мы предлагаем картон различной плотности и размеров. Наша компания оказывает комплекс услуг, от разработки дизайна и печати полиграфической продукции, до создания рекламных материалов и наружной рекламы. Команда специалистов подготавливают дизайн, соответствующий вашему бренду, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Печатные материалы создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, обеспечивая безупречный внешний вид материалов. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, что дает возможность выполнить заказ любой сложности. Помимо полиграфии разработка рекламных носителей, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Рекламные конструкции создаются с применением устойчивых материалов, и позволяет сохранять привлекательный вид в течение долгого времени. Мы сопровождаем проект на всех этапах, включая создание визуального решения, и заканчивая изготовлением и монтажом. Каждому заказчику уделяется особое внимание, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы используем современные технологии, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, не снижая качества продукции. Сотрудничая с нашей компанией, вы получаете профессиональный подход, позволяющий закрыть все потребности в дизайне и рекламе.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]картонные листы и упаковочные материалы[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, и у нас можно заказать разнообразные варианты под любые задачи. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, включая разработку дизайна, печать и постпечатную обработку, до создания рекламных материалов и наружной рекламы. Профессиональные сотрудники компании создают визуальные решения под конкретные задачи, чтобы обеспечить максимальную эффективность. Полиграфия различных форматов создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, и можем выполнить как небольшие партии, так и крупные тиражи. Кроме печатной продукции создание рекламных материалов, которые помогают привлекать внимание аудитории, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Внешние рекламные решения изготавливаются из долговечных материалов, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, начиная от разработки концепции, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждый клиент получает индивидуальный подход, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. В работе применяются инновационные методы, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Выбирая наши услуги, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, позволяющий закрыть все потребности в дизайне и рекламе.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, а мы предлагаем разнообразные варианты под любые задачи. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, от разработки дизайна и печати полиграфической продукции, а также разработку и производство наружной рекламы. Профессиональные сотрудники компании подготавливают дизайн, соответствующий вашему бренду, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Полиграфия различных форматов создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, обеспечивая безупречный внешний вид материалов. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, и готовы реализовать проект любого масштаба. Помимо полиграфии разработка рекламных носителей, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, и использовать их можно как в помещениях, так и на улице. Рекламные конструкции производятся с учетом климатических нагрузок, и позволяет сохранять привлекательный вид в течение долгого времени. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, включая создание визуального решения, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждый клиент получает индивидуальный подход, что обеспечивает точное соответствие требованиям. Мы основываемся на актуальных производственных технологиях, которые обеспечивают высокую скорость выполнения, не снижая качества продукции. Выбирая наши услуги, вы получаете профессиональный подход, позволяющий закрыть все потребности в дизайне и рекламе.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://carburater.com/]Vehicle number check[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a brand specializing in classic motorcycle, car and vintage restoration projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover previous ownership records, maintenance history and structural notes, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers unique project opportunities for those who love rebuilding classic machines, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides professional support based on years of restoration expertise. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, each project is approached with respect for its history and engineering. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to structured guidance that makes even complex projects achievable, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two understands the historical and technical character of each engine, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but an important tool that shapes the future of any restoration project. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://carburater.com/
[url=https://skladpart.ru/]Комфортные кресла Metta [/url]оптимально вписываются в пространство образовательных учреждений, создавая удобные условия для сидения на протяжении всего дня. Мебель для школ и детских садов от крупнейших поставщиков производится по современным стандартам качества, что позволяет использовать ее многие годы. Помещения в образовательных центрах требуют качественных элементов для оснащения рабочих мест, и кресла Metta становятся отличным дополнением. Многие модели обладают гибкой настройкой, что делает посадку максимально удобной. При формировании кабинетов и игровых зон первостепенным является качество материалов, именно поэтому бренды с хорошей репутацией предлагают прочную, безопасную и комфортную мебель. Также поставщики предлагают детские стульчики и игровые модули, которые помогают создать полноценную учебную среду. Покупая мебель у надежных производителей, вы получаете консультации специалистов, которые подберут мебель с учетом задач помещения. Часто присутствует возможность ускоренной доставки, что значительно экономит время. Каждая модель соответствует образовательным стандартам, поэтому может использоваться в любых учебных пространствах. Кресла Metta в сочетании с другой мебелью помогает создать комфортную зону для занятий, что положительно влияет на качество образовательного процесса.
https://skladpart.ru/
[url=https://skladpart.ru/]Комфортные кресла Metta [/url]оптимально вписываются в пространство образовательных учреждений, создавая удобные условия для сидения в течение длительных занятий. Современная мебель для образовательных учреждений от ведущих брендов разрабатывается с приоритетом на надежность и долговечность, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы. Учебные классы требуют эргономичных решений для организации пространства, и кресла Metta становятся отличным дополнением. Многие модели обладают гибкой настройкой, что делает посадку максимально удобной. При выборе мебели для ДОУ и учебных классов важно учитывать безопасность, именно поэтому бренды с хорошей репутацией предлагают прочную, безопасную и комфортную мебель. Кроме кресел Metta доступны учебные парты и столы, которые помогают создать полноценную учебную среду. При обращении к крупным поставщикам, вы можете рассчитывать на помощь экспертов, которые помогут составить оптимальную комплектацию. Часто присутствует возможность ускоренной доставки, что значительно экономит время. Вся мебель адаптирована под современные требования, поэтому может использоваться в любых учебных пространствах. Применение кресел Metta в готовых комплектах делает учебное пространство более удобным и эргономичным, что особенно важно для работы педагогов и детей.
https://skladpart.ru/
[url=https://skladpart.ru/]Офисные кресла Metta [/url]подходят для оснащения учебных помещений, гарантируя эргономичную посадку в течение длительных занятий. Современная мебель для образовательных учреждений от ведущих брендов разрабатывается с приоритетом на надежность и долговечность, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы. Кабинеты в школах требуют эргономичных решений для организации пространства, где продукция Metta показывает себя максимально эффективно. Они имеют регулируемую конструкцию, что делает посадку максимально удобной. При выборе мебели для ДОУ и учебных классов ключевым фактором остается надежность, поэтому крупные производители выпускают модели, прошедшие все необходимые проверки. Помимо кресел Metta можно приобрести комплекты для оснащения учебных зон, которые позволяют сформировать удобное пространство для занятий. При обращении к крупным поставщикам, вам всегда помогут подобрать подходящее решение, которые помогут составить оптимальную комплектацию. Кроме того предлагается быстрая доставка, что значительно экономит время. Каждая модель соответствует образовательным стандартам, что делает ее универсальной и практичной. Кресла Metta в сочетании с другой мебелью позволяет сформировать современный и функциональный кабинет, что положительно влияет на качество образовательного процесса.
https://skladpart.ru/
[url=https://skladpart.ru/]Комфортные кресла Metta [/url]часто используются при организации рабочих зон в школах и детских садах, обеспечивая комфорт и поддержку во время учебного процесса. Мебель для школ и детских садов от крупнейших поставщиков разрабатывается с приоритетом на надежность и долговечность, что позволяет использовать ее многие годы. Кабинеты в школах требуют эргономичных решений для организации пространства, и модели Metta прекрасно справляются с этой задачей. Они имеют регулируемую конструкцию, что делает посадку максимально удобной. При оснащении школ и детских садов ключевым фактором остается надежность, поэтому крупные производители выпускают модели, прошедшие все необходимые проверки. Кроме кресел Metta доступны детские стульчики и игровые модули, которые позволяют сформировать удобное пространство для занятий. При обращении к крупным поставщикам, вы получаете консультации специалистов, которые помогут составить оптимальную комплектацию. Часто присутствует возможность ускоренной доставки, что делает процесс покупки простым. Каждая модель соответствует образовательным стандартам, что делает ее универсальной и практичной. Кресла Metta в сочетании с другой мебелью делает учебное пространство более удобным и эргономичным, что положительно влияет на качество образовательного процесса.
https://skladpart.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Картонные коробки[/url] подходят для упаковки, хранения и перемещения различных вещей, и в интернет-магазине Канцто легко подобрать оптимальные коробки под конкретные нужды. Канцто предлагает большой выбор продукции для офиса и бытового использования, собирающий в одном каталоге мебель, канцтовары, бумагу, технику и множество других товаров. Здесь можно найти офисную и домашнюю мебель, которая помогает создать удобные условия для работы. Товары для офиса представлены в широком выборе, чтобы закрыть любые задачи, связанные с документами. Офисная и многофункциональная бумага используется для ежедневной работы с документами, и каждый может подобрать упаковку под свой объем работы. Кроме того доступны различная бытовая техника, оргтехника, строительные и отделочные материалы, ручной и электрический инструмент. Магазин также предлагает расходные материалы, хозтовары, средства для уборки и профессиональную химию, а также продукты питания, что делает Канцто универсальной площадкой. Покупатели могут воспользоваться быстрым оформлением заказа, гибкими вариантами получения заказа, а также получить консультацию специалистов, которые помогут подобрать товары под любые задачи. Ассортимент постоянно пополняется, поэтому пользователи всегда находят актуальные предложения. Магазин Канцто предлагает сочетание выгоды и разнообразия, что делает его отличным решением для повседневных и рабочих задач.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Коробки из картона[/url] часто используются для складирования и транспортировки, и в каталоге магазина Канцто легко подобрать оптимальные коробки под конкретные нужды. Канцто предлагает большой выбор продукции для офиса и бытового использования, в котором собрано всё — от мебели и бумаги до оргтехники и инструментов. В ассортименте представлены эргономичную и практичную мебель, для оформления кабинета, офиса или домашнего рабочего места. Различные канцелярские принадлежности включают сотни позиций, что помогает полностью укомплектовать рабочую зону. Офисная и многофункциональная бумага используется для ежедневной работы с документами, и каждый может подобрать упаковку под свой объем работы. Дополнительно можно приобрести бытовая техника, оргтехника, разные стройматериалы и отделочную продукцию, ручной и электрический инструмент. В ассортименте есть расходные товары, бытовые и хозяйственные принадлежности, различные чистящие и моющие средства, а также продукты питания, что превращает Канцто в комплексный магазин. Пользователи могут оформить покупку в несколько кликов, разными вариантами доставки, и обратиться за помощью менеджеров, которые подскажут оптимальные решения. Каталог регулярно обновляется, и покупатели могут выбирать из свежих новинок. Магазин Канцто предлагает сочетание выгоды и разнообразия, что делает его надежной платформой для покупок.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Коробки из картона[/url] подходят для упаковки, хранения и перемещения различных вещей, и в каталоге магазина Канцто доступны модели разного размера и прочности. Канцто предлагает большой выбор продукции для офиса и бытового использования, собирающий в одном каталоге мебель, канцтовары, бумагу, технику и множество других товаров. Здесь можно найти офисную и домашнюю мебель, подходящую для организации рабочего пространства. Товары для офиса доступны в разных категориях, что позволяет подобрать всё необходимое. Бумага для печати и копирования предназначена для офисной техники, и каждый может подобрать упаковку под свой объем работы. Также в каталоге Канцто представлены оборудование для дома, офисные технические устройства, разные стройматериалы и отделочную продукцию, инструменты для работ разного уровня. Можно приобрести самые разные расходники, хозтовары, средства для уборки и профессиональную химию, а также продукты питания, что превращает Канцто в комплексный магазин. Пользователи могут оформить покупку в несколько кликов, удобными способами доставки, а также получить консультацию специалистов, которые порекомендуют подходящие позиции. Ассортимент постоянно пополняется, поэтому пользователи всегда находят актуальные предложения. Интернет-магазин Канцто сочетает удобство выбора и широкий ассортимент, что делает его надежной платформой для покупок.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]листы картонные[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, а мы предлагаем качественную продукцию любого формата. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, включая разработку дизайна, печать и постпечатную обработку, до изготовления рекламных конструкций и наружных решений. Команда специалистов разрабатывают макеты любой сложности, чтобы обеспечить максимальную эффективность. Полиграфия различных форматов производится на современном оборудовании, обеспечивая безупречный внешний вид материалов. Мы создаем визитки, листовки, журналы, и готовы реализовать проект любого масштаба. Помимо полиграфии создание рекламных материалов, которые помогают привлекать внимание аудитории, и использовать их можно как в помещениях, так и на улице. Рекламные конструкции производятся с учетом климатических нагрузок, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы сопровождаем проект на всех этапах, от продумывания дизайна, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждый клиент получает индивидуальный подход, что делает итоговый результат полностью адаптированным под нужды бизнеса. Мы используем современные технологии, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Сотрудничая с нашей компанией, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, который помогает реализовать любые рекламные задачи.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Картонные коробки[/url] подходят для упаковки, хранения и перемещения различных вещей, которые представлены в ассортименте магазина Канцто можно выбрать подходящий вариант для любых задач. Канцто — интернет-магазин товаров для офиса и дома, где представлены мебель, канцтовары, бумага и техника. Здесь можно найти эргономичную и практичную мебель, для оформления кабинета, офиса или домашнего рабочего места. Канцтовары представлены в широком выборе, что позволяет подобрать всё необходимое. Бумага для печати и копирования предназначена для офисной техники, и магазин предлагает множество вариантов. Кроме того доступны бытовая техника, оргтехника, материалы для ремонта и отделки, ручной и электрический инструмент. В ассортименте есть расходные товары, бытовые и хозяйственные принадлежности, различные чистящие и моющие средства, включая продукты ежедневного потребления, что делает Канцто универсальной площадкой. Пользователи могут оформить покупку в несколько кликов, гибкими вариантами получения заказа, а также получить консультацию специалистов, которые подскажут оптимальные решения. Каталог регулярно обновляется, поэтому пользователи всегда находят актуальные предложения. Канцто объединяет богатый ассортимент и доступность, что делает его удобным местом для комплексных закупок.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] подходят для хранения, перевозки и дальнейшей обработки, и у нас можно заказать картон различной плотности и размеров. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, от разработки дизайна и печати полиграфической продукции, до изготовления рекламных конструкций и наружных решений. Профессиональные сотрудники компании подготавливают дизайн, соответствующий вашему бренду, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Полиграфия различных форматов создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы работаем с визитками, буклетами, каталогами, и готовы реализовать проект любого масштаба. Помимо полиграфии создание рекламных материалов, которые помогают привлекать внимание аудитории, которые эффективно работают в различных условиях. Рекламные конструкции создаются с применением устойчивых материалов, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы сопровождаем проект на всех этапах, от продумывания дизайна, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждому заказчику уделяется особое внимание, что делает итоговый результат полностью адаптированным под нужды бизнеса. Мы используем современные технологии, которые позволяют ускорить изготовление, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Выбирая наши услуги, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, создающий удобный и эффективный процесс для бизнеса.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Коробки из картона[/url] необходимы для хранения и перевозки, и в каталоге магазина Канцто легко подобрать оптимальные коробки под конкретные нужды. Канцто — интернет-магазин товаров для офиса и дома, в котором собрано всё — от мебели и бумаги до оргтехники и инструментов. В ассортименте представлены эргономичную и практичную мебель, которая помогает создать удобные условия для работы. Товары для офиса представлены в широком выборе, что позволяет подобрать всё необходимое. Офисная и многофункциональная бумага предназначена для офисной техники, и покупатель может выбрать любые объемы поставки. Кроме того доступны различная бытовая техника, офисные технические устройства, строительные и отделочные материалы, инструменты. В ассортименте есть расходные товары, бытовые и хозяйственные принадлежности, профессиональную и бытовую химию, а также продукты питания, что делает Канцто универсальной площадкой. Пользователи могут оформить покупку в несколько кликов, удобными способами доставки, и рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку, которые подскажут оптимальные решения. Каталог регулярно обновляется, и покупатели могут выбирать из свежих новинок. Магазин Канцто предлагает сочетание выгоды и разнообразия, что делает его надежной платформой для покупок.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] используются для упаковки, складирования и производства, и наша компания предоставляет разнообразные варианты под любые задачи. Наша компания оказывает комплекс услуг, от разработки дизайна и печати полиграфической продукции, а также разработку и производство наружной рекламы. Команда специалистов разрабатывают макеты любой сложности, делая акцент на привлекательности и функциональности. Полиграфическая продукция производится на современном оборудовании, что обеспечивает яркость, точность и устойчивость изображений. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, что дает возможность выполнить заказ любой сложности. Также в числе наших услуг изготовление рекламной продукции, которые повышают узнаваемость бренда, которые эффективно работают в различных условиях. Наружная реклама изготавливаются из долговечных материалов, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы ведем проекты от идеи до реализации, от продумывания дизайна, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Мы работаем с каждым проектом персонально, что обеспечивает точное соответствие требованиям. Мы используем современные технологии, которые позволяют ускорить изготовление, при неизменно высоком уровне исполнения. Обращаясь к нам, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, создающий удобный и эффективный процесс для бизнеса.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] подходят для хранения, перевозки и дальнейшей обработки, и наша компания предоставляет картон различной плотности и размеров. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, включая разработку дизайна, печать и постпечатную обработку, до создания рекламных материалов и наружной рекламы. Профессиональные сотрудники компании создают визуальные решения под конкретные задачи, чтобы обеспечить максимальную эффективность. Печатные материалы изготавливается с использованием профессиональной техники, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы создаем визитки, листовки, журналы, что дает возможность выполнить заказ любой сложности. Помимо полиграфии создание рекламных материалов, которые помогают привлекать внимание аудитории, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Наружная реклама изготавливаются из долговечных материалов, и позволяет сохранять привлекательный вид в течение долгого времени. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, начиная от разработки концепции, и до полного производства и установки. Каждый клиент получает индивидуальный подход, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы используем современные технологии, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, не снижая качества продукции. Выбирая наши услуги, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, создающий удобный и эффективный процесс для бизнеса.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Упаковочные картонные коробки[/url] часто используются для складирования и транспортировки, и в интернет-магазине Канцто доступны модели разного размера и прочности. Онлайн-магазин Канцто объединяет товары для дома и офиса, в котором собрано всё — от мебели и бумаги до оргтехники и инструментов. Здесь можно найти эргономичную и практичную мебель, которая помогает создать удобные условия для работы. Канцтовары доступны в разных категориях, что помогает полностью укомплектовать рабочую зону. Офисная и многофункциональная бумага используется для ежедневной работы с документами, и магазин предлагает множество вариантов. Кроме того доступны оборудование для дома, принтеры, сканеры и другая оргтехника, строительные и отделочные материалы, ручной и электрический инструмент. Можно приобрести самые разные расходники, хозтовары, средства для уборки и профессиональную химию, а также продукты питания, что превращает Канцто в комплексный магазин. Пользователи могут оформить покупку в несколько кликов, гибкими вариантами получения заказа, и рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку, которые порекомендуют подходящие позиции. Коллекция товаров периодически расширяется, и клиентам доступны актуальные позиции для любых сфер. Интернет-магазин Канцто сочетает удобство выбора и широкий ассортимент, что делает его отличным решением для повседневных и рабочих задач.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, и у нас можно заказать качественную продукцию любого формата. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, которые охватывают создание макетов, печать и производство продукции, а также разработку и производство наружной рекламы. Профессиональные сотрудники компании создают визуальные решения под конкретные задачи, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Полиграфия различных форматов изготавливается с использованием профессиональной техники, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы работаем с визитками, буклетами, каталогами, и можем выполнить как небольшие партии, так и крупные тиражи. Кроме печатной продукции изготовление рекламной продукции, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Наружная реклама создаются с применением устойчивых материалов, что гарантирует длительную эксплуатацию. Мы ведем проекты от идеи до реализации, начиная от разработки концепции, и заканчивая изготовлением и монтажом. Мы работаем с каждым проектом персонально, что делает итоговый результат полностью адаптированным под нужды бизнеса. В работе применяются инновационные методы, которые позволяют ускорить изготовление, при неизменно высоком уровне исполнения. Сотрудничая с нашей компанией, вы получаете профессиональный подход, позволяющий закрыть все потребности в дизайне и рекламе.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]картонные листы и упаковочные материалы[/url] используются для упаковки, складирования и производства, а мы предлагаем картон различной плотности и размеров. Мы предоставляем полный набор решений, которые охватывают создание макетов, печать и производство продукции, до создания рекламных материалов и наружной рекламы. Наши дизайнеры и технические специалисты создают визуальные решения под конкретные задачи, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Полиграфическая продукция создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, что позволяет добиться четкости, насыщенности и долговечности. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, и можем выполнить как небольшие партии, так и крупные тиражи. Также в числе наших услуг изготовление рекламной продукции, которые повышают узнаваемость бренда, и использовать их можно как в помещениях, так и на улице. Рекламные конструкции создаются с применением устойчивых материалов, что обеспечивает надежность и стойкость. Мы сопровождаем проект на всех этапах, начиная от разработки концепции, и до полного производства и установки. Мы работаем с каждым проектом персонально, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы основываемся на актуальных производственных технологиях, которые обеспечивают высокую скорость выполнения, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Обращаясь к нам, вы получаете профессиональный подход, который помогает реализовать любые рекламные задачи.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Упаковочные картонные коробки[/url] часто используются для складирования и транспортировки, и в интернет-магазине Канцто доступны модели разного размера и прочности. Канцто — интернет-магазин товаров для офиса и дома, собирающий в одном каталоге мебель, канцтовары, бумагу, технику и множество других товаров. Здесь можно найти офисную и домашнюю мебель, для оформления кабинета, офиса или домашнего рабочего места. Канцтовары включают сотни позиций, что помогает полностью укомплектовать рабочую зону. Офисная и многофункциональная бумага используется для ежедневной работы с документами, и магазин предлагает множество вариантов. Также в каталоге Канцто представлены оборудование для дома, офисные технические устройства, строительные и отделочные материалы, инструменты для работ разного уровня. Можно приобрести самые разные расходники, хозтовары, профессиональную и бытовую химию, и даже продукты питания, что делает Канцто универсальной площадкой. Пользователи могут оформить покупку в несколько кликов, гибкими вариантами получения заказа, и рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку, которые помогут подобрать товары под любые задачи. Каталог регулярно обновляется, и клиентам доступны актуальные позиции для любых сфер. Интернет-магазин Канцто сочетает удобство выбора и широкий ассортимент, что делает его удобным местом для комплексных закупок.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]коробки и листы картонные[/url] используются для упаковки, складирования и производства, и наша компания предоставляет разнообразные варианты под любые задачи. Наша компания оказывает комплекс услуг, которые охватывают создание макетов, печать и производство продукции, до изготовления рекламных конструкций и наружных решений. Наши дизайнеры и технические специалисты разрабатывают макеты любой сложности, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Печатные материалы производится на современном оборудовании, обеспечивая безупречный внешний вид материалов. Мы предлагаем изготовление буклетов, брошюр и каталогов, что дает возможность выполнить заказ любой сложности. Кроме печатной продукции изготовление рекламной продукции, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, которые эффективно работают в различных условиях. Внешние рекламные решения изготавливаются из долговечных материалов, и позволяет сохранять привлекательный вид в течение долгого времени. Мы ведем проекты от идеи до реализации, начиная от разработки концепции, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Мы работаем с каждым проектом персонально, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы используем современные технологии, которые обеспечивают высокую скорость выполнения, не снижая качества продукции. Обращаясь к нам, вы получаете комплексный сервис, создающий удобный и эффективный процесс для бизнеса.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]картонные листы и упаковочные материалы[/url] используются для упаковки, складирования и производства, и у нас можно заказать картон различной плотности и размеров. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, от разработки дизайна и печати полиграфической продукции, а также разработку и производство наружной рекламы. Профессиональные сотрудники компании подготавливают дизайн, соответствующий вашему бренду, делая акцент на привлекательности и функциональности. Полиграфия различных форматов создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, обеспечивая безупречный внешний вид материалов. Мы создаем визитки, листовки, журналы, и готовы реализовать проект любого масштаба. Помимо полиграфии создание рекламных материалов, которые повышают узнаваемость бренда, подходящих для размещения в любых пространствах. Наружная реклама производятся с учетом климатических нагрузок, что гарантирует длительную эксплуатацию. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, включая создание визуального решения, и до полного производства и установки. Каждому заказчику уделяется особое внимание, что обеспечивает точное соответствие требованиям. Мы используем современные технологии, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Обращаясь к нам, вы обеспечиваете полный цикл работ в одном месте, позволяющий закрыть все потребности в дизайне и рекламе.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://kancto.ru/]Коробки из картона[/url] подходят для упаковки, хранения и перемещения различных вещей, и в интернет-магазине Канцто доступны модели разного размера и прочности. Онлайн-магазин Канцто объединяет товары для дома и офиса, в котором собрано всё — от мебели и бумаги до оргтехники и инструментов. Здесь можно найти комплекты мебели для рабочих зон и дома, для оформления кабинета, офиса или домашнего рабочего места. Товары для офиса представлены в широком выборе, что позволяет подобрать всё необходимое. Офисная и многофункциональная бумага используется для ежедневной работы с документами, и покупатель может выбрать любые объемы поставки. Дополнительно можно приобрести различная бытовая техника, офисные технические устройства, разные стройматериалы и отделочную продукцию, инструменты для работ разного уровня. Магазин также предлагает расходные материалы, товары для хозяйственных задач, профессиональную и бытовую химию, а также продукты питания, что делает Канцто универсальной площадкой. Покупатели могут воспользоваться быстрым оформлением заказа, удобными способами доставки, и рассчитывать на профессиональную поддержку, которые подскажут оптимальные решения. Ассортимент постоянно пополняется, и покупатели могут выбирать из свежих новинок. Канцто объединяет богатый ассортимент и доступность, что делает его удобным местом для комплексных закупок.
https://kancto.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]картонные листы и упаковочные материалы[/url] подходят для хранения, перевозки и дальнейшей обработки, и у нас можно заказать качественную продукцию любого формата. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, которые охватывают создание макетов, печать и производство продукции, а также разработку и производство наружной рекламы. Наши дизайнеры и технические специалисты подготавливают дизайн, соответствующий вашему бренду, делая акцент на привлекательности и функциональности. Полиграфия различных форматов производится на современном оборудовании, что обеспечивает яркость, точность и устойчивость изображений. Мы создаем визитки, листовки, журналы, что дает возможность выполнить заказ любой сложности. Помимо полиграфии изготовление рекламной продукции, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, которые эффективно работают в различных условиях. Рекламные конструкции производятся с учетом климатических нагрузок, и позволяет сохранять привлекательный вид в течение долгого времени. Мы сопровождаем проект на всех этапах, от продумывания дизайна, и завершая монтажом на объекте. Каждый клиент получает индивидуальный подход, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы основываемся на актуальных производственных технологиях, которые обеспечивают высокую скорость выполнения, сохраняя при этом высокое качество. Выбирая наши услуги, вы получаете профессиональный подход, создающий удобный и эффективный процесс для бизнеса.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://bannerr.ru/]картонные листы и упаковочные материалы[/url] широко применяются в упаковочных и производственных задачах, и наша компания предоставляет качественную продукцию любого формата. Наша компания оказывает комплекс услуг, включая разработку дизайна, печать и постпечатную обработку, а также разработку и производство наружной рекламы. Наши дизайнеры и технические специалисты создают визуальные решения под конкретные задачи, чтобы ваши материалы выделялись среди конкурентов. Полиграфическая продукция создается по технологиям, гарантирующим высокое качество, что обеспечивает яркость, точность и устойчивость изображений. Мы работаем с визитками, буклетами, каталогами, и можем выполнить как небольшие партии, так и крупные тиражи. Кроме печатной продукции создание рекламных материалов, которые усиливают коммуникацию с клиентами, которые эффективно работают в различных условиях. Наружная реклама создаются с применением устойчивых материалов, что гарантирует длительную эксплуатацию. Мы обеспечиваем полностью контролируемый процесс, от продумывания дизайна, и до полного производства и установки. Каждому заказчику уделяется особое внимание, что позволяет создавать решения, максимально соответствующие задачам. Мы основываемся на актуальных производственных технологиях, которые уменьшают сроки реализации проектов, при неизменно высоком уровне исполнения. Выбирая наши услуги, вы получаете профессиональный подход, который помогает реализовать любые рекламные задачи.
https://bannerr.ru/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle number check[/url] is a crucial step before choosing any restoration project, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a professional workshop dedicated to rebuilding motorcycles, cars and unique automotive classics. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover previous ownership records, maintenance history and structural notes, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers unique project opportunities for those who love rebuilding classic machines, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides detailed guidance throughout the entire process. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every rebuild is crafted with passion, precision and technical understanding. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to a combination of technical research, hands-on expertise and artistic restoration vision, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two focuses on creating high-quality, accurate and authentic rebuilds, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but an important tool that shapes the future of any restoration project. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle number check[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a brand specializing in classic motorcycle, car and vintage restoration projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover previous ownership records, maintenance history and structural notes, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers rare models waiting to be revived with professional craftsmanship, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides a personalized approach to help shape each project according to the owner’s style. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every machine is treated not just as a tool but as a piece of automotive heritage. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to professional evaluation, mechanical planning and tailored upgrade recommendations, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two lives and breathes mechanical culture, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but an important tool that shapes the future of any restoration project. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle history lookup[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a leading name in the field of custom mechanical restoration and classic vehicle projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover important insights that help evaluate whether a machine is suitable for a full rebuild, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers rare models waiting to be revived with professional craftsmanship, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides professional support based on years of restoration expertise. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every rebuild is crafted with passion, precision and technical understanding. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to professional evaluation, mechanical planning and tailored upgrade recommendations, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two lives and breathes mechanical culture, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but a gateway to discovering hidden mechanical potential. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle number check[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a leading name in the field of custom mechanical restoration and classic vehicle projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover key details that reveal the mechanical background of the vehicle, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers unique project opportunities for those who love rebuilding classic machines, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides detailed guidance throughout the entire process. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, each project is approached with respect for its history and engineering. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to structured guidance that makes even complex projects achievable, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two focuses on creating high-quality, accurate and authentic rebuilds, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but a gateway to discovering hidden mechanical potential. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle history lookup[/url] is a crucial step before choosing any restoration project, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a leading name in the field of custom mechanical restoration and classic vehicle projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover previous ownership records, maintenance history and structural notes, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers rare models waiting to be revived with professional craftsmanship, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides a personalized approach to help shape each project according to the owner’s style. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every machine is treated not just as a tool but as a piece of automotive heritage. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to a combination of technical research, hands-on expertise and artistic restoration vision, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two understands the historical and technical character of each engine, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but a gateway to discovering hidden mechanical potential. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle number check[/url] is a reliable way to understand the real condition of a vehicle before investing, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a brand specializing in classic motorcycle, car and vintage restoration projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover key details that reveal the mechanical background of the vehicle, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers unique project opportunities for those who love rebuilding classic machines, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides professional support based on years of restoration expertise. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every rebuild is crafted with passion, precision and technical understanding. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to structured guidance that makes even complex projects achievable, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two focuses on creating high-quality, accurate and authentic rebuilds, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but the first move toward building a unique machine with personality and history. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle history lookup[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a professional workshop dedicated to rebuilding motorcycles, cars and unique automotive classics. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover key details that reveal the mechanical background of the vehicle, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers a wide selection of vehicles and motorcycles ready for restoration, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides professional support based on years of restoration expertise. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every machine is treated not just as a tool but as a piece of automotive heritage. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to structured guidance that makes even complex projects achievable, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two understands the historical and technical character of each engine, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but a gateway to discovering hidden mechanical potential. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle history lookup[/url] is a crucial step before choosing any restoration project, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a brand specializing in classic motorcycle, car and vintage restoration projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover previous ownership records, maintenance history and structural notes, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers a wide selection of vehicles and motorcycles ready for restoration, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides professional support based on years of restoration expertise. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, every machine is treated not just as a tool but as a piece of automotive heritage. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to professional evaluation, mechanical planning and tailored upgrade recommendations, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two focuses on creating high-quality, accurate and authentic rebuilds, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but an important tool that shapes the future of any restoration project. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Checking a vehicle by its registration number[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a brand specializing in classic motorcycle, car and vintage restoration projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover previous ownership records, maintenance history and structural notes, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers a wide selection of vehicles and motorcycles ready for restoration, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides a personalized approach to help shape each project according to the owner’s style. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, each project is approached with respect for its history and engineering. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to professional evaluation, mechanical planning and tailored upgrade recommendations, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two lives and breathes mechanical culture, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but a gateway to discovering hidden mechanical potential. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://backontwo.com/]Vehicle number check[/url] is an essential action for anyone considering a classic car or motorcycle rebuild, and it becomes especially valuable when exploring the world of Back On Two, a brand specializing in classic motorcycle, car and vintage restoration projects. With a simple number lookup, enthusiasts can discover key details that reveal the mechanical background of the vehicle, and such information often defines whether a project has true potential. Back On Two offers unique project opportunities for those who love rebuilding classic machines, giving every enthusiast a chance to find the project that fits their vision. Whether a person is just entering the restoration world or already experienced, Back On Two provides professional support based on years of restoration expertise. Many restoration journeys begin with a simple number check, which quickly evolves into a deep exploration of the vehicle’s story, and with Back On Two, each project is approached with respect for its history and engineering. Classic motorcycles, vintage cars and forgotten machines can be transformed into powerful, beautiful and fully functional creations when handled with the right knowledge. With Back On Two, enthusiasts gain access to professional evaluation, mechanical planning and tailored upgrade recommendations, allowing them to restore machines to life with confidence. The team behind Back On Two focuses on creating high-quality, accurate and authentic rebuilds, ensuring every restoration becomes a meaningful journey. A vehicle number check is therefore not just a bureaucratic step, but the first move toward building a unique machine with personality and history. Back On Two continues to lead this field by offering enthusiasts a trusted, knowledgeable and inspiring environment where every project — from motorcycles to classic cars — can grow into a masterpiece.
https://backontwo.com/
[url=https://balancecrm.ru/]интеграция CRM решений[/url] — важный инструмент для оптимизации работы компаний. Платформа BalanceCRM обеспечивает индивидуальные настройки под требования бизнеса и государственных структур. Внедрение начинается с аудита процессов и выявления ключевых задач. Автоматизация задач и процессов снижает ручной труд и ускоряет выполнение. CRM-платформа позволяет настроить функционал под уникальные требования. Эксперты BalanceCRM проводят обучение и помогают настроить систему под сотрудников. Система помогает оптимизировать рутинные задачи и снизить нагрузку на сотрудников. Интеграция с другими системами и сервисами повышает ценность CRM. CRM обеспечивает точную аналитику и отчеты для руководителей. С помощью CRM можно контролировать весь цикл взаимодействия с клиентом. CRM помогает минимизировать риски и повышает точность учета информации. Регулярные обновления и поддержка обеспечивают актуальность функционала. CRM помогает стандартизировать процессы и улучшить взаимодействие между отделами. Использование платформы помогает организациям работать слаженно и достигать поставленных целей.
https://balancecrm.ru/
[url=https://balancecrm.ru/]настройка CRM-системы[/url] — основа эффективного управления клиентскими и внутренними процессами. Использование BalanceCRM позволяет адаптировать CRM под уникальные нужды любой организации. Настройка CRM начинается с изучения рабочих потоков и бизнес-потребностей. Интеграция CRM упрощает контроль за проектами и повышает прозрачность процессов. BalanceCRM предлагает гибкие настройки под разные типы бизнеса. Поддержка специалистов обеспечивает правильное использование всех функций CRM. Система помогает оптимизировать рутинные задачи и снизить нагрузку на сотрудников. Подключение внешних сервисов и аналитических платформ расширяет возможности. Сбор и анализ данных позволяет принимать обоснованные решения. Платформа объединяет все бизнес-процессы в одной системе для удобства управления. Использование системы улучшает контроль над проектами и задачами. Платформа BalanceCRM постоянно обновляется и соответствует современным требованиям. Комплексное внедрение CRM с учетом специфики организации повышает эффективность работы и ускоряет рост бизнеса. Таким образом, BalanceCRM является надежным инструментом для частного и государственного сектора.
https://balancecrm.ru/
[url=https://balancecrm.ru/]внедрение CRM-платформ[/url] — важный инструмент для оптимизации работы компаний. BalanceCRM помогает настраивать CRM-системы для частных компаний и государственных организаций. Внедрение начинается с аудита процессов и выявления ключевых задач. Оптимизация взаимодействия с клиентами и сотрудниками повышает эффективность работы. BalanceCRM предлагает гибкие настройки под разные типы бизнеса. Эксперты BalanceCRM проводят обучение и помогают настроить систему под сотрудников. CRM упрощает управление задачами, контактами и внутренними процессами. Интеграция с другими системами и сервисами повышает ценность CRM. Сбор и анализ данных позволяет принимать обоснованные решения. С помощью CRM можно контролировать весь цикл взаимодействия с клиентом. Внедрение CRM повышает прозрачность процессов и снижает вероятность ошибок. Платформа BalanceCRM постоянно обновляется и соответствует современным требованиям. Комплексное внедрение CRM с учетом специфики организации повышает эффективность работы и ускоряет рост бизнеса. Таким образом, BalanceCRM является надежным инструментом для частного и государственного сектора.
https://balancecrm.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]обучение работе с Power BI, освоение аналитики в Power BI [/url]— система для обработки, анализа и представления информации в графическом виде. Обучение включает изучение интерфейса Power BI и создание собственных отчетов. Студенты изучают импорт данных из разных источников и их обработку. Обучение включает разработку графиков, диаграмм и интерактивных отчетов. Курс позволяет создавать сложные расчеты и KPI с помощью DAX. Платформа позволяет создавать отчеты, которые автоматически отражают актуальные данные. Платформа обеспечивает совместимость с различными источниками данных. В рамках курса студенты разрабатывают проекты с реальными данными. Особое внимание уделяется удобству представления информации для руководства и коллег. Студенты получают знания о безопасности данных и правильной организации работы в Power BI. После прохождения обучения учащиеся способны создавать отчеты, анализировать данные и принимать решения на основе визуализации. Курс ориентирован на новичков и профессионалов, которым нужен практический опыт. Таким образом, обучение Power BI помогает эффективно анализировать данные, визуализировать информацию и принимать обоснованные решения.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]power bi, обучение power bi [/url]— платформа для построения интерактивных отчетов и дашбордов. Курс поможет освоить основные функции Power BI и их применение на практике. Студенты изучают импорт данных из разных источников и их обработку. Обучение включает разработку графиков, диаграмм и интерактивных отчетов. Курс позволяет создавать сложные расчеты и KPI с помощью DAX. Обучение помогает настраивать автоматическое обновление данных и отчеты в реальном времени. Платформа обеспечивает совместимость с различными источниками данных. Практические задания помогают закрепить навыки и создавать собственные аналитические решения. Курс обучает структурированному подходу к визуализации данных. Программа обучения охватывает вопросы защиты информации и прав доступа. После прохождения обучения учащиеся способны создавать отчеты, анализировать данные и принимать решения на основе визуализации. Курс ориентирован на новичков и профессионалов, которым нужен практический опыт. Программа позволяет интегрировать аналитические навыки Power BI в повседневную практику.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]обучение работе с Power BI, освоение аналитики в Power BI [/url]— инструмент для анализа и визуализации данных. Обучение включает изучение интерфейса Power BI и создание собственных отчетов. На занятиях показывают, как объединять и трансформировать данные. Обучение включает разработку графиков, диаграмм и интерактивных отчетов. Курс позволяет создавать сложные расчеты и KPI с помощью DAX. Студенты узнают, как автоматизировать обновление данных и строить динамические отчеты. Курс обучает работе с Power BI в связке с Excel, SQL и облачными сервисами. В рамках курса студенты разрабатывают проекты с реальными данными. Курс обучает структурированному подходу к визуализации данных. Студенты получают знания о безопасности данных и правильной организации работы в Power BI. Освоив курс, студенты умеют использовать Power BI для бизнес-анализа. Курс ориентирован на новичков и профессионалов, которым нужен практический опыт. Таким образом, обучение Power BI помогает эффективно анализировать данные, визуализировать информацию и принимать обоснованные решения.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]обучение работе с Power BI, освоение аналитики в Power BI [/url]— инструмент для анализа и визуализации данных. Обучение включает изучение интерфейса Power BI и создание собственных отчетов. На занятиях показывают, как объединять и трансформировать данные. Практика по визуализации помогает представлять данные в удобном формате. Изучаются формулы DAX и методы расчетов внутри Power BI. Студенты узнают, как автоматизировать обновление данных и строить динамические отчеты. Курс обучает работе с Power BI в связке с Excel, SQL и облачными сервисами. В рамках курса студенты разрабатывают проекты с реальными данными. Курс обучает структурированному подходу к визуализации данных. Студенты получают знания о безопасности данных и правильной организации работы в Power BI. Освоив курс, студенты умеют использовать Power BI для бизнес-анализа. Обучение подходит как для начинающих, так и для специалистов, желающих улучшить навыки работы с данными. Таким образом, обучение Power BI помогает эффективно анализировать данные, визуализировать информацию и принимать обоснованные решения.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]power bi, обучение power bi [/url]— инструмент для анализа и визуализации данных. Программа обучения позволяет научиться подключать данные и строить визуализации. На занятиях показывают, как объединять и трансформировать данные. Обучение включает разработку графиков, диаграмм и интерактивных отчетов. Программа включает освоение языка DAX для вычислений и анализа. Платформа позволяет создавать отчеты, которые автоматически отражают актуальные данные. Платформа обеспечивает совместимость с различными источниками данных. В рамках курса студенты разрабатывают проекты с реальными данными. Курс обучает структурированному подходу к визуализации данных. Курс помогает выстроить систему безопасного обмена данными и отчетности. После прохождения обучения учащиеся способны создавать отчеты, анализировать данные и принимать решения на основе визуализации. Программа позволяет каждому освоить Power BI на практических примерах. Курс обеспечивает полное понимание функционала Power BI и применение его в реальной работе.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]power bi, обучение power bi [/url]— инструмент для анализа и визуализации данных. Курс поможет освоить основные функции Power BI и их применение на практике. На занятиях показывают, как объединять и трансформировать данные. Особое внимание уделяется созданию дашбордов и визуализации ключевых показателей. Курс позволяет создавать сложные расчеты и KPI с помощью DAX. Студенты узнают, как автоматизировать обновление данных и строить динамические отчеты. Платформа обеспечивает совместимость с различными источниками данных. Практические задания помогают закрепить навыки и создавать собственные аналитические решения. Курс обучает структурированному подходу к визуализации данных. Курс помогает выстроить систему безопасного обмена данными и отчетности. Освоив курс, студенты умеют использовать Power BI для бизнес-анализа. Курс ориентирован на новичков и профессионалов, которым нужен практический опыт. Курс обеспечивает полное понимание функционала Power BI и применение его в реальной работе.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]power bi, обучение power bi [/url]— система для обработки, анализа и представления информации в графическом виде. Программа обучения позволяет научиться подключать данные и строить визуализации. Студенты изучают импорт данных из разных источников и их обработку. Особое внимание уделяется созданию дашбордов и визуализации ключевых показателей. Изучаются формулы DAX и методы расчетов внутри Power BI. Студенты узнают, как автоматизировать обновление данных и строить динамические отчеты. Курс обучает работе с Power BI в связке с Excel, SQL и облачными сервисами. Практические задания помогают закрепить навыки и создавать собственные аналитические решения. Обучение включает рекомендации по созданию понятных и наглядных отчетов. Студенты получают знания о безопасности данных и правильной организации работы в Power BI. Программа позволяет работать с Power BI для оценки эффективности процессов и прогнозирования. Обучение подходит как для начинающих, так и для специалистов, желающих улучшить навыки работы с данными. Курс обеспечивает полное понимание функционала Power BI и применение его в реальной работе.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://microsoftbi.ru/]Power BI курс, изучение Power BI [/url]— платформа для построения интерактивных отчетов и дашбордов. Программа обучения позволяет научиться подключать данные и строить визуализации. Учащиеся осваивают методы работы с таблицами и базами данных внутри Power BI. Практика по визуализации помогает представлять данные в удобном формате. Курс позволяет создавать сложные расчеты и KPI с помощью DAX. Студенты узнают, как автоматизировать обновление данных и строить динамические отчеты. Платформа обеспечивает совместимость с различными источниками данных. Обучение предполагает решение кейсов и создание функциональных дашбордов. Обучение включает рекомендации по созданию понятных и наглядных отчетов. Программа обучения охватывает вопросы защиты информации и прав доступа. После прохождения обучения учащиеся способны создавать отчеты, анализировать данные и принимать решения на основе визуализации. Обучение подходит как для начинающих, так и для специалистов, желающих улучшить навыки работы с данными. Курс обеспечивает полное понимание функционала Power BI и применение его в реальной работе.
https://microsoftbi.ru/
[url=https://telegramhub.ru/]telegram, телеграмм, новости из телеграмм [/url]— оперативные новости и тенденции. Платформа позволяет следить за важными событиями в режиме реального времени. Тематика каналов варьируется от актуальных новостей до аналитики и лайфхаков. Пользователи могут подписываться на интересующие каналы и получать уведомления. Каналы облегчают распространение информации и обсуждение событий. Новости публикуются экспертами и аналитиками для точного освещения событий. Обзор событий сопровождается аналитикой и прогнозами. Новости поступают в любое время, обеспечивая оперативность. Содержание каналов отражает актуальные события и обсуждаемые темы. Телеграмм позволяет легко находить нужные каналы и темы. Система уведомлений позволяет не пропустить важные публикации. Сервис гарантирует надежность и сохранность личной информации. Использование мультимедиа делает информацию более информативной и интересной. Telegram каналы становятся источником свежих новостей и трендов.
https://telegramhub.ru/
[url=https://telegramhub.ru/]новости из Telegram каналов [/url]— последние события и обновления. Через телеграмм легко получать обновления без задержек. Содержание каналов разнообразно: от финансовых новостей до культурных событий. Подписка на каналы обеспечивает доступ к эксклюзивным материалам. Каналы облегчают распространение информации и обсуждение событий. Контент формируется администраторами каналов и редакторами новостных ресурсов. Обзор событий сопровождается аналитикой и прогнозами. Телеграмм обеспечивает постоянный поток информации без задержек. Через телеграмм можно отслеживать, что обсуждают и на что реагируют аудитории. Поиск и сортировка помогают подписаться на наиболее актуальные источники. Подписчики всегда в курсе новостей благодаря оперативным обновлениям. Платформа защищает данные пользователей и обеспечивает конфиденциальность. Использование мультимедиа делает информацию более информативной и интересной. Таким образом, новости из телеграмм каналов предоставляют актуальную, оперативную и разнообразную информацию.
https://telegramhub.ru/
[url=https://telegramhub.ru/]telegram, телеграмм, новости из телеграмм [/url]— последние события и обновления. Через телеграмм легко получать обновления без задержек. Новости охватывают различные темы: политика, экономика, технологии и развлечения. Каждый подписчик получает свежую информацию напрямую в мессенджере. Каналы облегчают распространение информации и обсуждение событий. Контент формируется администраторами каналов и редакторами новостных ресурсов. Обзор событий сопровождается аналитикой и прогнозами. Телеграмм обеспечивает постоянный поток информации без задержек. Содержание каналов отражает актуальные события и обсуждаемые темы. Поиск и сортировка помогают подписаться на наиболее актуальные источники. Система уведомлений позволяет не пропустить важные публикации. Сервис гарантирует надежность и сохранность личной информации. Публикации сопровождаются мультимедийным контентом для удобного восприятия. Таким образом, новости из телеграмм каналов предоставляют актуальную, оперативную и разнообразную информацию.
https://telegramhub.ru/
[url=https://telegramhub.ru/]telegram, телеграмм, новости из телеграмм [/url]— актуальная информация из разных источников. Telegram каналы предоставляют новости практически мгновенно. Новости охватывают различные темы: политика, экономика, технологии и развлечения. Подписка на каналы обеспечивает доступ к эксклюзивным материалам. Каналы облегчают распространение информации и обсуждение событий. Публикации включают текст, фото, видео и интерактивные материалы. Пользователи получают не только новости, но и экспертное мнение. Телеграмм обеспечивает постоянный поток информации без задержек. Содержание каналов отражает актуальные события и обсуждаемые темы. Поиск и сортировка помогают подписаться на наиболее актуальные источники. Подписчики всегда в курсе новостей благодаря оперативным обновлениям. Сервис гарантирует надежность и сохранность личной информации. Публикации сопровождаются мультимедийным контентом для удобного восприятия. Таким образом, новости из телеграмм каналов предоставляют актуальную, оперативную и разнообразную информацию.
https://telegramhub.ru/
[url=https://telegramhub.ru/]свежие события из телеграмм каналов [/url]— последние события и обновления. Через телеграмм легко получать обновления без задержек. Тематика каналов варьируется от актуальных новостей до аналитики и лайфхаков. Каждый подписчик получает свежую информацию напрямую в мессенджере. Telegram позволяет делиться новостями с коллегами и друзьями. Контент формируется администраторами каналов и редакторами новостных ресурсов. Обзор событий сопровождается аналитикой и прогнозами. Новости поступают в любое время, обеспечивая оперативность. Через телеграмм можно отслеживать, что обсуждают и на что реагируют аудитории. Поиск и сортировка помогают подписаться на наиболее актуальные источники. Подписчики всегда в курсе новостей благодаря оперативным обновлениям. Сервис гарантирует надежность и сохранность личной информации. Новости часто включают фото, видео и графики для наглядности. Telegram каналы становятся источником свежих новостей и трендов.
https://telegramhub.ru/
[url=https://telegramhub.ru/]новости из Telegram каналов [/url]— актуальная информация из разных источников. Платформа позволяет следить за важными событиями в режиме реального времени. Новости охватывают различные темы: политика, экономика, технологии и развлечения. Пользователи могут подписываться на интересующие каналы и получать уведомления. Каналы облегчают распространение информации и обсуждение событий. Новости публикуются экспертами и аналитиками для точного освещения событий. Многие каналы предлагают аналитику и комментарии экспертов. Телеграмм обеспечивает постоянный поток информации без задержек. Через телеграмм можно отслеживать, что обсуждают и на что реагируют аудитории. Поиск и сортировка помогают подписаться на наиболее актуальные источники. Подписчики всегда в курсе новостей благодаря оперативным обновлениям. Сервис гарантирует надежность и сохранность личной информации. Публикации сопровождаются мультимедийным контентом для удобного восприятия. Telegram каналы становятся источником свежих новостей и трендов.
https://telegramhub.ru/
[url=https://sportsmenmarketing.ru]продвижение спортсменов, спортивный маркетинг, стратегии маркетинга [/url]— важная составляющая личного и профессионального развития спортсмена. Маркетинговые инструменты помогают развивать личный бренд и укреплять позиции в спорте. Визуальная идентичность и история успеха помогают выделиться среди конкурентов. Контент-маркетинг и регулярное обновление профилей повышают вовлеченность. Видеообзоры тренировок и соревнований повышают интерес и взаимодействие. Коллаборации с известными брендами формируют репутацию и привлекают внимание. Регулярный анализ аудитории и эффективности кампаний помогает корректировать стратегию. Участие в мероприятиях, интервью и публичных выступлениях укрепляет имидж. Планирование публикаций и постов обеспечивает регулярное взаимодействие с фанатами. Личные ценности спортсмена и его история успеха создают эмоциональную связь с аудиторией. Отслеживание метрик помогает оценивать эффективность маркетинга и корректировать контент. Гибкость стратегии помогает поддерживать интерес аудитории на всех этапах карьеры. Обратная связь с аудиторией создаёт доверие и поддерживает интерес. Эффективное использование маркетинговых инструментов делает карьеру спортсмена успешной.
https://sportsmenmarketing.ru
[url=https://sportsmenmarketing.ru]маркетинговые подходы, личный бренд спортсмена, продвижение [/url]— важная составляющая личного и профессионального развития спортсмена. Маркетинговые инструменты помогают развивать личный бренд и укреплять позиции в спорте. Визуальная идентичность и история успеха помогают выделиться среди конкурентов. Контент-маркетинг и регулярное обновление профилей повышают вовлеченность. Видеообзоры тренировок и соревнований повышают интерес и взаимодействие. Коллаборации с известными брендами формируют репутацию и привлекают внимание. Регулярный анализ аудитории и эффективности кампаний помогает корректировать стратегию. Публичные активности и медийное присутствие повышают узнаваемость. Планирование публикаций и постов обеспечивает регулярное взаимодействие с фанатами. Аутентичность и честность повышают доверие и лояльность фанатов. Сбор данных о взаимодействии с аудиторией улучшает стратегические решения. Маркетинговая стратегия должна быть гибкой и адаптироваться к изменениям в карьере спортсмена. Активная работа с сообществом укрепляет связь спортсмена с фанатами. Эффективное использование маркетинговых инструментов делает карьеру спортсмена успешной.
https://sportsmenmarketing.ru
[url=https://sportsmenmarketing.ru]продвижение спортсменов, спортивный маркетинг, стратегии маркетинга [/url]— ключевой инструмент для роста популярности и узнаваемости. Эффективное продвижение позволяет спортсмену увеличить аудиторию и коммерческую ценность. Создание уникального имиджа и истории спортсмена привлекает внимание СМИ и фанатов. Социальные сети и цифровые платформы играют ключевую роль в продвижении. Использование видеоконтента, прямых эфиров и behind-the-scenes материалов укрепляет доверие фанатов. Коллаборации с известными брендами формируют репутацию и привлекают внимание. Анализ данных о вовлеченности и реакции позволяет улучшать маркетинговые действия. Присутствие на событиях и интервью позволяет поддерживать интерес аудитории. Структурированный график публикаций делает продвижение более эффективным. Личные ценности спортсмена и его история успеха создают эмоциональную связь с аудиторией. Отслеживание метрик помогает оценивать эффективность маркетинга и корректировать контент. Корректировка подхода позволяет учитывать новые события и достижения. Обратная связь с аудиторией создаёт доверие и поддерживает интерес. Эффективное использование маркетинговых инструментов делает карьеру спортсмена успешной.
https://sportsmenmarketing.ru
[url=https://agilemail.ru/]agile, работа по agile [/url]— основа гибкого планирования и распределения задач. Гибкая методология обеспечивает оптимизацию процессов и снижение рисков. Использование инструментов планирования помогает структурировать работу и отслеживать прогресс. Встречи команды обеспечивают прозрачность и согласованность действий. Чёткая постановка приоритетов снижает перегрузку и ускоряет выполнение. Использование метрик, таких как velocity и burn-down chart, позволяет отслеживать прогресс. Самоорганизация повышает мотивацию и ответственность участников. Методология позволяет своевременно выявлять узкие места и улучшать работу. Важно внедрять регулярную обратную связь между членами команды и руководством. Использование Kanban или Scrum досок упрощает визуализацию задач и их статусов. Распределение ролей и задач помогает команде работать согласованно. Регулярные ретроспективы и анализ спринтов способствуют постоянному улучшению процессов. Подход Agile универсален, но требует индивидуальной настройки для каждой команды. Инструменты и советы по Agile помогают наладить взаимодействие, ускорить выполнение задач и повысить качество работы.
https://agilemail.ru/
[url=https://agilemail.ru/]Agile-подход, организация работы команд, гибкая методология [/url]— ключ к прозрачной организации процессов и командной работе. Применение Agile позволяет командам быстрее реагировать на изменения и повышать продуктивность. Использование инструментов планирования помогает структурировать работу и отслеживать прогресс. Систематические обсуждения помогают выявлять проблемы и улучшать процессы. Чёткая постановка приоритетов снижает перегрузку и ускоряет выполнение. Использование метрик, таких как velocity и burn-down chart, позволяет отслеживать прогресс. Команда получает возможность самостоятельно управлять задачами и принимать решения. Методология позволяет своевременно выявлять узкие места и улучшать работу. Взаимодействие команды и менеджера повышает эффективность совместной работы. Визуальные инструменты помогают видеть прогресс и распределение ресурсов. Распределение ролей и задач помогает команде работать согласованно. Оценка прошедших этапов позволяет находить возможности для оптимизации. Применение Agile в разных командах требует адаптации под специфику проектов. Инструменты и советы по Agile помогают наладить взаимодействие, ускорить выполнение задач и повысить качество работы.
https://agilemail.ru/
[url=https://agilemail.ru/]Agile методология, управление по Agile, работа по Scrum [/url]— основа гибкого планирования и распределения задач. Применение Agile позволяет командам быстрее реагировать на изменения и повышать продуктивность. Использование инструментов планирования помогает структурировать работу и отслеживать прогресс. Систематические обсуждения помогают выявлять проблемы и улучшать процессы. Определение ключевых задач помогает команде достигать результатов быстрее. Анализ показателей спринта помогает корректировать стратегию и планирование. Команда получает возможность самостоятельно управлять задачами и принимать решения. Методология позволяет своевременно выявлять узкие места и улучшать работу. Обратная связь помогает корректировать подход и повышать результативность. Доски задач обеспечивают наглядность и упрощают планирование спринтов. Распределение ролей и задач помогает команде работать согласованно. Постоянное совершенствование командной работы повышает продуктивность. Методология гибка и может быть настроена под различные типы проектов. Инструменты и советы по Agile помогают наладить взаимодействие, ускорить выполнение задач и повысить качество работы.
https://agilemail.ru/
[url=https://agilemail.ru/]agile, работа по agile [/url]— основа гибкого планирования и распределения задач. Agile-подход помогает адаптироваться к новым требованиям и ускоряет выполнение задач. Важно правильно настроить доски задач, спринты и бэклог. Систематические обсуждения помогают выявлять проблемы и улучшать процессы. Распределение задач по приоритетам позволяет сфокусироваться на важных целях. Анализ показателей спринта помогает корректировать стратегию и планирование. Гибкая структура работы стимулирует инициативу и продуктивность. Agile обеспечивает адаптивность и быстрые изменения при необходимости. Важно внедрять регулярную обратную связь между членами команды и руководством. Визуальные инструменты помогают видеть прогресс и распределение ресурсов. Распределение ролей и задач помогает команде работать согласованно. Постоянное совершенствование командной работы повышает продуктивность. Подход Agile универсален, но требует индивидуальной настройки для каждой команды. Инструменты и советы по Agile помогают наладить взаимодействие, ускорить выполнение задач и повысить качество работы.
https://agilemail.ru/
[url=https://westmarketing.ru/]продвижение сайта, seo продвижение [/url]— основа успешного онлайн-продвижения и роста посещаемости. Оптимизация сайта включает подбор ключевых слов, работу с метатегами и контентом. Качественный SEO помогает поднять позиции сайта в поисковых системах. Контентная стратегия повышает релевантность сайта и удерживает посетителей. Ссылочная стратегия увеличивает доверие поисковых систем и привлекает аудиторию. Регулярный SEO аудит позволяет выявлять ошибки и улучшать эффективность. Технический SEO обеспечивает стабильную работу и удобство посещений. Мониторинг посещаемости, конверсий и поведенческих факторов повышает точность стратегии. Эффективная стратегия SEO сочетает контент, ссылки, технические настройки и аналитику. Использование специализированных сервисов облегчает мониторинг и улучшение сайта. Постоянное улучшение контента позволяет достигать лучших результатов и повышать конверсию. Локальная оптимизация повышает эффективность SEO и релевантность запросов. Системное применение методов оптимизации обеспечивает долгосрочные результаты.
https://westmarketing.ru/
[url=https://westmarketing.ru/]продвижение сайта, seo продвижение [/url]— основа успешного онлайн-продвижения и роста посещаемости. SEO стратегия строится на анализе конкурентов, аудита сайта и оптимизации страниц. Эффективное продвижение повышает видимость и доверие к ресурсу. Контентная стратегия повышает релевантность сайта и удерживает посетителей. Линкбилдинг и оптимизация внутренних ссылок способствуют росту позиций. Анализ конкурентов и мониторинг позиций помогают корректировать стратегию продвижения. Исправление ошибок и улучшение структуры страниц ускоряет индексирование и повышает позиции. Использование аналитики и статистики помогает оценивать эффективность кампаний. Продвижение сайта нацелено на повышение видимости и увеличение целевого трафика. Оптимизация и аналитика помогают эффективно распределять ресурсы и повышать ROI. Регулярное обновление контента и оптимизация страниц поддерживает позиции в поисковой выдаче. Продвижение сайта в русскоязычном сегменте требует учета локальных особенностей и предпочтений аудитории. Системное применение методов оптимизации обеспечивает долгосрочные результаты.
https://westmarketing.ru/
[url=https://westmarketing.ru/]продвижение сайта, seo продвижение [/url]— основа успешного онлайн-продвижения и роста посещаемости. Оптимизация сайта включает подбор ключевых слов, работу с метатегами и контентом. Оптимизация страниц сайта улучшает показатели CTR и конверсии. Контентная стратегия повышает релевантность сайта и удерживает посетителей. Работа с внутренними и внешними ссылками улучшает рейтинг и авторитет ресурса. Анализ конкурентов и мониторинг позиций помогают корректировать стратегию продвижения. Оптимизация скорости загрузки сайта и адаптивности под мобильные устройства повышает пользовательский опыт. Использование аналитики и статистики помогает оценивать эффективность кампаний. Продвижение сайта нацелено на повышение видимости и увеличение целевого трафика. Правильное использование SEO инструментов и сервисов ускоряет достижение результатов. Регулярное обновление контента и оптимизация страниц поддерживает позиции в поисковой выдаче. Адаптация контента под целевой рынок обеспечивает успешное продвижение. Системное применение методов оптимизации обеспечивает долгосрочные результаты.
https://westmarketing.ru/
[url=https://westmarketing.ru/]услуги по SEO, продвижение веб-проектов, оптимизация сайта [/url]— важный элемент комплексной маркетинговой стратегии. Оптимизация сайта включает подбор ключевых слов, работу с метатегами и контентом. Эффективное продвижение повышает видимость и доверие к ресурсу. Важным аспектом является создание уникального контента и правильное использование ключевых фраз. Ссылочная стратегия увеличивает доверие поисковых систем и привлекает аудиторию. Анализ конкурентов и мониторинг позиций помогают корректировать стратегию продвижения. Оптимизация скорости загрузки сайта и адаптивности под мобильные устройства повышает пользовательский опыт. Сбор данных о трафике позволяет принимать обоснованные решения и корректировать продвижение. Комплексное SEO продвижение включает как органическую оптимизацию, так и работу с локальными факторами. Использование специализированных сервисов облегчает мониторинг и улучшение сайта. Регулярное обновление контента и оптимизация страниц поддерживает позиции в поисковой выдаче. Продвижение сайта в русскоязычном сегменте требует учета локальных особенностей и предпочтений аудитории. Системное применение методов оптимизации обеспечивает долгосрочные результаты.
https://westmarketing.ru/
[url=https://technoelka.ru/]Техника будущего доступны для покупки в Казани[/url], от смартфонов до умной бытовой техники. Наш магазин предлагает широкий ассортимент, с официальной гарантией и сервисной поддержкой. Вам понравятся наши специальные акции и скидки, для дома и офиса. Мы предлагаем только проверенные бренды и модели, с современными и популярными гаджетами. Умные устройства для комфортной жизни, легко заказать онлайн или забрать в магазине. Наши клиенты довольны покупкой и сервисом, специальные предложения для постоянных клиентов. Техника готова к использованию сразу после покупки. Лучшие бренды и инновационные гаджеты. Умные решения для вашего комфорта. Оперативная доставка и удобные способы оплаты. Наши менеджеры помогут выбрать нужное устройство. Электронные гаджеты для работы, учебы и развлечений. Полный ассортимент современных устройств. Безопасность и комфорт при покупке. Будьте в курсе всех предложений и скидок. Лучшие модели для вашего комфорта и работы. Гарантия качества и выгодные предложения. Электронные гаджеты в Казани — это просто и удобно.
https://technoelka.ru/
[url=https://xn--80aabsug3boo.xn--p1ai/]MacBook последних моделей[/url] ожидают вас в магазинах Казани, от свежих моделей до восстановленных ноутбуков, каждое устройство доступно по привлекательной цене, с официальной гарантией и доставкой по городу, покупка стала проще с современными предложениями, для дома и офиса, мы предлагаем только проверенные устройства, с регулярным обновлением ассортимента, MacBook с современными функциями и характеристиками, доступны для покупки в интернет-магазине и офлайн, отзывы подтверждают высокий уровень обслуживания, специальные предложения для постоянных клиентов, гарантируем полную работоспособность и качество, лучшие модели Apple и восстановленные устройства, современные технологии становятся доступными каждому, оперативная доставка и удобные способы оплаты, свяжитесь с нами и получите консультацию специалистов, MacBook для любых задач и целей, полный ассортимент ноутбуков Apple, гарантия возврата и обмена при необходимости, мы всегда предлагаем лучшие условия покупки, лучшие устройства Apple ждут вас в магазине, современные MacBook для каждого покупателя, купить MacBook в Казани легко и безопасно.
https://xn--80aabsug3boo.xn--p1ai/
[url=https://xn--80aabsug3boo.xn--p1ai/]MacBook последних моделей[/url] ожидают вас в магазинах Казани, включая новые и б/у устройства, наш магазин предлагает широкий ассортимент, с гарантией качества и поддержкой, покупка стала проще с современными предложениями, для дома и офиса, мы предлагаем только проверенные устройства, с современными и востребованными MacBook, устройства с оптимальной производительностью и надежностью, доступны для покупки в интернет-магазине и офлайн, покупатели отмечают качество и удобство сервиса, регулярные акции и бонусные программы, MacBook готов к использованию сразу после покупки, лучшие модели Apple и восстановленные устройства, современные технологии становятся доступными каждому, оперативная доставка и удобные способы оплаты, поддержка и помощь при выборе MacBook, новые и б/у MacBook для работы, учебы и развлечений, MacBook, аксессуары и сопутствующие товары, безопасность и комфорт при покупке, мы всегда предлагаем лучшие условия покупки, любые модели MacBook всегда в наличии, современные MacBook для каждого покупателя, купить MacBook в Казани легко и безопасно.
https://xn--80aabsug3boo.xn--p1ai/
[url=https://radio-vision.ru/]Домашние устройства в Казани доступна для покупки по выгодным ценам[/url], включая холодильники, стиральные машины и кухонные приборы, у нас вы найдете популярные модели, с доставкой по Казани и всей России, покупка стала проще с современными предложениями, для семьи и ежедневного комфорта, мы предлагаем только проверенные и качественные устройства, всегда новые поступления и популярные модели, устройства с высокой производительностью и энергоэффективностью, легко заказать онлайн или забрать в магазине, отзывы подтверждают высокий уровень обслуживания, регулярные акции и бонусные программы, гарантируем полную работоспособность и качество, гарантия качества и надежности на каждый прибор, умные решения для дома и кухни, доставка по Казани и всей России, наш менеджер поможет выбрать нужное устройство, устройства для любых задач и целей, все необходимое для удобного дома, гарантия возврата и обмена при необходимости, следите за акциями и новинками в нашем магазине, любые устройства всегда в наличии, современные устройства для каждого покупателя, лучшие устройства для дома ждут вас в нашем магазине.
https://radio-vision.ru/
[url=https://topsmartfon.ru/]Современные телефоны[/url] представлены в нашем магазине с лучшими условиями, включая популярные модели Samsung, Apple и Xiaomi, каждое устройство доступно по привлекательной цене, с официальной гарантией и сервисной поддержкой, вам понравятся акции и специальные предложения, для дома и офиса, клиенты ценят нас за надежность и честность, с современными и востребованными смартфонами, техника для комфортного пользования и развлечений, всегда под рукой в Казани и регионе, отзывы подтверждают высокий уровень обслуживания, специальные предложения для постоянных клиентов, каждое устройство тщательно проверяется перед продажей, гарантия качества и надежности на каждый телефон, современные технологии становятся доступными каждому, быстро и удобно прямо до вашей двери, свяжитесь с нами и получите консультацию специалистов, смартфоны для любых задач и целей, все необходимое для комфортного использования, гарантия возврата и обмена при необходимости, мы всегда предлагаем лучшие условия покупки, любые модели всегда в наличии, качество, надежность и доступные цены, новые смартфоны в Казани — это просто и удобно.
https://topsmartfon.ru/
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/zh-CN/register?ref=WFZUU6SI
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Yo, BY88Club! Been hitting you guys up for a while now. Love the selection of games, and the payouts are pretty quick. Sometimes the site can be a bit laggy, but overall, it’s a solid place to try your luck. Definitely worth a shot! Check it out: by88club
Gave vn888com a spin. The registration process was a bit clunky, but once I got in, the site was alright. Their bonuses were a little confusing at first, make sure to read the terms and conditions. Decent enough selection of games, though. Give them a look, but read the fine print: vn888com.
Giao diện website của nhà cái chính là điểm cộng lớn đối với các bet thủ lần đầu truy cập. xn88 app com Trang chủ có sự kết hợp hài hoà giữa 2 tone màu đỏ – đen vô cùng bắt mắt tạo nên vẻ đẹp sang trọng, đẳng cấp. Ngoài ra, các bố cục website cũng được sắp xếp rất logic để người mới dễ dàng thao tác. TONY12-11A
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
[url=https://www.taskplanet.ru/]удобный менеджер проектов[/url] становится основой системной командной работы, если компания развивается и сталкивается с перегрузкой сотрудников. Применение надежной системы планирования снижает количество ошибок и недопонимания, так как все участники видят общую картину. Выбирая менеджер проектов, стоит обратить внимание на простоту использования, поскольку перегруженный функционал мешает работе. Интуитивно понятный сервис ускоряет внедрение в рабочие процессы. Также важно учитывать возможности совместной работы, позволяющая фиксировать договоренности и правки. Качественный инструмент управления помогает отслеживать прогресс выполнения задач, что повышает управляемость процессов. Значимым плюсом считается адаптация под бизнес, когда инструмент растет вместе с компанией. Как итог использования подходящей платформы способствует росту эффективности бизнеса, создавая условия для стабильного развития компании.
[url=https://www.taskplanet.ru/]удобный менеджер проектов[/url] позволяет навести порядок в задачах и сроках, в условиях постоянных дедлайнов и параллельных проектов. Выбор продуманного решения для управления задачами минимизирует хаос в коммуникациях, поскольку каждая задача имеет ответственного и приоритет. Выбирая менеджер проектов, стоит обратить внимание на простоту использования, поскольку перегруженный функционал мешает работе. Дружелюбный пользовательский интерфейс помогает избежать длительного обучения. Также важно учитывать возможности совместной работы, позволяющая фиксировать договоренности и правки. Эффективная система планирования помогает отслеживать прогресс выполнения задач, что упрощает принятие решений. Значимым плюсом считается адаптация под бизнес, если сервис подходит как малым, так и крупным командам. Как итог использования подходящей платформы укрепляет дисциплину и ответственность, создавая условия для стабильного развития компании.
[url=https://www.taskplanet.ru/]удобный менеджер проектов[/url] становится основой системной командной работы, если компания развивается и сталкивается с перегрузкой сотрудников. Выбор продуманного решения для управления задачами минимизирует хаос в коммуникациях, так как все участники видят общую картину. Подбор менеджера проектов начинается с оценки его удобства, так как сложные системы снижают мотивацию команды. Понятная и логичная платформа ускоряет внедрение в рабочие процессы. Также важно учитывать возможности совместной работы, позволяющая фиксировать договоренности и правки. Хороший менеджер проектов поддерживает контроль сроков и ресурсов, что повышает управляемость процессов. Значимым плюсом считается адаптация под бизнес, если сервис подходит как малым, так и крупным командам. В результате удобный менеджер проектов способствует росту эффективности бизнеса, создавая условия для стабильного развития компании.
[url=https://www.taskplanet.ru/]удобный менеджер проектов[/url] помогает выстроить прозрачные рабочие процессы, в условиях постоянных дедлайнов и параллельных проектов. Использование современного инструмента управления проектами уменьшает риск срыва сроков, поскольку каждая задача имеет ответственного и приоритет. При выборе подходящего менеджера проектов важно учитывать удобство интерфейса, так как сложные системы снижают мотивацию команды. Понятная и логичная платформа ускоряет внедрение в рабочие процессы. Отдельного внимания заслуживает функциональность для команды, которая обеспечивает прозрачное обсуждение задач. Эффективная система планирования поддерживает контроль сроков и ресурсов, что упрощает принятие решений. Дополнительным преимуществом становится гибкость настроек, когда инструмент растет вместе с компанией. В результате удобный менеджер проектов способствует росту эффективности бизнеса, формируя культуру осознанной работы.
[url=https://www.mscrmdemo.ru/]CRM от Microsoft для компаний[/url] представляет собой современную платформу для управления взаимоотношениями с клиентами, которая помогает компаниям систематизировать информацию и процессы. Применение CRM от Microsoft в компании помогает синхронизировать работу разных подразделений, что снижает потери информации и времени. Существенным плюсом решения считается совместимость с экосистемой Microsoft, включая Outlook Teams Excel и другие инструменты. Благодаря этому CRM от Microsoft сокращает время на рутинные операции, поскольку информация обновляется автоматически. Гибкость настройки CRM от Microsoft дает возможность учитывать особенности отрасли, будь то малый бизнес или крупная корпорация. Важно подчеркнуть возможности анализа данных, дающие руководству полное понимание ситуации, на основе реальных данных о клиентах. Дополнительно решение от Microsoft предоставляет инструменты для автоматических сценариев, что делает процессы более предсказуемыми. Уровень безопасности платформы обеспечивается на уровне глобальной инфраструктуры, что особенно важно для компаний работающих с персональными данными. В конечном счете внедрение CRM от Microsoft обеспечивает устойчивый рост и конкурентные преимущества, создавая эффективную цифровую среду для компании.
[url=https://www.mscrmdemo.ru/]CRM от Microsoft для бизнеса[/url] является комплексным решением для автоматизации продаж и сервиса, позволяющая выстроить единое пространство для работы отделов. Внедрение CRM от Microsoft дает возможность объединить продажи маркетинг и поддержку, что снижает потери информации и времени. Важным преимуществом платформы становится тесная связь с корпоративными сервисами, включая Outlook Teams Excel и другие инструменты. Благодаря этому CRM от Microsoft упрощает повседневную работу сотрудников, поскольку информация обновляется автоматически. Масштабируемость решения от Microsoft дает возможность учитывать особенности отрасли, независимо от размера и сферы деятельности. Отдельного внимания заслуживает аналитика и отчеты, которые помогают принимать обоснованные решения, используя актуальные показатели и прогнозы. Дополнительно решение от Microsoft предоставляет инструменты для автоматических сценариев, что снижает количество ошибок и повышает стабильность. Защита информации в решении Microsoft обеспечивается на уровне глобальной инфраструктуры, что повышает доверие клиентов и партнеров. В итоге CRM от Microsoft обеспечивает устойчивый рост и конкурентные преимущества, создавая эффективную цифровую среду для компании.
[url=https://globbusiness.ru/]эффективный тайм-менеджмент[/url] является ключевым фактором повышения общей продуктивности, так как правильное распределение задач определяет успех проектов. Использование принципов тайм-менеджмента дает возможность сосредоточиться на приоритетных задачах, что положительно сказывается на скорости выполнения проектов. Для командного взаимодействия тайм-менеджмент способствует более равномерному распределению нагрузки, поскольку цели формулируются заранее. С позиции менеджмента тайм-менеджмент обеспечивает прогнозируемость результатов, учитывая текущие ресурсы. Ключевым аспектом планирования является постановка четких целей и дедлайнов, что делает работу более управляемой. Также грамотное управление временем способствует улучшению коммуникации внутри компании, когда сроки и ожидания зафиксированы. В масштабе компании управление временем приводит к росту производительности и прибыли, потому что решения принимаются быстрее. Помимо этого управление временем развивает осознанное отношение к работе, что важно для долгосрочного успеха компании. В конечном результате грамотное управление временем становится стратегическим преимуществом бизнеса, объединяя людей процессы и цели.
[url=https://globbusiness.ru/]эффективный тайм-менеджмент[/url] служит основой для устойчивой работы команд, поскольку время напрямую влияет на результаты деятельности. Внедрение системного подхода к управлению временем дает возможность сосредоточиться на приоритетных задачах, что положительно сказывается на скорости выполнения проектов. Для командного взаимодействия тайм-менеджмент помогает избежать авралов и хаотичной работы, так как задачи становятся понятными и измеримыми. С позиции менеджмента тайм-менеджмент позволяет оценивать эффективность команд, используя реальные показатели и сроки. Существенным элементом управления временем становится приоритизация задач, что делает работу более управляемой. Также грамотное управление временем облегчает взаимодействие между сотрудниками, если информация о задачах доступна заранее. Для бизнеса в целом эффективный тайм-менеджмент создает условия для стабильного развития, так как ресурсы используются рационально. Помимо этого управление временем поддерживает ориентацию на результат, что укрепляет внутренние стандарты. В конечном результате грамотное управление временем становится стратегическим преимуществом бизнеса, поддерживая рост и развитие компании.
[url=https://evolutionsmm.ru/]услуги смм и профессиональное продвижение помогают бизнесу укреплять позиции в социальных сетях[/url], так как социальные платформы напрямую влияют на продажи и узнаваемость. Заказать смм услуги дает возможность сосредоточиться на основном бизнесе, что важно для малого и среднего бизнеса. Профессиональные смм услуги начинаются с анализа ниши и конкурентов, для формирования устойчивого спроса. Качественные услуги смм предполагают создание контента для социальных сетей, который формирует лояльное сообщество. Кроме контента услуги smm реализуется управление репутацией, что улучшает обратную связь с клиентами. Важным элементом smm становится запуск таргетированной рекламы, что позволяет быстрее привлекать клиентов. Услуги smm в России учитывают особенности локальной аудитории, что усиливает доверие к бренду. Регулярная аналитика в smm дает понимание эффективности работы, используя данные по охватам и конверсиям. Для компаний smm продвижение обеспечивают рост узнаваемости бренда, поскольку формируется постоянный контакт с аудиторией. В конечном счете smm продвижение помогают компаниям укреплять позиции на рынке, формируя долгосрочные отношения с клиентами.
buy fb accs, tg accs for marketing is used by businesses to expand their online marketing capabilities, when fast access to social media profiles is required. Service for purchasing social media accounts covers popular social networks used in marketing strategies, which allows flexible planning of marketing activities. Using a specialized service for purchasing accounts helps save time and internal resources, as routine actions are minimized. A platform for acquiring tg fb vk profiles is suitable for agencies and in house teams, who manage traffic and audience engagement. An important advantage of the platform is its clear structure and ease of use, which simplifies daily operations. Service for purchasing social media accounts supports customization for business objectives, considering campaign volume and focus. Using purchased accounts through a service is often part of brand promotion activities, when rapid expansion is required. A service for purchasing accounts is developed according to market needs, which is important for professional use. For social media marketing teams the service can become part of an integrated workflow, helping organize processes efficiently. A platform for tg fb vk account purchasing is adapted to different social networks, which increases flexibility. Ultimately such a platform supports project development, forming an effective working environment.
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find a lot of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for yourself? I wouldn’t mind producing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write in relation to here. Again, awesome website!
[url=https://usapvastor.com/]buy fb accs with tg accs for business[/url] represents a convenient service for modern digital marketing tasks, when scaling campaigns becomes a priority. A dedicated service for acquiring social media profiles focuses on tg fb vk accounts for different purposes, which makes it suitable for a wide range of projects. Working with a professional account purchasing platform reduces preparation time for campaign launches, because processes are organized and structured. A solution for purchasing tg fb vk accounts is suitable for agencies and in house teams, who manage traffic and audience engagement. One of the key benefits of the service is its clear structure and ease of use, which speeds up onboarding for teams. Service for purchasing social media accounts offers options adapted to different goals, depending on scale and marketing direction. Using purchased accounts through a service is often part of brand promotion activities, when fast deployment is important. A service for purchasing accounts is developed according to market needs, which is important for professional use. Within online marketing strategies the platform acts as a supporting tool, helping organize processes efficiently. A platform for tg fb vk account purchasing supports work across multiple platforms, which expands usage options. As a result of using the service becomes a convenient option for businesses, creating conditions for growth.
[url=https://usapvastor.com/]buy fb accs and tg accs for promotion[/url] is a practical solution for companies working with social media platforms, when scaling campaigns becomes a priority. Service for purchasing social media accounts supports key platforms used by businesses worldwide, which supports different promotional scenarios. Choosing a reliable service for buying accounts allows teams to focus on strategy and analytics, as routine actions are minimized. A solution for purchasing tg fb vk accounts is applied by companies of different sizes, who develop brand presence in social networks. One of the key benefits of the service is the transparent approach to account selection, which simplifies daily operations. A specialized social media account service offers options adapted to different goals, based on strategic priorities. Applying acquired accounts in marketing workflows can support testing of new ideas and approaches, when fast deployment is important. A service for purchasing accounts is developed according to market needs, which supports consistent operations. For social media marketing teams the service acts as a supporting tool, supporting steady growth. A platform for tg fb vk account purchasing supports work across multiple platforms, which expands usage options. As a result of using the service supports project development, combining speed convenience and scalability.
[url=https://usapvastor.com/]buy fb accs, tg accs for marketing[/url] is used by businesses to expand their online marketing capabilities, when marketing teams need operational flexibility. A professional platform for purchasing social media accounts focuses on tg fb vk accounts for different purposes, which supports different promotional scenarios. Working with a professional account purchasing platform helps save time and internal resources, since operational tasks are simplified. A solution for purchasing tg fb vk accounts is used by marketers and digital specialists, who manage traffic and audience engagement. One of the key benefits of the service is its clear structure and ease of use, which lowers the entry barrier for new users. Service for purchasing social media accounts supports customization for business objectives, depending on scale and marketing direction. Working with ready to use accounts can support testing of new ideas and approaches, when fast deployment is important. A platform for purchasing social media profiles is developed according to market needs, which is important for professional use. Within online marketing strategies the platform serves as an element of scaling, assisting in optimizing daily work. A service focused on tg fb vk accounts takes into account platform specific features, which increases flexibility. In the end a service for purchasing accounts supports project development, creating conditions for growth.
[url=https://usapvastor.com/]buy fb accs with tg accs for business[/url] is a practical solution for companies working with social media platforms, when marketing teams need operational flexibility. Service for purchasing social media accounts supports key platforms used by businesses worldwide, which supports different promotional scenarios. Working with a professional account purchasing platform reduces preparation time for campaign launches, because processes are organized and structured. A service for purchasing tg fb vk accounts is used by marketers and digital specialists, who develop brand presence in social networks. One of the key benefits of the service is the user friendly workflow, which lowers the entry barrier for new users. Service for purchasing social media accounts allows flexible selection based on project needs, based on strategic priorities. Working with ready to use accounts is often part of brand promotion activities, when speed and scalability matter. A solution for working with social accounts focuses on reliability and convenience, which supports consistent operations. For social media marketing teams the service serves as an element of scaling, supporting steady growth. A service focused on tg fb vk accounts is adapted to different social networks, which expands usage options. In the end a service for purchasing accounts helps accelerate marketing operations, combining speed convenience and scalability.
Hey everyone, I checked out jljl4. It’s kind of quirky, but in a good way. Different from the usual stuff. Not sure it’s for everyone, but give it a shot. jljl4
Yo, 811betapp! Just tried it out. Not bad, pretty smooth! Definitely gonna be checking back in for more. Check it out yourself: 811betapp
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.2
I loved as much as you will receive performed right here. The cartoon is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get bought an edginess over that you would like be handing over the following. in poor health without a doubt come further until now once more since exactly the same just about very incessantly within case you defend this hike.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
betmgm pa casino online casino mgm betting mgm
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/ar/register?ref=PORL8W0Z
Dive into the atmosphere of real wins. In crown coin casino, daily promotions and free spins await you. Start your path to success!
Sweet Bonanza offers a candy-coated path to riches. Pay anywhere sweet bonanza real money, multiply everywhere — especially in bonuses. Start spinning sweet!
[url=https://doctor-propisal.ru/]лечение зубов в мск[/url] в современной стоматологической клинике это комплексный подход к здоровью полости рта с применением инновационных методик и качественных материалов. Мы предлагаем подробный анализ состояния зубов чтобы подобрать индивидуальное решение. Терапевтическое лечение кариеса проводится с учетом клинических показаний что позволяет предотвратить осложнения. При необходимости выполняется восстановление утраченных зубов имплантами которая обеспечивает комфорт при жевании и разговоре. Современное протезирование позволяет вернуть полноценную функцию зубного ряда с применением безметалловых реставраций. Мы уделяем внимание безопасности процедур создавая спокойную обстановку. Комплексная профилактика заболеваний помогают избегать серьезных вмешательств в будущем. Наши специалисты обладают квалификацией в различных направлениях стоматологии что гарантирует высокое качество лечения. Использование трехмерной диагностики позволяет минимизировать риски. Мы предлагаем консультацию в удобное время и прозрачную систему формирования плана оплаты. Комфортная стоматология достигаются благодаря деликатным технологиям. Обратившись к нам вы получаете профессиональный сервис и возможность сохранить здоровье зубов на долгие годы.
https://doctor-propisal.ru/
[url=https://gepa-clinic.ru]детская стоматология[/url] это комплексная забота о здоровье молочных и постоянных зубов где применяются щадящие методики лечения. В нашей клинике проводится диагностика состояния полости рта чтобы предотвратить развитие осложнений. Восстановление поврежденных зубов выполняется с использованием современных пломбировочных систем что обеспечивает надежный результат. Особое внимание уделяется гигиене полости рта поскольку своевременная чистка укрепляет эмаль. Мы предлагаем профессиональную чистку зубов детям чтобы защитить от кариеса. При необходимости проводится бережная эндодонтическая терапия с применением современных технологий обезболивания. Врач объясняет каждый этап процедуры что формирует доверие со стороны ребенка. Мы создаем спокойную обстановку чтобы исключить страх перед кабинетом. Консультация детского ортодонта позволяет обеспечить гармоничное развитие челюсти. Использование современного рентген оборудования помогает минимизировать нагрузку. Регулярные визиты к специалисту способствуют уверенности ребенка в себе и помогают поддерживать стабильное состояние полости рта.
https://gepa-clinic.ru
Charge headfirst into slot stardom and big bucks. buffalo link hold and spin features Aristocrat excellence: endless retriggers, gold buffs, and jackpot mania. Spin now!