The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that can collect, share, and analyze data without human intervention. These devices, often embedded with sensors and software, communicate over the internet, providing real-time information and automation.
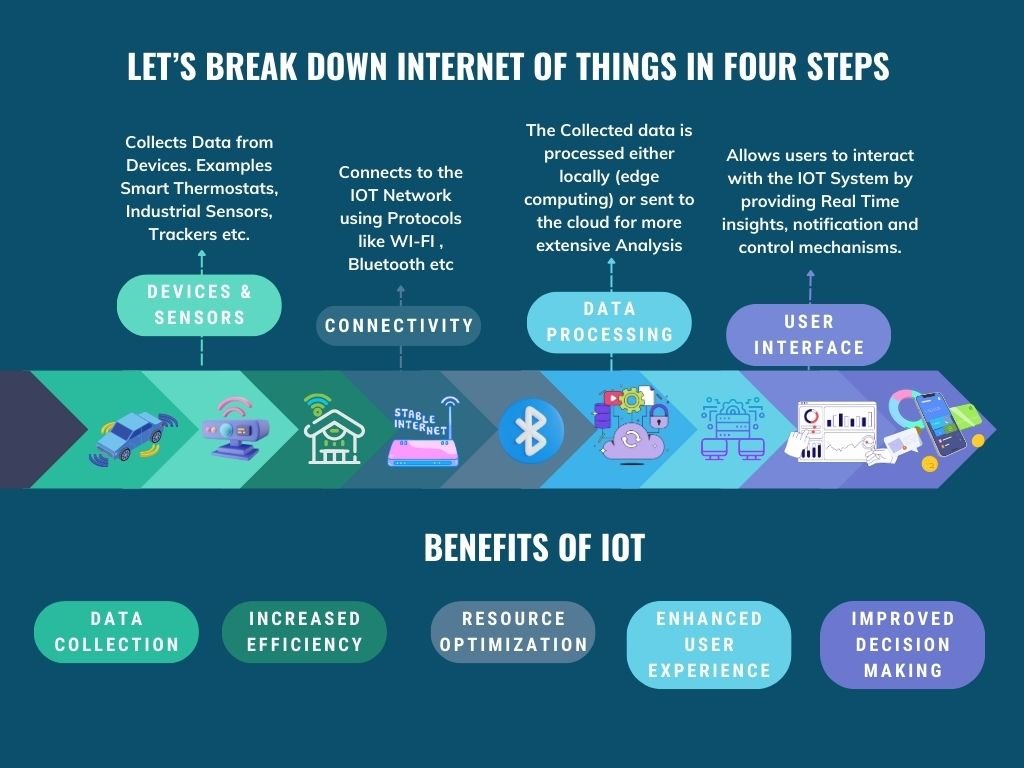
Key Components of IoT:
Devices and Sensors:
- These are physical objects like home appliances, wearables, industrial machines, vehicles, etc., equipped with sensors and actuators. Sensors collect data from the environment (temperature, humidity, motion, etc.).
Connectivity:
- Devices connect to an IoT gateway or directly to the internet using various communication protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks.
Data Processing:
- Once data is collected, it is processed either locally (edge computing) or sent to centralized servers (cloud computing). Processing can include real-time analytics, filtering, and actionable insights.
User Interface:
- The processed data is then made available to users through dashboards, apps, or other interfaces. Users can monitor, control, and interact with their IoT devices remotely.
Applications of IoT:
Smart Homes:
- IoT enables automation of home devices such as lighting, heating, and security systems, improving convenience, security, and energy efficiency.
Healthcare:
- Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems collect health data, enabling personalized healthcare, real-time monitoring, and improved patient outcomes.
Industrial IoT:
- In manufacturing, IoT sensors monitor equipment health, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
Smart Cities:
- IoT contributes to urban planning and management through smart traffic systems, waste management, environmental monitoring, and efficient energy use.
Agriculture:
- IoT devices monitor soil conditions, weather, and crop health, enabling precision farming and improving agricultural productivity.
Benefits of IoT:
- Efficiency and Automation: Automates routine tasks, reducing human effort and increasing productivity.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides real-time data for informed decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Optimizes resource use and reduces operational costs.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Improves service delivery and personalization.
Challenges:
- Security and Privacy: Ensuring data security and user privacy is a major concern.
- Interoperability: Integrating devices from different manufacturers can be challenging.
- Data Management: Handling large volumes of data effectively requires robust infrastructure.
The Internet of Things represents a significant shift in how we interact with technology, bringing more intelligence and connectivity to everyday objects and systems.


Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
canadian pharmacy in canada
https://expresscanadapharm.com/# canadian world pharmacy
canadian drug pharmacy
They have an extensive range of skincare products.
can you buy generic cipro without rx
Always up-to-date with international medical advancements.
Breaking down borders with every prescription.
get generic clomid without prescription
They take the hassle out of international prescription transfers.
Top 100 Searched Drugs.
can you get generic cipro
They have expertise in handling international shipping regulations.
Love their spacious and well-lit premises.
a cosa serve il farmaco gabapentin
Get warning information here.
Their global pharmacists’ network is commendable.
cost cheap cytotec online
I appreciate their late hours for those unexpected needs.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
where can i get cheap clomid price cost cheap clomid for sale cost of cheap clomid without insurance can i purchase cheap clomiphene without a prescription order generic clomiphene pills clomiphene contraindications clomiphene medication for women
I’ll certainly bring to review more.
The thoroughness in this draft is noteworthy.
buy zithromax for sale – flagyl where to buy buy flagyl generic
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
domperidone 10mg price – buy sumycin without prescription buy flexeril 15mg sale
buy inderal no prescription – order inderal 10mg online cheap methotrexate 2.5mg without prescription
purchase amoxil online cheap – buy ipratropium 100mcg pills ipratropium 100mcg uk
azithromycin 500mg tablet – buy bystolic 20mg pills nebivolol 5mg generic
order augmentin 625mg sale – atbio info buy acillin online
cost nexium – anexa mate buy esomeprazole 20mg generic
warfarin price – https://coumamide.com/ buy losartan 50mg sale
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
buy mobic pills for sale – https://moboxsin.com/ meloxicam for sale
deltasone 40mg cost – adrenal order deltasone generic
best ed pills online – site over the counter ed pills
buy amoxicillin tablets – buy amoxicillin without prescription cheap amoxil for sale
diflucan 200mg ca – https://gpdifluca.com/# buy cheap forcan
cenforce 100mg cheap – https://cenforcers.com/ cost cenforce 50mg
when should you take cialis – https://ciltadgn.com/ buying cheap cialis online
tadalafil and sildenafil taken together – generic cialis 5mg cialis overnight shipping
buy zantac 300mg online – https://aranitidine.com/# buy zantac generic
50 or 100mg viagra – https://strongvpls.com/ where can i buy cialis or viagra on line
More content pieces like this would create the web better. https://gnolvade.com/
I’ll certainly bring back to review more. amoxil without prescription
This is the kind of advise I turn up helpful. https://ursxdol.com/amoxicillin-antibiotic/
More posts like this would force the blogosphere more useful. https://prohnrg.com/product/metoprolol-25-mg-tablets/
I couldn’t weather commenting. Profoundly written! https://aranitidine.com/fr/en_france_xenical/
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
More posts like this would prosper the blogosphere more useful. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
With thanks. Loads of knowledge! where to buy generic motilium no prescription
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/en-NG/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/en-IN/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
The depth in this ruined is exceptional. http://furiouslyeclectic.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=24634
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
purchase dapagliflozin pills – https://janozin.com/# forxiga 10mg over the counter
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
xenical cost – janozin.com purchase xenical online
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
With thanks. Loads of erudition! http://iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=916843
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! sign up binance
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! binance
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! create a binance account
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. create binance account
Reading your article has greatly helped me, and I agree with you. But I still have some questions. Can you help me? I will pay attention to your answer. thank you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
You can keep yourself and your dearest close being wary when buying prescription online. Some druggist’s websites operate legally and sell convenience, privacy, sell for savings and safeguards as a replacement for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/kamagra.html kamagra
More posts like this would bring about the blogosphere more useful. TerbinaPharmacy
The vividness in this piece is exceptional.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for another informative site. Where else could I get that type of information written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/ka-GE/register?ref=ILE8IH9H
Just signed up on b66club.net! So far, so good. If you are looking for a new place, give it a try with this link: b66club
I tried to find something intresting, Goperyalogin is not bad choice. Website is easy to see, and have many game. Try it here: goperyalogin
Hello, Neat post. There’s a problem with your web site in web explorer, might test this… IE nonetheless is the marketplace leader and a good part of people will leave out your magnificent writing due to this problem.
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Whoa! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Superb choice of colors!
Really clear internet site, regards for this post.
Just signed into 789betmpls to place my bets. Feeling good, hoping to score some big wins! Good luck to all the serious betters out there! Find out more 789betmpls.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/register-person?ref=IXBIAFVY
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
Oi, judibola828bet, eh? A bit of a gamble, innit? But hey, if you fancy a punt, give it a go! Just remember, gamble responsibly! judibola828bet
There is perceptibly a bunch to identify about this. I assume you made some good points in features also.
люстра в комнату деревянная люстра
Играешь в казино? апх Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
заклепка вытяжная 4 8 заклепка вытяжная
За год использования кракен маркет даркнет ни разу не подвёл с доступом
дизайн окон дома дизайн коттеджа
дизайн прихожей в квартире дизайн двухкомнатной квартиры
теплый полотенцесушитель полотенцесушитель сталь купить
накрутка подписчиков тик ток накрутка подписчиков инстаграм
Занимаешься спортом? блины на штангу на заказ диски для пауэрлифтинга, бодибилдинга и фитнеса. Прочные покрытия, стандартные размеры и широкий выбор весов.
Wonderful work! This is the type of information that are meant to be shared across the internet. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this publish higher! Come on over and talk over with my site . Thank you =)
Осваиваешь арбитраж? https://corsairmedia.ru поможет разобраться в инструментах, выбрать первую партнерку и избежать типичных ошибок новичков. Подробные обзоры от практиков: плюсы, минусы и реальные цифры заработка без воды.
online casino real money no deposit
best real money online casinos
online blackjack olga
Лучшее онлайн казино? https://pokerinfo.ru/download/index.html онлайн-покер, турниры и кэш-игры для игроков разного уровня. Удобный интерфейс, доступ с ПК и мобильных устройств, регулярные события и акции.
Нужен стим аккаунт? общий аккаунты стим доступ к библиотеке игр по выгодной цене. Совместное использование, подробные условия, инструкции по входу и рекомендации для комфортной игры.
Здарова народ!
Наткнулся на годную тему.
Может кому пригодится.
Подробности здесь:
[url=https://eb-bayer.de/]блэкспрут тор[/url]
Всем удачи!
врачебная косметология услуги клиники косметологии
Всем привет!
Увидел любопытную статью.
Решил поделиться.
Линк:
[url=https://eb-bayer.de/]рулетка блэкспрут[/url]
Как вам?
betmgm РћРќ betmgm-play mgm 200 free bet
Всем привет!
Увидел годную информацию.
Решил поделиться.
Подробности здесь:
[url=https://gccassociation.org/]кракен ссылка onion[/url]
Пользуйтесь на здоровье.
Всем привет!
Наткнулся на полезную статью.
Думаю, многим будет полезно.
Смотрите тут:
[url=https://fieldmore.dk]Mega ссылка[/url]
Всем удачи!
Digital Buying Experience Store – Interactive touch with a clean look, perfect for learning and inspiration.
Velvet Vendor 2 Essentials – Located through search, the content is honest and well-presented.
Vendor Velvet Web Shop – Simple layout, items are prominent, and product details are honest and clear.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Venverra Collection – Modern feel, items are diverse, and browsing through them is easy.
Venvira Hub – Looked good immediately, site is easy to use and visually appealing.
visit this store – Smooth navigation and a tidy layout make shopping enjoyable.
direct store access – It’s refreshing to see stylish products and a fast payment process.
check it out here – Everything seems fresh and product details are very informative.
online stationery hub – It didn’t take long to spot precisely what I had in mind.
digital shopfront – The site has deals that are unique and not commonly found online.
official store page – Everything is structured clearly, making navigation effortless.
official discount portal – Getting promo codes is straightforward and very user-friendly.
this tech storefront – The speed is excellent and there’s a good mix of products.
this storefront – Browsing is smooth and the candies are displayed perfectly.
digital device marketplace – My concern was addressed fast with no extra back and forth.
secure shopping page – The site is reassuring and purchasing was effortless.
trusted product store – Prices appear fair and look competitive for what’s offered.
secure shopping page – Bright visuals and seamless navigation make the experience enjoyable.
Test your luck in the best slots. In crowncoin, deposit bonuses and tournaments await you. Join and triumph!
check it out here – Placing my order was easy and gave me confidence in the security.
secure order link – Helpful notifications made shopping easy and straightforward.
official shop link – The site feels welcoming and exploring the products was fun.
visit this site – The layout and visuals make it easy to understand what’s being offered.
explore the collection – Quick load times paired with a solid range of products.
premium storefront – Everything about ordering felt smooth, especially the timely delivery updates.
secure shopping site – The consistent design adds to its reliable appearance.
brassandbloom.shop – Such a delightful find, I’ll definitely be shopping here again.
discover great finds – Found some fantastic pieces and the checkout flow worked perfectly.
backcountry supply store – The gear shipped fast and everything was packed securely.
craft cocoa specialties – The selection feels exclusive and nicely put together.
urban scarf outlet – Stylish and practical scarves that are comfortable for regular use.
premium horse essentials – It’s great to see such a complete selection with pricing that feels justifiable.
this online cart store – Everything loaded fast and the purchase process was simple.
designer kettle outlet – The product lineup is excellent and the rapid dispatch was a pleasant surprise.
creative kitchenware hub – The tools I ordered helped me prepare meals with more ease.
unique workshop essentials – There are specialty items here that are not widely available.
professional display hub – Monitors are well-detailed and the range makes picking one easy.
premium casual sandals – Excellent materials and customer care was very approachable.
smart kitchen solutions – A diverse inventory with genuinely helpful product notes.
Tech Toolbox – I found a variety of handy tools here and the product info is very clear.
modern brand studio – The logos are thoughtfully designed and have a very contemporary feel.
discover green living items – I appreciate the natural visuals and easy-to-follow interface.
financial growth portal – I picked up several strategies that are already helping me stay on track.
blossom & bloom outlet – Gorgeous selection and checkout was simple and safe.
your grooming destination – I was pleased to see the items were packed well and correctly described.
elegant timber designs – The visual appeal is impressive and the craftsmanship feels top-tier.
creative interior hub – Designs feel fresh and thoughtfully made for my space.
quality woodcraft market – The fresh layout pairs perfectly with the high-grade offerings.
home dining shop – I received my order quickly, and the packaging kept everything safe.
workshop toolkit store – Tools here are practical and greatly simplify my projects.
wild exploration supply – Their inventory makes gearing up for adventures straightforward.
home luxury shop – Honestly speaking, the items are sturdy, well-made, and beyond what I imagined.
curated petal collection – Stunning choices available and the checkout experience was smooth from start to finish.
urban jungle store – The plants reached me in excellent condition and are already thriving.
Coffee Cabinet Store – The selection of brewing tools is great, and everything is budget-friendly.
the modern marketplace – It’s refreshing to find curated goods with such an easy payment flow.
this online income shop – Valuable products that make growing online revenue much easier.
the coffee hub shop – Fresh beans that brought intense aroma and smooth flavor to each brew.
Clover Cove Store – Beautiful decorative pieces that add warmth and style to my home.
amberdesigns – Exquisite handmade pieces delivered beautifully and on time.
homefitgear – Gear is strong, reliable, and makes my workouts efficient.
the electronics hub online – Smooth navigation and a wide range of tech gear make shopping enjoyable.
cablelinkshop – Items were delivered safely and function perfectly as expected.
this income growth store – Useful advice and tools for developing successful online revenue.
cocoacove treats – Rich and aromatic cocoa products enhanced my drinks wonderfully.
Ease Empire picks – Ordered paints and canvases arrived quickly and were high quality.
skyprintstudio – Vibrant, high-quality prints arrived on time and I’m very happy with them.
the coat and cap boutique – Quick turnaround time and elegant packaging really impressed me.
featherfancies – Lovely bird accents that make my rooms cheerful and inviting.
the shine and sparkle shop – Products look amazing and all details are clearly listed.
Revenue Roost Hub – Helpful tips and tools to expand your digital income.
arthub – Art supplies arrived high quality and inspired creativity in all my projects.
rankoptimizer – Accelerated my SEO efforts with tangible results.
printcorner – Supplies arrived on time and supported smooth project completion.
this passive income shop – Tools and insights that make earning online smoother and more effective.
Espresso Emporium Boutique – Machines are reliable and make every coffee experience enjoyable.
nestworkspace – Listings were easier to update and track with these tools.
this pattern design hub – Loved finding patterns that complemented my newest project.
the craft brew corner – Great assortment paired with prices that make sense.
canvascorner art shop – My artwork turned out better thanks to these dependable supplies.
tradehubworld – International items shipped quickly and were packaged carefully, arriving in perfect shape.
cybershieldmirror – System safety was enhanced effectively with these dependable security tools.
Revenue Roost picks – Useful products and tips for anyone growing digital income streams.
retailstreamline – Orders arrived quickly and exceeded my expectations in quality.
this snuggle corner – Comfy blankets that wrap me in warmth and relaxation.
the blade and gear shop – Quality craftsmanship and durability make these perfect for daily tasks.
ideajournal – Smooth, high-quality pages designed for daily writing inspiration.
Revenue Roost selections – Products and strategies that helped me expand my online income.
petwellnessshop – Pet items delivered safely and worked exactly as described.
ivoryhomestyle – Décor pieces arrived securely packaged and enhanced the aesthetic of my home beautifully.
aromabasil – Fresh and fragrant herbs that made cooking enjoyable and easy.
CloveCluster finds – The range here seems different from typical online catalogs.
the innovation supplies shop – Helpful items for building, crafting, or designing new concepts.
this convenient cart shop – Checkout was simple and my package arrived very fast.
the passive income corner – Resources here helped me improve my web-based earnings effectively.
freightfable materials – Packaging supplies came quickly and allowed me to ship orders smoothly.
atelierdelights – Almond goodies arrived promptly and tasted just as expected.
this spring supply hub – Fast shipping and top-quality products made everything simple.
harbornutplus – Nuts came on time, crunchy and delicious, perfect for cooking or snacking anytime.
safechoice – Allergy-friendly items that delivered exactly as described.
Pattern Pulse Hub treasures – Found patterns that perfectly complemented my recent project.
RevenueRoost treasures – Tips and tools that simplify boosting online income streams.
this aromatic spice shop – Cinnamon sticks that made desserts smell and taste incredible.
healthdock – Essential products arrived on time and supported my overall wellbeing.
fresh air arc shop – Air purifiers work quietly and efficiently, creating a refreshing environment.
the Adventure Aisle marketplace – Browsing around always gets me excited about traveling somewhere new.
quality leather boots – The impressive selection makes browsing enjoyable.
Silver Spire treasures – Elegant designs and attentive staff left a great impression.
this income growth store – Useful advice and tools for developing successful online revenue.
bloomingbuys – Shopping here is fun thanks to good quality and affordable prices.
the Lock & Luxe collection – Trendy pieces that feel high-end and are made to last.
stickernook – Stickers shipped quickly and were perfect for adding personality to notebooks and planners.
adapterpro – Products were delivered on time and work exactly as expected.
nomadbag – Lightweight essentials made for on-the-go lifestyles.
the handcrafted decor shop – Artistic crafts that make my living spaces feel welcoming.
the passive income corner – Resources here helped me improve my web-based earnings effectively.
my favorite handmade boutique – Every item feels personal, special, and crafted with attention.
signature shoe picks – Each product reflects attention to detail and a refined sense of style.
clustercanyon store – The assortment is intriguing and I’ll definitely return to check out more.
the imported treasures hub – I can buy unique international finds without breaking the bank on shipping.
modmintcollection – Men’s accessories arrived safely and were exactly as advertised.
the breezy marketplace – Shopping here is smooth and the vibe is stress-free.
protein porch picks – Supplements and health products are well organized and easy to find.
starfieldorganize – Reliable storage solutions arrived quickly and helped me declutter efficiently.
fishcareplus – Supplies came on time and ensured my aquarium stayed clean and healthy.
Media Mosaic Hub – Innovative media resources made managing my projects much simpler today.
the cozy decor shop – Stylish and warm accents that brightened up my bedroom instantly.
this tech productivity hub – Tools that make daily organization easy and efficient.
glove collection store – The assortment is both trendy and easy to wear day-to-day.
vanilla treasure trove – So many interesting options that won’t break the bank.
decorandprism – Beautifully designed items that arrived safely and look stunning.
the elegant leather store – Each product arrived beautifully wrapped and in perfect condition.
phoenix corner shop – User-friendly layout with plenty of music merchandise options.
hydratecentral – Water gear arrived promptly and has been very convenient daily.
charcoalcharm store online – Reliable charcoal that keeps the heat consistent and flavorful.
dreamhomehub – Accessories arrived quickly and are well crafted, making my home feel special.
the crispy cooking corner – The suggestions here help me whip up meals in no time.
children’s goodies corner – Browsing is enjoyable thanks to the variety of unique products.
this culinary spice corner – Fresh, flavorful spices that arrived in perfect condition.
Passport Parlor Essentials – Travel products are functional, stylish, and easy to organize.
inkandideas – Everything arrived promptly, making my crafts more enjoyable.
Hello everyone!
I came across a 158 great page that I think you should visit.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find valuable.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://naxacanada.com/how-to-glamp-to-enjoy-both-comfort-and-nature/]https://naxacanada.com/how-to-glamp-to-enjoy-both-comfort-and-nature/[/url]
Furthermore remember not to neglect, guys, — one always are able to within the publication discover responses to address the the absolute confusing inquiries. Our team tried — present all of the data in the most most accessible way.
crafted with passion – The detailed work in each listing makes browsing a pleasure.
eclipse tech shop – Sleek layout and diverse products create a smooth shopping experience.
the Supplement Summit collection – Quality products for health and wellness that I now trust fully.
bbqcorner – Accessories shipped quickly and made grilling more convenient and fun.
solesaga – The trendy shoe lineup immediately stood out to me.
smart sundial collection – Accurate, well-built tools make checking time both simple and stylish.
BarbellBayou Fitness Hub – Good variety of equipment with value-conscious pricing.
the hollow web host – I was up and running quicker than I anticipated.
Elm Exchange Store – Thoughtful arrangement and smooth navigation improve the shopping experience.
watercolor creative shop – Everything from pigments to brushes makes artistic tasks easier.
latte essentials hub – Comfortable vibes and a curated assortment make shopping a pleasure.
Wrap Wonderland Designs – Fun and lively gift wraps make the presentation as exciting as the gift itself.
Wool Warehouse Essentials – A curated yarn collection with clear instructions for knitters.
the wireless device hub – Setup was simple and all gadgets performed flawlessly.
pantryessentials – Pantry staples arrived on time and well packed, helping me stay efficient in the kitchen.
Discover ArtAisle – A blend of imaginative pieces and décor trends that stand out beautifully.
Shop DIY Depot – The selection of handy tools allows even novices to manage small projects with ease.
DeviceDockyard Boutique – Practical tech accessories and well-explained details make shopping simple.
shop Dockside specials – I appreciate how organized the listings are and how fast checkout goes.
sonnet essentials store – Visuals are clean, and each product description is clear and helpful.
Roti Roost Creations – Bread and recipe tips are showcased clearly for a smooth baking experience.
tablet deals shop – Helpful specs and affordable options made shopping effortless.
the stylish beanie corner – Hats are warm, comfortable, and full of great color choices.
the paint paradise store – Every product feels premium and the color selection is amazing.
Exclusive Bundle Deals – Handy multi-item offers create a smoother checkout process.
Sneaker Studio Zone – Exciting shoe options and easy-to-use site navigation make shopping pleasant.
Macro Mountain Store – Inspiring selection of arts and crafts items to kickstart new projects.
Velvet Verge Corner – Trendy and budget-friendly selections make this shop enjoyable.
riceridge finds hub – Easy to navigate pages make exploring the selection fast and convenient.
identityisle.shop – Personalized items are well made and feel special for gifting.
the reliable battery shop – Fast delivery and all products perform flawlessly.
inviting bay store – The entire catalog gives off a calm and charming presence.
Charming Mug Shop – Delightful mug artwork turns ordinary gifts into keepsakes.
Official Sender Sanctuary – They responded quickly and solved my issue right away.
shakers corner – Branding feels thoughtfully designed and consistently stylish.
Stitch Starlight Store – Gorgeous textiles presented beautifully with detailed product photos.
All About Tea Time Trader – Informative listings and fair pricing make it easy to choose teas.
Tech Pack Terra Finds – Tech organizers and handy gadgets are clearly presented and helpful.
the kitchen spice corner – Spices arrived fresh, fragrant, and neatly sealed.
the practical privacy boutique – Everyday privacy tools that are simple and reliable.
top blogging guide – An excellent place to discover smart strategies for growing your blog.
Pearl Parade Collection Hub – Everything was clearly shown, making the selection process smooth.
Happy Feet Styles – Cheerful patterns and gentle fabrics feel great all day.
dawn chic market – The interface is sleek and the products match a contemporary style beautifully.
BerryBazaar Essentials – Quick loading pages and a wide range of products make shopping easy.
SnippetStudio Resources – Creative ideas and assets provided help jumpstart new projects.
Lamp Lattice Market – Each lighting item is shown clearly with details that help in picking the right piece.
Urban Unison Corner – The collection is trendy and organized for simple online shopping.
workout essentials hub – Easy to browse and packed with high-quality fitness tools.
Mug & Merchant Creations – Artistic mugs provide a creative twist for gift exchanges.
curated chic collection – The fashionable vibe makes browsing enjoyable.
Visit RemoteRanch – Niche finds presented clearly with intuitive navigation for effortless browsing.
Thread Thrive Online Shop – Quality threads and vibrant hues make choices simple and fun.
Stretch Studio Finds – Gear options are well curated and the shopping experience feels effortless.
trendy lace marketplace – Fast dispatch and beautifully arranged contents made a great first impression.
Your Charger Destination – Modern accessories displayed with organized appeal.
Explore CreativeCrate – Fun shopping experience with unusual items and charming gifts.
Sticker Stadium World – Vibrant stickers with smooth shipping and reliable quality every time.
CollarCorner Essentials – Everyday pet accessories look functional and durable.
premium saffron shop – Each listing provides a thorough overview of the quality and origin of the products.
Spruce & Style Online – The minimalist setup makes it easy to navigate and shop.
meal hub meridian – Meal prep becomes easy with organized kits and recipe guides.
Explore SnowySteps – Cozy winter collection with fair pricing throughout.
Veranda VPN Hub – Plan summaries and options are presented with clarity.
Fit Fuel Fjord Online – Clear labeling on supplements makes shopping quick and simple.
ProteinPort Deals – Supplement choices are transparent, making them ideal for health-conscious buyers.
tech parts pavilion – Everything matched the specs I needed and arrived on time.
pearlpocket collection – Each jewelry item is displayed with clarity, making browsing enjoyable.
Visit BerryBazaar – Products are well-organized and the site performs quickly on phones.
Domain Dahlia Online Shop – Freshly curated flowers and charming decor pieces that uplift the home.
Creative Mug Corner – Fun and artistic drinkware makes gifting effortless.
Shop Zipper Zone – Practical zipper selection for all kinds of home sewing projects.
All About CyberShield – Cybersecurity options are easy to follow and feel solid and dependable.
content strategy hub – The information is highly useful and presented clearly.
coral goods store – Plenty of interesting products and shopping here feels very simple.
pearl boutique hub – Jewelry pieces are elegant and well-presented with clear images.
EmberAndOnyx Picks – Well-presented products and clear details make finding items simple.
CarryOn Corner Finds – Travel essentials presented clearly and delivered without delay.
seamsecret – Sewing essentials are organized well and easy to find.
SpatulaStation Picks – Affordable and functional tools help make cooking more enjoyable.
raven reports online – Well-structured, informative content with trustworthy analysis.
temple hub online – Navigation is simple and the design is clean, exploring was enjoyable.
Pepper Parlor Online Corner – Enjoying the overall presentation and the easy flow of navigation.
vaultvoyage corner – Simple layout and browsing through products is quick and easy.
digital datadawn shop – The interface is streamlined and using the tools is hassle-free.
explore setupsummit collection – The interface is smooth, and everything is easy to navigate.
linen lantern essentials – The range looks curated with intention and displayed attractively.
explore Catalog Corner – Browsing is effortless, and products are easy to view.
signature spice blends – The presentation looks polished and the goods seem expertly made.
The sweetest slot on the planet? Sweet Bonanza! Colorful sweet bonanza sugar rush symbols, pay-anywhere wins, and free spins loaded with multipliers. Your candy fix just got rewarding.
explore Warehouse Whim – Items are easy to find, and the site feels clean and well structured.
Phone Fix Shop Essentials Online – Helpful service details and making a booking was very simple.
shop Map & Marker – The interface is intuitive, and exploring products feels seamless.
explore Iron Ivy selections – The pages are organized well, and checkout was a breeze.
tech resource barn – The information is accessible and presented clearly for easy navigation.
shop winterwalk – Great selection and browsing through items feels effortless today.
Winter Walk Marketplace – Excellent assortment and navigation feels seamless.
Wander Warehouse Hub – Solid range of products and the pages feel structured.
explore fiberforge shop – Nicely organized sections and browsing feels fluid.
VanillaView Hub – Stylish aesthetic and easy-to-use interface make the experience fun.
my favorite warehouse shop – Layout is clear, and exploring the products feels effortless.
sugarsummit sweets – Delicious confections and treats presented beautifully for easy selection.
Cleair Cove picks – Layout is tidy, and exploring products is fast and effortless.
click for warehousewhim – The website is intuitive, and items are easy to explore.
official pilates plaza site – The vibe is motivating and everything looks crisp and modern.
shop Olive Orchard – I enjoy the aesthetic and how cleanly organized the pages are.
vps picks shop – Plan details are straightforward and performance indicators are reliable.
discover Winter Walk Gear – Diverse products and everything functions smoothly.
parcel paradise corner – Delivery flexibility is good and completing an order is quick.
MarkerMarket Online – Modern design and overall navigation is very intuitive.
winterwalkshop – Nice variety and everything loads smoothly without any issues here.
brightbanyan – Really clean design and pages load quickly on mobile.
Willow Workroom Store – Well-arranged craft items and descriptive labels help buyers quickly locate what they need.
marinersmarket treasures – Fresh goods and handcrafted selections make exploring the store worthwhile.
Metric Meadow picks – Everything is clearly displayed and exploring items is effortless.
explore Citrus Canopy – Everything is arranged nicely, making browsing very easy.
whim favorites – Products are well displayed, and navigation feels smooth and simple.
see cardio equipment – Everything is neatly arranged and browsing feels effortless.
Winter Walk Shop – Great range of items and pages open quickly without delays.
Sweater Station Online – Clean layout and browsing products feels smooth and effortless.
Winter Walk Essentials – Easy to navigate and shopping experience is very smooth.
Shop Hush Harvest – Items arrived fast, fresh, and neatly wrapped.
copper crown picks – Impressive variety and the checkout was smooth from start to finish.
pen pavilion corner – Innovative items with attention to detail make browsing enjoyable.
discover stablesupply – Browsing is fast and the interface makes checkout easy.
learning aurora hub – Step-by-step guides make understanding topics straightforward.
official mocha market site – A wide range of products and the payment process was straightforward.
browse Warehouse Whim online – Layout is organized, and moving through products feels effortless.
labellilac – The selection is great, and product details make browsing very easy.
vpsvista boutique – Hosting plans are clearly presented, with solid performance metrics.
Winter Walk Gear – Plenty of choices and the site runs seamlessly.
browse bakebox goodies – I like how neat and organized every section appears.
Trim Tulip Picks – Easy navigation and product pages load quickly and cleanly.
Winter Walk Finds Online – Smooth interface and shopping is effortless with clear product info.
see SSD Sanctuary products – Products are clearly displayed and moving through the site is smooth.
quartz quiver shop – Simple structure and helpful information included with each product.
fitness essentials hub – Well-structured product pages make finding nutrition and workout items simple.
sample suite boutique – Organized structure makes exploring the content straightforward and easy.
browse warehousewhim items – Layout is tidy, making it easy to move through products.
see the Ruby Rail catalog – Items are easy to find, and the experience feels seamless.
exclusive kicks marketplace – The designs stand out and the pricing seems honest.
Winter Walk Hub – Good variety and the overall experience is smooth.
Package Pioneer Hub Shop – Polished layout and selecting items feels easy and smooth.
see the Word Warehouse catalog – Layout is clean and browsing through pages is seamless.
shop ergonomic finds – Everything is well organized and product explanations are helpful.
discover winterwalk – Product listings are neat and pages load quickly with no problems.
anchor and aisle online shop – The interface is simple and spending time here feels worthwhile.
chair picks shop – A range of supportive chairs that make long work sessions easier.
visit warehousewhim – Items are well organized, making browsing simple and enjoyable.
peachparlor boutique corner – Lovely look and easy-to-follow layout make exploring products fun.
fabric falcon outlet – Lovely assortment and the product info is practical and clear.
click for cablecorner – Products are clearly shown, and navigating feels fast and simple.
Winter Walk Online – Good product range and browsing is fluid and easy.
surfacespark – Clean interface and browsing through items feels intuitive very easy.
my favorite Pine Path – Everything feels polished, and navigating through the products is quick.
explore restrelay collection – Everything is neatly structured, and finding items is simple.
Winter Walk Finds Online – Smooth interface and shopping is effortless with clear product info.
Profit Pavilion Online Corner – Clear breakdown of topics and helpful explanations throughout.
night vibe essentials – The overall presentation looks sleek and thoughtfully designed.
shop Warehouse Whim – Selection is impressive, and moving through products is effortless.
browse caffeinecorner items – Items are easy to navigate and shopping is hassle-free.
Roast & Route Essentials – The style is modern and mobile navigation is seamless.
discover Winter Walk Gear – Diverse products and everything functions smoothly.
Backpack Boutique Essentials – Clean design and discovering products takes no effort.
winterwalkshop – Nice variety and everything loads smoothly without any issues here.
browse Search Smith items – Content is well organized, and navigation is quick and easy.
premium stitchandsell – Everything is well displayed, and ordering is simple.
minimalmist picks – The aesthetic is clean, and every item feels carefully placed.
Warehouse Whim picks – Everything is organized neatly, making browsing fast and enjoyable.
see the Jacket Junction catalog – Products are clearly displayed, and navigating the site feels smooth.
discover Winter Walk Gear – Diverse products and everything functions smoothly.
Ram Rapids Essentials – Smooth browsing and organized presentation makes shopping simple.
wrap and wonder essentials – Presentation is appealing and every item looks carefully curated.
shop winterwalk – Great selection and browsing through items feels effortless today.
quality domain provider – The layout looks tidy and exploring the site is convenient.
visit fiberfountain – The website is well-organized and finding products is effortless.
discover barbellblossom – Layout is neat, and exploring items is quick and effortless.
Warehouse Whim Store – Items are clearly displayed, and browsing is easy and enjoyable.
explore Apparel Ambergris – The site feels refined and browsing through items is straightforward.
explore Winter Walk Essentials – Attractive assortment and everything loads cleanly without problems.
Logo Lighthouse Marketplace – Simple navigation and the design is very user-friendly.
island ink essentials – The visual theme is engaging and the branding feels polished.
browse winterwalkshop – Everything runs smoothly and descriptions make finding items simple.
cottage hub shop – Product displays are neat, and the checkout process is seamless.
SuedeSalon Marketplace – Well-presented items and curated collections make browsing effortless.
Warehouse Whim Online – The variety is excellent, and navigating the site feels seamless.
Print Parlor Official – Everything is logically laid out, making browsing simple and pleasant.
discover Winter Walk Gear – Diverse products and everything functions smoothly.
quality service hub – Service info is easy to follow and the site feels solid and dependable.
Seashell Studio Online – Crisp visuals and browsing categories feels effortless.
see the Pattern Parlor catalog – Everything is well arranged, and browsing products feels effortless.
official topaz trail site – The browsing flow is fluid and the layout makes sense right away.
this creative supply store – Diverse product choices with a streamlined checkout system.
winterwalkshop – Nice variety and everything loads smoothly without any issues here.
SeaBreezeSalon Finds Online – Calm and serene layout enhances the pleasure of exploring products.
Sparks Tow Online Store – Cute and organized shop, items I wanted were easy to find.
my favorite Ruby Rail – The site feels polished, and finding items is quick and easy.
stocksculpt collection – Great variety of investment tools and market guidance for beginners and pros.
ChairAndChalk Essentials – Artistic items make shopping fun and checkout is simple.
a refined cotton shop – The fabric lineup looks expertly made and upscale.
Voltvessel Online – Simple layout and intuitive navigation make exploring easy.
nutmeg lifestyle store – The idea is refreshing and the interface works flawlessly.
tidalthimble shop – Layout feels tidy and navigating the catalog is simple.
Explore SableAndSon – High-quality items with informative descriptions enhance the browsing experience.
Vivid Vendor Shopping – Bright colors and dynamic images make the browsing experience exciting.
sipandsupply picks – Product variety is excellent and the website looks neat and inviting.
official workbenchwonder site – Products feel functional and information provided is helpful.
RubyRoost Boutique – Delightful items shown beautifully with clear, attractive visuals.
Workspace solutions online – The clear layout and functional products streamline daily routines.
Art Attic Online – Inspiring selection and a very easy-to-use browsing layout.
Wagon Wildflower Essentials – Pleasing visuals and cheerful design make navigating the site enjoyable.
Basket Bliss Curated Store – Neatly arranged items and intuitive navigation create a seamless experience.
Cove Crimson Gallery – Visually appealing design and smooth navigation overall.
this Yoga Yard boutique – Soothing selections and a tranquil, peaceful feel throughout.
tablettulip essentials – Layout looks beautiful and site performance is smooth.
CypressCircle Finds Online – Cleanly organized pages and intuitive navigation enhance the overall experience.
Workbench Wonder Essentials Online – Items seem useful and product information is very clear.
Cypress Chic Hub – Clean layout and exploring items feels simple and intuitive.
visit Click for Actionable Insights – Easy navigation and quick page loads make accessing insights effortless.
modern invoicing outlet – I like how the elegant setup highlights the quality of the selection.
Shop VeroVista Online – Smooth browsing with fast loading pages and clear item descriptions.
Astrevio Product Hub – The simple structure ensures every item is displayed distinctly.
your ChairChase hub – Finding products is simple thanks to a tidy and intuitive layout.
The Bowl Shop – Smooth browsing experience and the site feels user-friendly.
Clarvesta Marketplace – Navigation is intuitive and the overall layout feels sleek.
briovista.shop – Very clean layout and everything loads fast without lag.
Cozy Carton Select – Visually appealing layout and browsing feels effortless.
Trust Solutions Center – Organized layout and clear headings help users navigate content easily.
Bath Breeze Shop Hub – Premium items and straightforward navigation make exploring easy.
CourierCraft Collection – Creative offerings combined with an effortless ordering system.
journaljetty online shop – Extensive selection and descriptions are easy to read and informative.
layout lagoon treasures – The site is tidy and browsing through pages is easy.
Dalvanta Studio Hub – Clean layout and the shopping process feels simple today.
Official Velvet Vendor 2 – Adding to bookmarks, the products are really one-of-a-kind.
discover Trusted Commercial Network – Smooth interface and logical layout make browsing effortless.
PolyPerfect online collection – Smooth navigation and a user-friendly payment process keep me satisfied.
explore ChargeCharm – Finding gadgets is quick thanks to a neat and organized interface.
Attic Amber Curated Store – Friendly aesthetic and clear navigation make the site enjoyable.
trusted brew retailer – A dependable site with plenty of items and quick responsiveness.
briovista.shop – Very clean layout and everything loads fast without lag.
Rosemary Roost favorites – Everything feels carefully selected and visually inviting.
NauticalNarrative Online – Coastal decor and accessories with a user-friendly browsing experience.
Cozy Copper Vault – Items appear high quality and navigating the site is easy.
Bay Biscuit Essentials – Cute items paired with a smooth ordering experience.
Sheet Sierra Essentials Online – Nice collection and ordering worked perfectly today.
Professional Collaboration Online Portal – Organized pages and clear menus make navigating content effortless.
Sketch Station Collection – Well designed pages and content that feels engaging.
Visit Vendor Velvet – Modern design makes it easy to move around without any confusion.
Decordock World – Great variety of items and details help make informed choices.
explore ClickForActionableInsights – Well-structured pages and responsive design make reading content simple.
Clever Checkout Online – Intuitive layout and smooth purchasing experience keep things simple.
official Woolen Whisper hub – I love the cozy vibe and easy browsing that makes exploring a pleasure.
your Long Term Business Partnerships – Structured pages and intuitive design make exploring services simple.
Aura Arcade Collections – Unique finds and a flawless checkout process make shopping seamless.
camping essentials – Navigation is straightforward and locating items is quick.
Brondyra Design Hub – User-friendly layout and modern visuals make browsing enjoyable.
Color Cairn Hub – A collection of colorful products that immediately catch attention.
Craft Cabin Lane – User-friendly design and product details are easy to follow.
Beard Barge Essentials – Good variety and informative descriptions make choosing easy.
wellnesswilds shop – Peaceful theme and finding products is simple.
Venverra Shop Now – The layout is clean and gives a sense of trustworthiness for online buyers.
sleepsanctuary collection – Restful design and very pleasant user experience overall.
Trusted Business Connections Online Hub – Smooth interface and logically organized pages make accessing content fast.
Yavex Online Picks – The site runs efficiently, with content loading almost instantly.
Dorvani Corner – Smooth experience with quick-loading pages.
Bond Solutions Center – Logical layout and responsive design make exploring content straightforward.
Corporate Partnership Site – The design is neat and navigation feels effortless.
premium card collection – Finding unique designs is quick thanks to the user-friendly setup.
Auracrest Essentials – Products are well-organized and the descriptions provide useful details.
TabTower Collection – Clean presentation and informative details make exploring products enjoyable.
Casa Cable Storefront – Clean interface and practical product details make shopping stress-free.
official BuildBay hub – High-quality products and smooth ordering make shopping easy.
Craft Curio Boutique – Layout is simple and exploring items feels effortless.
A convenient car catalog http://www.auto.ae/catalog/ brands, models, specifications, and current prices. Compare engines, fuel consumption, trim levels, and equipment to find the car that meets your needs.
official samplesunrise site – Creative concept with a clean and thoughtful arrangement.
Birch Bounty Collections – Clear layout and thoughtfully arranged products make exploring enjoyable.
this business trust hub – Easy-to-follow design and structured layout improve browsing efficiency.
schemasalon online shop – Content is easy to read and moving around the site is effortless.
Clever Cove Corner – Well-organized categories and clean layout simplify product discovery.
Ravion Platform – Professional look with smooth browsing and clear layout.
Corporate Unity Access – Clean pages with intuitive navigation make exploring offerings smooth.
organized success hub – Its clean interface and tools make managing tasks straightforward.
Aurora Atlas Favorites – Fast, responsive site and a wide variety of products available.
explore Growth Alliances Portal – Clear layout and logical menus simplify finding details.
Caldoria Picks – Clear product presentation and smooth navigation make exploring simple.
Calveria collection – Beautifully designed pages make scrolling through products enjoyable.
Crate Cosmos Hub – Easy to navigate and all pages load really fast.
Xorya Top Picks – The modern aesthetic and clean interface create a smooth browsing experience.
Blanket Bay Essentials Store – Inviting collection and pages load instantly.
explore LongTermCommercialBonds – Fast-loading sections and organized content simplify finding information.
Qulavo Central – Effortless browsing and pages respond instantly.
sunsetstitch boutique – Well-arranged items and the order process was effortless.
a href=”https://findyournextdirection.shop/” />explore FindYourNextDirection Hub – Helpful content and organized layout make browsing fast and easy.
Aurora Avenue Curated Picks – Sleek design and well-chosen products make shopping simple and enjoyable.
CalmCrest Online Marketplace – Pleasant color scheme and quick load times improve navigation.
this chrome marketplace – The streamlined design and well-sorted products create a smooth experience.
shop CardamomCove – Every product is easy to understand, and the site feels cozy.
Crisp Collective Boutique Hub – Great range of items and browsing feels effortless.
ClickForBusinessLearning Portal – Clear headings and well-laid-out pages improve the browsing experience.
tagtides marketplace – The style is attractive and the experience feels smooth.
Blanket Bay Selections – Comfortable vibe and pages respond instantly.
Click Courier Portal – Simple design and fast access to service info enhance usability.
BusinessGrowthPartnerships Portal – Easy-to-read sections and intuitive navigation simplify exploring.
Qulavo Holdings Portal – Navigation is simple and pages respond almost instantly.
Yavex Boutique Online – Fast navigation and smooth performance enhance the browsing experience.
this value partnership hub – Structured content and intuitive layout make accessing details effortless.
Watch Wildwood Studio – Attractive design and moving between pages is smooth.
ChicChisel Top Picks – Attractive design and product details make finding items effortless.
Auroriv Store – Browsing is effortless, and the site has a sleek, modern feel.
CardCraft studio – Creative concepts and a clean, fast ordering system stand out.
Crisp Crate Finds – Layout feels intuitive and browsing the selection is effortless.
level-up loot store – The exciting atmosphere and broad collection guarantee a longer stay.
Bloom Beacon Online Marketplace – Navigation is easy and the shopping flow feels natural.
ClickToExploreInnovations Portal – Fast-loading pages and organized sections make accessing information smooth.
Global Enterprise Bonds Resources – Fast-loading pages and structured layout improve the user experience.
Explore Spirit of the Aerodrome – The information here is clear, compelling, and enjoyable to read.
Explore The Front Room Chicago – Enjoy an inviting environment with interesting details and helpful information.
Xelivo Gate – Smooth navigation and overall site flow feels natural and simple.
explore Modern Purchase Hub – Clear sections and responsive interface make shopping convenient.
CinnamonCorner Design Hub – Friendly visuals with intuitive navigation make browsing simple.
Auto Aisle Online Marketplace – The product variety is solid and filtering helps narrow down options.
Crystal Corner Nook – Browsing is smooth and the catalog is easy to follow.
streetwearstorm.shop – The clothing selection is trendy and really fits my current style.
Storefront design corner – The tidy pages and clear labels simplify the browsing process for newcomers.
Xorya Store – The interface is sleek, and the overall layout feels very modern.
Bright Bento Online – Excellent product range with descriptions that guide purchasing decisions.
Explore 34Crooke – Discover a streamlined website built for comfort and clarity.
your Trusted Business Framework – Clean sections and logical design make exploring the site effortless.
Sleep Cinema Hotel online access – Find engaging content and a unique browsing experience on every page.
Cloud Curio World – Varied products and efficient loading speed enhance browsing.
Blue Quill Studio – Pleasant interface and pages load quickly without issues.
top SecureCommercialBonding site – Clean layout and responsive pages make accessing details effortless.
CircuitCabin Online – Smooth navigation and product display makes shopping simple.
Bag Boulevard Store – Stylish bags and browsing the site is very easy.
Official Lofts on Lex Site – I like how the listings are organized with clear and helpful information.
Workspace Wagon essentials – Items are displayed logically, making daily workspace setup effortless.
a radiant shopping spot – Its colorful theme and smooth navigation feel refreshing.
Latanya Collins info page – Enjoy helpful tips and organized guidance for easy comprehension.
Bright Bloomy Online Marketplace – Cheerful aesthetic and simple layout make browsing effortless.
PressBros info page – Browse content that is neatly presented and easy to navigate for all visitors.
Bold Basketry Boutique – Smooth interface and items are displayed neatly for shoppers.
Aisle Alchemy finds – I noticed a few items that were refreshingly different and eye-catching.
official ClickToLearnStrategically site – Well-structured pages and smooth navigation simplify accessing information.
Go to OlympicsBrooklyn – The presentation is engaging and informative for area guests.
The Call Sports online – Enjoy curated content and easy-to-read coverage of the latest matches.
gym gear paradise – The strong athletic theme pairs perfectly with high-quality selections.
Visit Updating Parents – Discover helpful guidance that’s simple to understand and apply.
explore GPU Grotto – Solid assortment of graphics tech arranged with clarity.
Clove Crest Spot – Attractive assortment and explanatory details make browsing enjoyable.
Visit Brandon Lang Site – I always find the commentary shared here insightful and well thought out.
Explore Long-Term Opportunities Online Portal – Logical structure and responsive design help users navigate efficiently.
Discover The Winnipeg Temple – Read thoughtful articles and uplifting messages shared throughout the site.
In The Saddle Philly info page – Explore stories and resources that showcase community support and enthusiasm.
modern product hub – The layout is clean and each item stands out clearly.
the Ledger Lantern hub – Product info is easy to follow, and the layout is thoughtfully organized.
Power Up WNY Community – The highlighted projects show real passion and tangible results.
Open Energy Near site – Discover organized pages featuring meaningful discussions.
Coffee Courtyard Essentials – Relaxing vibe and simple navigation throughout the site.
Visit Al Forne Philly – Explore a site with clear content and neatly structured information for all visitors.
Enterprise Framework Center – Clear headings and responsive design help users navigate easily.
Explore Flour and Oak – I appreciate the creativity woven into every section of the website.
the Audit Amber site – Straight-to-the-point explanations paired with seamless browsing.
Learn about Elmhurst services – Access helpful content aimed at strengthening local connections.
Arden Luxe marketplace – The upscale visuals and helpful details make exploring products easy and enjoyable.
Check out 9E2 Seattle – Browse content presented neatly with effortless site navigation.
Access Republic W4 – Navigating through the site is simple thanks to its clear design.
explore Apricot Alcove online – Stylish atmosphere with a seamless flow from product to purchase.
Energy Near official site – Explore detailed insights and current information in one place.
Collar Cove Essentials – High-quality items with easy navigation throughout.
Learn about Kionna West – Explore content that reflects authenticity and thoughtful insights.
Pepplish Platform – I appreciate the clear structure paired with an original idea.
Ardenzo outlet – The site layout is smooth, making exploring products straightforward.
Learn from Reinventing Gap – Find essential topics explained with clarity and purpose.
this art supply hub – Large selection and intuitive checkout make shopping easy.
Explore ulayjasa resources – Find helpful information and smooth browsing designed for all users.
1911 PHL online hub – Discover helpful sections and well-organized updates at a glance.
Official democracy awareness site – Access meaningful commentary designed to spark thoughtful discussion.
Natasha for Judge web portal – Navigate a professional, informative site with a confident voice throughout.
Simple Online Shopping Zone – Browsing products is easy and the checkout process is smooth.
Skillet Street Marketplace – Loved the product options and the site feels seamless to explore.
ryzen rocket electronics – Browsing is fast and the site feels well-organized.
Learn about PMA Joe 4 Council – Access meaningful updates and well-organized information designed for residents.
Leanne’s Fairy World – The charming updates and thoughtful storytelling are simply delightful.
Best Value Storefront – Layout is tidy, and products are easy to explore with no confusion.
Coral Crate Nook – Well-presented products and site loads fast.
Planner Port Online Hub – Useful content and exploring pages is straightforward.
handpicked goodies here – I’m impressed by how beautifully the products are highlighted.
Explore Play-Brary resources – Read imaginative content delivered in a warm and approachable manner.
Feel the thunder of the plains in every spin of this legendary game. buffalo link hold and spin unleashes golden buffalo bonuses, endless free spins, and massive payouts for non-stop excitement. Start your stampede to fortune today!
DiBruno Bottles Hub – Interesting finds and regular news make visiting this site a treat.
Local PHL Goods – Really enjoy exploring local offerings and keeping up with updates.
Basket Bliss Curated Store – Neatly arranged items and intuitive navigation create a seamless experience.
see Pearl Vendor products – Everything feels organized and the information is easy to follow.
skilletstreet store – Loved the choices available and browsing works flawlessly.
Canyon Market shopping hub – Happened to discover it and it seems top notch.
MDC Community Portal – Helpful local insights paired with an approachable and friendly style make this stand out.
Flake Vendor website – Pages load instantly and navigating feels smooth.
handpicked toys – The site is visually clean and products are easy to review.
visit this market site – The interface is clear and navigating through pages is effortless.
Gary Masino Portal – Clean design and well-explained content make understanding the message simple.
Bath Breeze Store – High-quality items and a clean, easy-to-navigate layout.
Timber Aisle Collections – Browsing is seamless and the interface looks modern.
this online vendor – Found my items fast and the checkout experience was simple.
Cobalt Vendor Items – The site is polished and exploring different sections is easy.
Scarlet Crate Store – Everything is well-organized and easy to find on this site.
benchbazaar selections – Well-organized pages and product descriptions are very clear.
Winter Aisle Store – Everything is well-organized and easy to navigate.
visit Clover Crate today – Smooth navigation and simple interface make this site a pleasure to use.
browse Topaz Aisle items – Found exactly the kind of unique products I was hoping for.
timekeepertide – The site looks great and all the product details are easy to read.
check out Echo Aisle – Site layout is clear and everything feels easy to access.
learn with Snow Vendor – Support responded quickly and made the process simple and fast.
Community Care Initiatives – The steady flow of informative posts shows real commitment to service.
this Bay Biscuit boutique – Cute selection and purchasing is effortless.
Elect Cateria RMcCabe Hub – Open and clear content makes understanding goals straightforward.
lanternmarket.shop – Really liking the product variety and easy to follow layout.
PrimeShop – Browsing feels intuitive and the layout is very clean.
find unique items here – Navigation is clean and browsing is enjoyable.
check out Quartz Vendor – Everything is well-structured, so I can find what I need fast.
official chairchic shop – Smooth navigation and product details are clear and helpful.
shop the Firefly Crate brand – The selection feels deliberate and the layout is tidy.
shop the East Vendor brand – The process to complete my purchase was quick and easy.
browse Dawn Vendor deals – The craftsmanship looks impressive and the rates are competitive.
Zinc Vendor Online – Really happy with the selection and the pricing seems fair overall.
dyedandelion corner – Love the playful designs and easy-to-use interface.
Beard Barge Store – Great variety with clear descriptions that make products easy to understand.
O’Rourke Philly Portal – Easy-to-use layout with well-presented, helpful information.
discover North Crate – Checkout was fast, simple, and worked without a hitch.
Terra Vendor marketplace – Reasonable costs and a variety of quality products.
Oak Vendor Store – The site is intuitive and products are easy to find.
Headline Hub Picks – Easy to read and the pages load quickly every time.
Featured Poems and Essays – The expressive writing style and clean presentation stand out immediately.
find great items here – The site is easy to move around and pages load rapidly.
see Meadow Aisle products – Navigation is simple and the browsing experience is enjoyable.
this online berry shop – Support responded in no time and gave clear instructions.
shop the Crown Vendor brand – Support answered immediately and solved the issue without delay.
Birch Bounty Shop Hub – Clear layout with products that feel thoughtfully curated.
SeaportStore – Loved how quickly everything loads and how clean the layout is.
Philly Beer Fest Resources – Exciting lineup and informative updates make this festival stand out.
Garnet Aisle Marketplace – Finding products is quick thanks to the clean design.
learn with Meridian Vendor – Came across quality products that seem promising.
visit Silver Vendor – The checkout went smoothly and didn’t take much time at all.
Lake Vendor resources – Everything is laid out cleanly and details are easy to absorb.
Fit Fuel Hub Online – Well organized and placing an order was simple.
Zena Aisle Collections – Pages load instantly and everything looks sharp on phones.
find great items here – Layout is neat and menus are user-friendly, very straightforward.
find great items here – Clean, intuitive design makes finding products easy.
Blanket Bay Essentials Store – Inviting collection and pages load instantly.
PP4FDR Advocacy Hub – Well-structured information and passionate messaging bring the mission to life.
Dew Vendor Online Shop – Pages load quickly and browsing feels natural and easy.
Natalia Kerbabian Hub – Thoughtful background and interesting content keep readers engaged.
Cove of Cut & Sew – Loved the clear descriptions and the selection is well-curated.
Meadow Vendor marketplace – Everything is organized well and loads in seconds.
wildcrate.shop – The design feels modern and pages load very quickly on mobile.
see Dune Vendor products – Organized sections and a simple design make browsing pleasant.
Woodland Vendor hub – The layout is intuitive and pages respond immediately.
this online vendor – Clear design and helpful product information make exploring easy.
fitfuelshop picks – Navigation is intuitive and checkout worked perfectly.
Harbor Aisle marketplace – Categories are easy to find and descriptions are very helpful.
TransparentShop – Everything on mobile felt responsive and completing an order was easy.
Blanket Bay Online Marketplace – Warm ambiance and quick-loading pages make shopping easy.
Hearth Vendor Collections – I can quickly explore products thanks to the fast and smooth interface.
FernCrate Selection – Love the assortment of items and how simple it is to shop here.
Robin Market marketplace – They responded without delay and were very informative.
Denim Dusk Picks – Items are well-presented and exploring the site is effortless.
explore Glade Vendor shop – Finding items was easy and completing checkout was stress-free.
Stone Vendor Items – Helpful and responsive support made the whole experience smooth.
Wood Vendor shopping hub – Really pleased with everything and I’ll revisit soon.
explore Pine Crate shop – Navigation was simple and I found products that are really handy.
KS4TheKids Official Website – A dynamic environment that blends inspiration with practical learning tools.
Cup & Craft Boutique – Items are easy to explore and interface is very user-friendly.
Bloom Beacon Online Marketplace – Navigation is easy and the shopping flow feels natural.
chestnutvendor.shop – Customer support was helpful and responded to my question promptly.
Opal Aisle Official – Love the beautiful product selection and how easy it is to browse.
browse Bright Aisle items – The design is minimal and easy to follow.
willowvendor.shop – The overall vibe is modern fresh and welcoming to visitors.
explore Plum Vendor X – The site feels clean and everything is easy to navigate.
this online resource – The explanations stay brief while covering what beginners need.
visit this boutique – A cozy selection that feels thoughtfully arranged throughout.
this lovely webshop – I’m impressed by how neat and inviting the setup is.
browse Wind Vendor items – Ordering was fast and hassle-free.
illustrationinn hub – Inspiring artwork and site navigation is intuitive and fast.
browse Quartz Aisle here – Clean and organized interface makes shopping hassle-free.
visit Autumn Crate shop – Everything is neatly structured and very welcoming to users.
Bright Bento Showcase – Excellent assortment with detailed and helpful product explanations.
Hill Vendor Selections – Layout is modern and fresh, giving users a positive browsing experience.
browse Iris Crate items – Website is simple to use and sections are very clearly defined.
Family Fun at Moe’s – I love the upbeat environment and the new updates shared regularly.
shop the Silk Market brand – Interface feels up-to-date and very accessible.
Wheat Market Finds – Impressive selection with a clear focus on quality and curation.
Ruby Aisle Shop – The menu is straightforward and everything is easy to access.
CharmVendor specials – Such an appealing mix of goods, I enjoyed every minute of it.
discover Apricot Market – Sleek design and practical filtering make shopping enjoyable.
visit Cedar Aisle today – The site runs smoothly and purchasing products couldn’t be easier.
benchbreeze – Interface is clean and browsing through pages feels effortless.
skilletstreet kitchenware – Great variety and moving through the site is intuitive.
visit this boutique – Well-curated items that make the shopping experience enjoyable.
Moss Vendor online store – Bookmarking this to stay updated and make future purchases easily.
reedvendor.shop – Love the simplicity and the clear categorization of items here.
Bright Bloomy Collections – Pleasant visuals and simple navigation make exploring enjoyable.
discover Satin Vendor – Marking this down for future orders.
Walnut Aisle Store – The layout is simple and the products are visually appealing, making browsing fun.
Iron Vendor Store – The items feel sturdy and well-crafted, a dependable selection overall.
Spring Crate Online – Planning to return soon because the site is very user-friendly.
Alpine Crate marketplace – Feels dependable and exploring further could be rewarding.
German Beer Festival Guide – Eager to attend and impressed by the detailed insights about the event.
LilacMarket – Quick, professional help that addressed the issue perfectly.
ryzenrocket devices – Navigation is simple and purchasing works without complications.
browse Bronze Vendor – Found the interface user-friendly and I’ll definitely return soon.
this online shop – Pleasant and easy to navigate, I’ll return for more.
Feather Market online – I found the lineup to be distinctive compared to mainstream shops.
check Sage Vendor – User-friendly design makes browsing effortless and secure.
Ultimate Club Choices – Really like the fresh concept and the interactive content makes it a fun visit.
Uncommitted NJ Updates Hub – Straightforward explanations and transparency make the content easy to trust.
Glow Vendor online – The modern design really draws you into the products.
official Coral Vendor site – Descriptions are detailed and the items feel durable and reliable.
LoftHubShop – Searching for items is smooth thanks to the organized menus.
Home Essentials Hub – I enjoyed how simple it was to find exactly what I needed.
Nectar Picks Hub – Enjoyed browsing and located all the products I was searching for.
Violet Trend Store – The site is intuitive and products are displayed in an organized manner.
Sea Deals Online – Great variety of items and a smooth, hassle-free checkout.
official Amber Crate site – The presentation is neat and keeps the shopping experience hassle-free.
Remi PHL Portal Info – Clean pages and practical updates make exploring seamless.
Shop Granite Collection – Smooth navigation and products are displayed clearly and appealingly.
browse Cotton Market here – Smooth flow and user-friendly design make exploring easy.
NuPurple Pricing Transparency – Helpful breakdowns and clear numbers make pricing easy to digest.
Top Ginger Crate – Navigation is seamless and everything is easy to explore.
Teal Vendor Deals – Fast navigation, pages are clear, and shopping felt very straightforward.
Ridge Vendor Online – Excellent product quality paired with responsive and helpful support.
Jovenix Hub – Great selection and the site is very easy to browse.
Delta Supply Online – Really liked the items and checkout went smoothly.
Aurora Favorites – Everything is easy to find thanks to clear layout.
Vale Deals Online – Found a few interesting items and payment went without a hitch.
this online shop – Noticed some pretty cool selections, worth checking out again later.
Ash Vendor Hub – Browsing was hassle-free and locating products was straightforward.
Top Bay Products – Really enjoyed the selection and checkout was simple.
Community Vaccine Updates – Straightforward guidance and reliable updates make this a go-to resource.
Retail Glow Hub – Enjoyed shopping, everything is organized and the checkout process was smooth.
Wave Vendor Official – Found the product variety excellent and checkout went smoothly.
Ridge Vendor Favorites – High-quality selections and assistance from customer care was outstanding.
shop at LinenVendor – Clean presentation and quick purchase process make shopping effortless.
EmberVendor Picks – Products are well organized and the payment process was seamless.
Best of Lavender Crate – Unique selections and the site feels very dependable.
AshMarket marketplace – User-friendly structure with an easy final payment step.
Zen Vendor Boutique – Layout is straightforward and the descriptions provide helpful guidance.
Indigo Vendor Boutique – Layout is simple and every product looks thoughtfully presented.
Caramel Shopping Spot – Clean design and smooth navigation make the overall experience enjoyable.
Opal Wharf Online Spot – Layout is intuitive and product descriptions make everything easy.
Cycling Science Initiative – The event is well laid out, and the inspiring mission is easy to follow.
fairvendor.shop – Found exactly what I needed, site feels trustworthy overall today.
Field Marketplace – Shopping here made it incredibly easy to get what I came for.
PlumVendor Online Store – Loved the layout and overall shopping experience felt professional.
Ember Aisle storefront – Found some distinctive items, I’ll be back to explore more.
CreekHub – Fast loading and well-structured pages make browsing enjoyable.
Best of West Vendor – Quick pages and a clear layout make exploring products easy.
SolaIsle deals – A tidy layout and clearly showcased products make the site enjoyable.
Best of Acorn Vendor – Shopping is easy thanks to the clean and organized layout.
FrostTrack Hub Online – Browsing feels enjoyable and effortless thanks to the simple design.
Shop Brass Collection – Great clarity in product descriptions and quick page loads.
Top Pebble Products – Browsing the collection today was enjoyable and hassle-free.
Shop Tide Vendor – Easy to navigate and products are organized neatly.
O’Neill Public Platform – Transparent goals and easy navigation make understanding the vision simple.
Shop Jasper Collection – The rates are sensible and the website comes across as trustworthy.
WhimHarbor Online – Pleasant shopping experience, items are organized and easy to find.
Explore Flora Deals – The simple design makes it quick to find everything I need.
OrchidAisle marketplace – Pleasantly organized, with selections that seem thoughtfully chosen.
Pine Vendor online – Well-organized interface and speedy loading create a smooth experience.
Wicker Lane Online Store – Clear product layout, effortless navigation, and checkout was quick.
Clear Product Hub – Navigation is simple and the products are appealing and interesting.
Morning Crate Products – Smooth browsing, got exactly what I needed in no time at all.
Grove Aisle Spot – Fast site performance and products are simple to find.
Ocean Online Shop – Fast-loading pages and a good variety of products make browsing easy.
EmberBasket Select – Clear info on products and browsing the site feels effortless.
Juniper Vendor Online – I was impressed by the quick shipping and the careful packaging.
SunCrateHub – I’ll save this site for later, it makes finding items very easy.
N3rd Market Shop – Entertaining content and a vibrant feel make this site stand out.
Thistle Marketplace – Plenty of items to choose from and the descriptions are very thorough.
JollyMart Store – Pages load fast and the selection of items is really convenient.
Hazel Essentials Shop – Navigation is simple and the team responded quickly to my messages.
Shore Vendor Online – Very easy to browse and the layout is clean and organized.
official Oak Market site – Shopping feels relaxed and enjoyable thanks to the clean design.
Lunar Vendor Deals – Assistance was timely and staff were very accommodating.
QuickCarton Corner – Great selection and easy-to-use interface, makes checkout simple.
Birch Collection Hub – Items are showcased nicely and the store feels dependable.
Raven Vendor Online – The navigation flows naturally and the pages are clean and readable.
Shop Icicle Crate – Items arrived quickly and everything feels high quality.
Walnut Vendor Picks – Checkout was effortless and the store feels very professional.
Hagins Election Info – Clearly stated priorities and sincere commitment make the campaign transparent.
Shop Floral Collection – Enjoyed browsing, everything is neatly organized and easy to find.
Shore Vendor Selection – Website feels organized and finding items is very easy.
discover CartCatalyst – Navigation is intuitive, and the overall feel is modern and sleek.
Explore Mist Vendor – Found the items appealing and descriptions made shopping simple.
explore Nest Vendor – The site layout is clean and structured, so finding exactly what I needed was quick.
Yornix Deals Hub – Customer support answered all my questions, making browsing enjoyable.
Blossom Vendor Picks – Detailed descriptions combined with timely posts make shopping easier.
MinimalCart – The layout is simple, making it effortless to browse product details.
Drift Vendor Store – Browsing was seamless and the product descriptions are very informative.
Quick Meadow Spot – Pleasantly surprised by how organized and smooth the browsing experience is.
this online shop – Sleek site design, browsing feels natural and hassle-free.
check out Item Cove – Looked over the offers and they seem pretty great.
Visit Maple Aisle – Browsing was enjoyable and I found many intriguing items.
Shop Key Collection – Products are top-notch and delivery was impressively fast.
Mint Vendor Store – Smooth shopping experience, everything feels professional and trustworthy.
Chris Hall Election Info – Thorough explanations of policies and background give a clear overview.
curated aisle goods – Discovered this shop and the materials appear high quality.
Bouton Market – Stylish design and browsing feels natural without any hassle.
Olive Vendor Picks – Easy navigation and product sections are well organized.
MarketPearl Shop Hub – Product variety is impressive and the checkout process is seamless.
Hovanta Essentials – Layout is clear and everything is easy to browse through.
Finch Online Store – The team was fast, helpful, and professional throughout the process.
the Kettle Market selection – Found some cool products, all nicely showcased.
Brook Collection Hub – Positive first impression and I’ll be back to explore more.
Explore Pebble Deals – Very clean design and intuitive navigation made finding products effortless.
shop Market Whim – Nice variety makes exploring the products fun for anyone.
harborvendor.shop – Pleasant experience, everything loaded quickly and looked professional.
Ivory Trend Store – Enjoyed the clean interface and all products are easy to find.
Smyrna Festival Portal – The schedule is packed and the updates are clear and engaging.
your CedarCeleste hub – Products are easy to find thanks to an intuitive and clean layout.
Honey Market Marketplace – Simple navigation, product photos are very professional.
Lumvanta Boutique – User-friendly design and products are simple to find.
visit KnickNook – Sweet selection of goodies, I plan to come back and shop again.
CelNova Shop Online – Browsing is effortless, pages load fast, and checkout was seamless.
Coast Vendor Boutique – I plan on shopping here again, so it’s safely bookmarked.
curious shopper’s hub – Enjoy the rustic look, and site navigation is very user-friendly.
jewelvendor.shop – The images are crisp and have a professional quality.
Leaf Vendor Boutique – Good craftsmanship and the costs are fair.
North Vendor Spot – Very simple browsing, detailed product info makes shopping stress-free.
Best of Frost Vendor – Items match the description perfectly and payment was quick.
chiccheckout.shop – Checkout is easy and the layout keeps shopping simple and fast.
Lemon Crate Hub Online – Pricing is fair, products are nice, planning to shop again.
DepotGlow Collections – Quality is consistent, checkout was smooth, and the prices are great.
Chumba Casino: free coins, real wins, endless fun. Sign up today for your welcome chumba casino sweeps coins bonus and play the hottest games around. Join now!
the Mist Market selection – Interesting items and the checkout works efficiently.
browse Loft Crate – Clear and organized pages make the shopping process feel effortless.
online wharf finds – The look and feel are cozy, with items displayed in an appealing way.
Luster Collection Hub – Browsed the new uploads and enjoyed exploring the fresh items.
curated Xernita collection – Sharp images and categories arranged sensibly for smooth browsing.
Kovique Boutique Online – A sleek destination offering handpicked items for contemporary tastes.
Dapper Aisle – A sleek and modern shopping space offering refined selections for everyday style.
Gild Vendor – A polished online marketplace offering premium selections and curated deals.
Xerva Picks – The store is well organized, making product browsing a breeze.
Discover Zen Wharf – Lately, navigating the store has been straightforward and enjoyable.
official Lorvana site – Lots of appealing items that seem worth exploring.
Amber Select – Fantastic items available and the checkout process was seamless.
opalvendor.shop – Very pleased with the variety of products and smooth browsing experience.
check this marketplace – Everything is easy to find and the prices are appealing.
cormira.shop – The design is appealing and browsing feels smooth and enjoyable.
Pebble Vendor – A thoughtfully curated marketplace featuring compact yet impactful products.
Xolveta Shop – A fresh online destination focused on innovative products and smooth browsing.
Night Marketplace – Good assortment and fair prices make buying simple.
Browse Xerva – Store design is intuitive, so navigating items today was smooth.
OrbitCrate Online Shop – Very user friendly with quick page load times.
Smart Picks Cart – Amazing deals available and my order reached me very quickly.
modern Sernix store – Fast site performance makes shopping smooth and easy.
Go to QuickWharf – Checkout was straightforward and items came ahead of schedule.
curious shopper’s hub – Inviting layout, I’d happily return to explore more.
Explore Sorniq – A creative marketplace offering both distinctive products and daily essentials.
Browse Zintera – Quick load times combined with a neat and updated design.
Xerva Store – Really like the layout, browsing products today was simple and smooth.
discover Yorventa – The shop has a distinctive vibe that grabbed my interest right away.
Browse Joy Vendor – Quick, helpful support resolved my issue without any problems.
visit MerchGlow – Great assortment that made me want to explore further right away.
Melvora Online Shop – Modern interface and moving through product sections is smooth.
smart shopping spot – Fair prices and straightforward product descriptions help with decisions.
Aisle Whisper Corner – Really interesting items here that are worth taking a closer look at.
Ravlora Marketplace – Customer service was fast and resolved my concerns without hassle.
Cobalt Crate – A bold and reliable platform delivering standout selections with confidence.
Xerva Online – Clean and intuitive layout makes exploring items very straightforward.
Trend Choice – Simple navigation and clearly defined sections improve the shopping experience.
CraftQuill Storefront – Very happy with my purchase, items feel durable and well made.
Silk Vendor – A polished platform delivering quality finds with a touch of elegance.
official Value Whisper site – Products are priced well and descriptions are straightforward.
curated Quelnix collection – Navigation feels smooth, and the little layout details make a difference.
modern quill boutique – Nicely spaced sections make it easy to locate products.
Worvix Marketplace – Simple and efficient checkout with trustworthy payment options.
Timber Cart – A warm and grounded online shop inspired by rustic charm and practical choices.
Xerva Select – The interface is organized, making it effortless to check out different items.
Browse Farniq – Found stylish items online that perfectly fit my aesthetic today.
Shop at YarrowCrate – Helpful details made finding the right items a breeze.
favorite online boutique – Categories are cleanly arranged, making browsing easy.
favorite online boutique – Impressive assortment and browsing is smooth and fast.
Inqvera Collection – The user experience is polished and checkout moves along quickly.
Explore Irnora – Found rare products that I haven’t seen on other sites.
Gild Vendor – A polished online marketplace offering premium selections and curated deals.
Frost Aisle – A cool and refreshing store presenting crisp deals and clean design.
Xerva Choice – Layout is very user-friendly, and checking out products today was simple.
discover Quick Vendor – First look suggests reliability, and the cart process seems uncomplicated.
Visit the Ripple Aisle Shop – Attractive prices and crisp visuals make it simple to choose items.
stylish Birch Vista finds – Pleasant organization and a stress-free shopping flow.
Explore Silk Basket – Fair prices and impressive quality make shopping here enjoyable.
retarget shopping spot – Quite a few appealing items, I’ll drop by again sometime soon.
serverstash.shop – Excellent selection of tools, the layout is neat and easy to navigate.
the holvex website – Straightforward interface and tidy layout made browsing effortless.
Fintera Finds – Categories are clear, and navigating the site is easy and enjoyable.
Zarnita – A modern and distinctive platform showcasing unique items for curious shoppers.
Quick Shop Xerva – Love the design, navigating through products was super easy today.
Orqanta Essentials – A clean and efficient online shop showcasing standout items with ease.
zenvorax product page – Modern layout with smooth flow, browsing feels intuitive and quick.
itemtrail.shop – Support responded promptly and handled my issue without any hassle.
Nook Essentials – Clear, user-friendly layout ensures a pleasant shopping experience.
shadowshowcase feature page – Plenty of cool items, definitely a site I’ll revisit.
shop Yovrisa – First glance and the assortment of products is impressive.
GoodsQuarry Products – The lineup is varied and the rates look affordable.
RevenueHarbor shop online – A solid starting point for refining your online earning strategies.
kelnix collection – Interesting variety with each item seeming intentionally picked.
Acorn Treasures – Very neat and professional design, browsing items is quick and simple.
Smart Picks Cerlix – A sleek online destination built for convenient shopping and clear navigation.
Xerva Picks – The store is well organized, making product browsing a breeze.
Elegant Aerlune – A chic marketplace offering seamless browsing and tasteful selections.
Liltharbor Marketplace – Navigation is intuitive and products are easy to browse.
Velvet Stop – Smooth, secure checkout, perfect for newcomers making their first purchase.
Shaker Station Store – Wide range of products, easy to browse and find what you need.
browse keepcrate – Collection is well-structured and easy to navigate for quick access to products.
prenvia gallery hub – Smooth interface and fast page loads make product browsing straightforward.
revenueharbor resource center – Delivers concepts focused on strengthening recurring online earnings.
Everyday Amber – Pricing feels fair, and product details are presented clearly.
Shop Xerva – Nice layout, and exploring items today was very easy.
modern essentials store – The presentation is sleek and the details answer key questions.
Icicle Mart – A sharp and efficient marketplace focused on clarity and convenience.
Discover Wavlix – Selection is impressive and purchasing was straightforward and pleasant.
sheetstudio.shop – Sleek, modern designs with a polished look that really catches the eye.
JollyVendor Storefront – Fair costs and the process from cart to payment was seamless.
GarnetDock Online – Content is organized logically and flows nicely.
visit cometcrate – Fun and unique selection, items seem carefully handpicked.
Dapper Choice – Seamless process and overall pleasant shopping experience.
RyzenRealm online – Everything loaded nicely and the tech-centric style kept things interesting.
Discover Xerva – Layout is clear and shopping through items today felt smooth.
ShieldShopper shop online – Smooth navigation and secure presentation make exploring products easy.
Yield Mart – A practical and value-driven store offering rewarding choices every day.
WhimVendor Storefront – Dependable and efficient, I’ll come back soon for more.
NimbusCart picks – I had a seamless visit and completing my order took no effort.
Grenvia offers – Easy-to-navigate site with a quick and hassle-free checkout experience.
JewelAisle collections – I appreciate the organized design and the variety of items available.
MeridianBasket marketplace – Great assortment and pricing looks balanced and appealing.
discover Umbramart – Shopping felt effortless and everything loaded without delay.
briskparcel gallery hub – Smooth and secure checkout, shopping is fast and hassle-free.
Shop n Shine Store – Bright, appealing concept and products that look both stylish and budget-friendly.
check these discounts – I’m finding solid price drops that really help manage monthly spending.
MaplePick collections – Lots of options available and nothing seems overpriced.
quirkcove.shop – Unique vibe throughout the store, really stands apart visually.
Wenvix shop online – The purchasing process was quick, easy, and completely hassle-free.
Plumparcel specials – The simple design and easy-to-navigate categories made shopping enjoyable.
signalstation learning page – Useful marketing tips that are simple to follow and apply.
LagunaVend shop online – Visually appealing setup, products arranged in a modern, organized style.
seamstory.shop – A delightful assortment presented with style, I loved browsing through the pieces.
ParcelMint specials – Finding the right products was quick and effortless.
glenvox shopping corner – Smooth navigation paired with a secure and simple checkout.
Zestycrate picks – Products were fun to browse and checkout felt safe and easy.
RavenAisle collections – Found a few interesting items that I haven’t noticed elsewhere.
sitefixstation solutions hub – Troubleshooting tips are straightforward and simple to implement.
check these products – Nice variety, worth exploring again in the near future.
the search signal website – Informative content that supports realistic marketing improvements.
browse latchbasket – Plenty of interesting products, I’ll definitely return here.
Jaspercart deals – Fair prices and smooth ordering made shopping convenient.
QuillMarket shop online – Everything is laid out neatly and browsing the catalog is easy.
official sitemapstudio site – Clean and organized interface makes generating sitemaps effortless.
visit HollowCart today – I could move through pages smoothly and intuitively on my older device.
Dollyn picks – Customer support answered fast and solved my problem effortlessly.
stocklily shopping corner – Clear product visuals and helpful descriptive text make browsing simple.
ZephyrMart shop online – Clear layout and smooth browsing make finding items quick and simple.
socialsignal branding corner – Creative, up-to-date approach with lively and engaging marketing content.
official Harlune site – I received a prompt reply and the assistance was genuinely helpful.
seasprayshop deals page – Ocean vibes meet practical pricing in this curated selection.
discover BasketBerry – Support handled my inquiries promptly and professionally yesterday evening.
this shopping hub – Simple navigation with a clean, modern design feels very user-friendly.
Lemon Lane deals – Great mix of products and the browsing experience feels structured.
their shopping portal – Clean and stylish interface with professional-looking product visuals.
securestack.shop – Clean professional design, the emphasis on safety is immediately noticeable.
DahliaNest products – Listings are detailed, clear, and informative for anyone browsing.
Gildcrate online – Delivery was speedy and the product quality felt top tier.
WovenCart shopping hub – Shipping was quick and everything arrived in perfect order.
Serp Link Rise – Informative tips presented clearly, making search optimization approachable for beginners.
loftlark boutique – Easy navigation and intuitive interface ensure smooth browsing.
KettleCart catalog – The structure is clean and the product explanations are easy to read.
YoungCrate collections – I found the prices reasonable and aligned with what other shops offer.
Scarlet Crate Items – Minimalistic design and intuitive navigation make browsing enjoyable.
xarnova boutique – Carefully curated items and fresh branding give a reliable impression.
Werniq shop online – Payment was handled quickly and the process felt seamless.
Dorlix marketplace – A clean interface with a modern style, leaving a professional impression.
Quartz Vendor Hub – Navigation is seamless and all products are easy to access.
Indigo Aisle offers – Everything was enjoyable to explore and I’ll return again.
Official TerVox Site – Representatives responded quickly and provided useful guidance.
JetStreamMart essentials – Shopping here has been smooth, pleasant, and effortless.
Oak Vendor Collections – The website feels responsive and navigation is very easy.
Rackora Marketplace – The assortment is fantastic and the overall experience is easy and convenient.
Zen Online – The layout makes shopping pleasant, smooth, and efficient lately.
Brisk Harbor Essentials – Orders arrived promptly, and the whole experience felt easy and stress-free.
Urbanparcel Deals – Very easy to explore and the product range looks interesting.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Willowvend Home – Layout feels organized and moving through the site is effortless.
find Silver Vendor products – Checkout was effortless and I completed my order in no time.
Copper Aisle website – Quick to load and very easy to use on mobile devices.
Acornmuse Store – Enjoyed exploring the site, all items appear high quality.
TrendNook Collection – Fast browsing and products are shown in a very clear way.
For those seeking an exceptional online gaming experience, [maxispin.us.com](https://maxispin.us.com/) stands out as a premier destination. At Maxispin Casino, players can enjoy a vast array of pokies, table games, and other thrilling options, all accessible in both demo and real-money modes. The casino offers attractive bonuses, including free spins and a generous welcome offer, along with cashback promotions and engaging tournaments. To ensure a seamless experience, Maxispin provides various payment methods, efficient withdrawal processes, and reliable customer support through live chat. Security is a top priority, with robust safety measures and a strong focus on responsible gambling tools. Players can easily navigate the site, with detailed guides on account creation, verification, and payment methods. Whether you’re interested in high RTP slots, hold and win pokies, or the latest slot releases, Maxispin Casino delivers a user-friendly and secure platform. Explore their terms and conditions, read reviews, and discover why many consider Maxispin a legitimate and trustworthy choice in Australia.
MaxiSpin.us.com serves as a modern solution for content creators and marketers alike.
**Features of MaxiSpin.us.com**
The platform also includes a built-in editor, enabling on-the-spot adjustments for optimal results.
**Benefits of Using MaxiSpin.us.com**
MaxiSpin.us.com is cost-effective, delivering high-quality content at a much lower cost than traditional approaches.
Fioriq Styles – Came across fresh designs and the checkout system was very intuitive.
Listaro Online – Simple navigation and easy-to-read product pages make shopping smooth.
Night Vendor – Wide range of products and pricing feels reasonable for everyone.
Xerva Picks – The store is well organized, making product browsing a breeze.
Torviq Products – Discovered a few standout items while browsing the catalog.
Tiny Harbor Store – Found some excellent deals, will be checking back often.
Evoraa Marketplace – The layout is smooth and item descriptions are clear.
Visit Isveta – Came across this shop and was impressed by the range of items.
shop Wild Crate online – Pages load quickly and the layout feels fresh and well-organized.
liltstore.shop – Very smooth browsing experience and easy to find what I needed.
Slate Vendor online store – Navigation is intuitive and the browsing experience is very pleasant.
Inqora Products – User-friendly design with fast-loading pages.
Browse Yovique – Loved how fast the site is and how easily I could browse products.
Upcarton Products – I’m impressed by how fast and organized it feels.
Artisanza Collection – Attractive options in stock and the mobile version loads in seconds.
Shop at RoseOutlet – Products caught my eye and checkout was very straightforward.
Zintera Finds – Fast loading and a fresh, organized design make browsing pleasant.
Yolkmarket Store – Very easy and fast checkout experience today.
Xerva Curated – Clear layout and simple navigation make shopping enjoyable today.
Visit VioletVend – Smooth navigation and the products look attractive.
visit Stone Vendor shop – Customer service was prompt, friendly, and answered everything I asked.
Tillora Direct – Easy browsing and fast payment process.
Shop Parcelbay Online – Organization is excellent and placing my order was very fast.
Ulveta Store – Everything is clearly described and the website is easy to navigate.
Grain Vendor online store – Fair pricing and good craftsmanship is evident in the items.
QuartzCart Website – My search wrapped up quickly once I landed here.
Easy Carta Direct – Very user-friendly site and the payment process was hassle-free.
Official BasketMint Site – Site is responsive and browsing through product sections is simple.
Visit the OrderWharf Shop – Product info was informative and made decisions easier.
Ravlora – Support team was quick to respond and resolved my problem efficiently.
Ivory Aisle Finds – The support desk was responsive and provided all the information I needed.
Dervina Shopping – Wide selection available and pages load almost instantly.
Xerva Hub – Simple, neat layout makes it easy to browse products quickly.
visit Plum Vendor X – Clean design and well-organized sections make browsing effortless.
Shop at Harniq – Exactly what I wanted was available and checkout was seamless.
Shop at BloomTill – Pages load quickly and the site feels well-organized.
frentiq.shop – The products seem top-notch and completing my purchase was smooth.
Marketlume Deals – Many options and the website runs smoothly.
Wistro Direct – The product layout is user-friendly and completing checkout was a breeze.
Explore ZenCartel – Layout is tidy and modern, making the shopping experience enjoyable.
Worvix Online – Payment process was smooth and checkout went without any issues.
Thistletrade Hub – Sections are neatly arranged and navigating the catalog is effortless.
Quvera Selection – Pages load quickly and items are easy to locate.
Quickaisle Products – The site lists deals often and browsing is quick and easy.
Everyday Xerva – The interface is neat and makes exploring products quick and effortless.
Ruby Aisle Store – Navigation is intuitive and I can quickly locate what I need.
Discover Quistly – Nice range of products with a layout that’s easy to use.
KindleMart Deals – Lots of options to choose from and pages load in seconds.
Browse Walnutware – Products explained well, navigation is easy to follow.
Mistcrate Online Shop – Some unique finds here are worth taking a look at.
PureValue Deals – Creative and immersive website that inspires exploration.
Ebon Lane Picks – Fast-loading pages with a minimal and elegant design make shopping enjoyable.
Varnelo Products – Easy-to-read product pages and navigating the website is effortless.
Irnora Select – Hard-to-find items make this shop stand out from regular online marketplaces.
Irvanta Marketplace – Products look great and the cost seems reasonable.
Explore Xerva – Store design is clean and navigating products feels effortless.
Official Knickbay Site – Every listing includes comprehensive details that guide purchasing decisions.
giftmora.shop – Found some unique items, pages load quickly without issues.
Official Jarvico Site – Everything loads quickly and moving between pages is simple.
Spring Crate Selections – Smooth experience and easy checkout make this worth saving for later.
AisleGlow Store – Easy to move around the site and sections are clearly organized.
Cindora Collection – Simple interface with clear and accessible categories.
Kiostra Boutique – Pages load quickly and exploring products is very easy.
Shop at Mavdrix – User-friendly design, fast page loads, and easy buying experience.
Borvique Shopping – Modern interface with very clear and easy navigation.
Fintera Picks – Browsing through well-organized categories feels smooth and natural.
Zinniazone Store – Had fun exploring the website and coming across interesting items.
Explore Xerva – Store design is clean and navigating products feels effortless.
Hivelane Store – The simple interface and well-sorted categories make shopping pleasant.
Explore Volveta – Everything is well-laid out and locating products was simple.
check out Sage Vendor – Pages load fast and the interface feels trustworthy overall.
Find Lark Online – Very smooth navigation and items are easy to find.
Visit Ulvika – Helpful product details and smooth overall browsing experience.
Sovique Hub – Product browsing is effortless and costs appear fair.
LemonVendor Deals – It was a user friendly journey from start to checkout.
Shop at XoBasket – The menus are straightforward and browsing feels easy.
Wardivo Deals – Items are clearly displayed and moving through categories is easy.
Acorn Curated – Professional look with smooth browsing makes shopping stress-free.
Xyloshop Hub – Modern design and smooth mobile navigation overall.
Explore Xerva – Store design is clean and navigating products feels effortless.
Uplora Styles – The catalog is fun to navigate and pricing seems good.
EchoStall Webstore – Simple, organized pages with well-written product descriptions.
Shop Prolfa Online – Completing my purchase was hassle-free and payments were seamless.
IrisVendor Products – Speedy loading times and merchandise appears high quality.
Click for Clovent – Pages load instantly and the overall site looks fresh and modern.
Click Flarion – Smooth browsing and product details are clear and helpful.
Browse FernBasket – Items look durable and moving around the site is effortless.
KindBasket Deals – Products are attractive and the details are easy to read and understand.
Amber Select – Love how pricing is honest and product details are easy to read.
Discover Glentra – Seamless experience overall and the product information is very helpful.
Xerva Essentials – Browsing items is hassle-free with the clean and organized layout.
Discover FlairDock – Everything looks great and ordering is quick and easy.
Caldexo Boutique – Each item has clear explanations and is simple for shoppers to understand.
Softstall Store – Great variety of items and current prices seem very attractive.
OliveOrder Deals – Everything is well organized and navigation runs smoothly.
JunoPick Shopping – Items look great and purchasing was seamless.
XenoDeals Marketplace – Clean, structured site and finding products is straightforward.
Pentrio Shopping – The entire checkout experience was seamless and reliable.
Iventra Webstore – Pages load fast and finding products is effortless.
Dapper Select – Overall shopping experience was smooth and very satisfying today.
Xerva Marketplace – Nice, clean layout made browsing products today fast and easy.
serviq.shop – I’ll be returning soon to check out more items.
noblevend.shop – I’m saving this site to revisit for future purchases.
Merchio Store – I like the contemporary layout and the items look well-made overall.
shopping page – Moving between categories is smooth and everything feels well-planned.
Grivor Finds – Browsing was convenient and all features worked without problems.
this web store – Navigation is smooth, and the content is presented neatly.
Click for Elnesta – Site worked perfectly and finishing the purchase was easy.
Quinora Webshop – Browsing feels effortless and the design is very user-friendly.
VelvetHub Shopping – Bookmarking this for next time I need to shop online.
Olvesta Store – I’ll be coming back here when I’m ready to shop again.
Xerva Hub – Simple, neat layout makes it easy to browse products quickly.
Auricly Collection – Great looking items and navigation feels natural.
FlintCove marketplace – Found some nice items and prices are quite reasonable currently.
Zest Vendor – A vibrant shop filled with energetic picks and exciting discoveries.
featured website – I found the browsing experience refreshingly straightforward.
official storefront – The interface is simple yet functional, making navigation easy.
Visit Everaisle – I’ll be returning here next time I need to shop.
Discover Lormiq – Marked this website to return to for future orders.
official Larnix site – Browsing feels intuitive thanks to the clean and user-friendly design.
web resource – After looking around, I found the material genuinely informative.
visit workwhim – Clean design, fast browsing, very user-friendly.
wavento.shop – Pages load fast, navigation is intuitive and very user-friendly.
retail destination – The content seems thoughtfully prepared and relevant.
Up Vendor – A forward-thinking store built to elevate your everyday shopping experience.
Funnels & growth tools – Well-organized content and smooth browsing throughout.
Explore Birch Boutique – The interface feels polished and moving around is simple.
Click for Spice Craft – Logical layout ensures a smooth and efficient user experience.
Wardrobe Wisp Marketplace – Organized layout with intuitive navigation between sections.
trailtrekshop.shop – Very smooth browsing, pages load fast and sections are well arranged.
Yelnix online store – Navigation is user-friendly, helping me find items quickly and efficiently.
topic website – Clear presentation and meaningful updates make it informative.
visit this platform – Well-arranged sections make the content accessible and clear.
online retail site – Everything looks organized and easy to access.
ecommerce site – The platform performs flawlessly and responds immediately.
Discover Hyvora – User-friendly design and smooth overall experience.
Inbox Institute resources – Pleasant interface and the layout makes content easy to follow.
Kind Vendor – A friendly and thoughtful marketplace offering reliable and pleasant service.
Shop Soil and Sun – Tidy design and fast-loading pages make exploring simple.
Emporium Hub – Pages are logically arranged, making browsing simple.
Pot & Petal Official – Pages are clearly structured and finding what you need is straightforward.
Luggage Ledger Store – Content is easy to follow, and finding products is hassle-free.
DuneParcel specials – Really grateful for the quick replies and helpful guidance from support.
click for info – Pages are arranged clearly, making navigation smooth.
online boutique – Smooth navigation and tidy structure throughout.
direct shop link – Simplicity in design and clarity in content make this very user-friendly.
Leather deals store – The pages are organized logically and simple to explore.
Explore Heirloom Horizon – Clear sections and fast-loading pages for smooth browsing.
Gym Gear Junction Online – Simple design with organized content for easy navigation.
Shop Wardrobe Wisp – Pages are clear, fast-loading, and easy to explore.
Elevated Trend Space – A sharp and stylish platform aligned with today’s design sensibilities.
Interior Hub Online – Pages load quickly and information is easy to find.
Relvaa shop online – I enjoyed the easy checkout and flexible payment methods offered.
featured website – The layout is smooth, and finding content is effortless.
online shop link – Everything is presented clearly, making it convenient to find what you need.
this education resource – Navigation is simple, and the content is straightforward to access.
Explore Mint & Mason – Fast-loading sections and clear presentation make browsing easy.
Logo resources page – Structured pages and easy-to-read content.
this web store – The site flows nicely and everything is easy to access.
Ginger products online – Vibrant design and clear sections make it easy to explore.
Online revenue portal – Fast, intuitive navigation and neatly arranged pages.
Silk Online Hub – Layout is straightforward and content is easy to digest.
Shop Meadow – A peaceful shopping hub featuring handpicked items with natural appeal.
Zarniq online – My package arrived quickly, and everything was safely wrapped.
cutandsew.shop – Site loads quickly and the layout makes information easy to follow.
check this website – Fast loading speeds and seamless navigation stand out.
Visit Salt & Satin – Interface is tidy and all content is easy to access.
Shop Stream Sprout – Well-structured pages make moving through content enjoyable.
Explore Macro Merchant – Pages are structured neatly, creating a pleasant browsing experience.
digital storefront – The interface reacts fast and keeps the flow uninterrupted.
Investment portal – Organized content with easy browsing and clear sections.
Lotus Loft Official – Pages are well-organized, making navigation intuitive for all users.
Zolveta specials – Clear categories and straightforward design made finding products easy and quick.
product hub – Everything is well organized, and navigating feels effortless.
Item Whisper – A smart and intuitive platform helping you discover hidden gems with ease.
Culinary Marketplace Hub – Clear interface and tidy pages enhance the browsing experience.
ecommerce page – Everything feels intuitive and easy to navigate.
cider info page – There’s a real sense of character in the way it’s displayed.
Online thrift store – Well-structured pages and intuitive design make browsing enjoyable.
check this website – I like how clean and user-friendly the design feels.
Visit Finance Fjord – Pages are organized logically and browsing is effortless.
Sublime Summit Online Hub – Well-structured layout and professional presentation throughout.
DepotLark essentials – Each item has accurate, detailed information to help customers.
honeyandhustle.shop – Layout is clean and navigating through pages is effortless.
check this site – Smooth navigation and clear organization make browsing enjoyable.
monarchmosaic.shop – The layout is clean and navigating the site feels effortless.
festival overview – The site is easy to read, with all important info presented cleanly.
Explore Embroidery Eden – Smooth interface with neatly arranged content throughout.
click to explore – The overall setup feels coherent and accessible.
SEO Tools Portal – Simple structure and clear sections enhance the overall experience.
ecommerce site – The pages are tidy and it’s simple to find the information you need.
discover HazelAisle – The experience has been positive and browsing the site is a pleasure.
Click for Server Summit – Logical layout keeps navigation intuitive and fast.
this online store – Layout is clear, making it easy to explore all items.
Online filter store – Layout is clean and sections are easy to scan.
browse here – I liked how engaging and smooth the experience felt.
Fork & Foundry Store – Simple interface with well-arranged pages for smooth browsing.
direct shop link – Its overall feel comes across as new and distinctive.
Explore Kitchen Kite – Fast-loading sections make reading and navigating simple.
Click for Clean Cabin – Layout is straightforward and browsing is smooth.
Play DraftKings casino Casino delivers massive rewards. Get 500 bonus spins after $5 + up to $1K in day-one credits. Your jackpot journey begins!
email guide online – Pages are logically structured, making it simple to find information.
Click for White Noise Wonder – Content is well-arranged with a user-friendly interface.
check this site – Interesting layout and the articles feel creative.
Lifestyle fashion store – Smooth navigation and clean layout make exploring effortless.
ecommerce site – Browsing is effortless with fast-loading pages and a neat layout.
Design Driftwood Official – Navigation is smooth and content is clearly presented.
check this website – Sections are well-arranged, and moving around the site is effortless.
Supply Symphony Essentials Online – Impressive assortment and the interface is clean and simple.
Cotton Corner Resources – Well-organized sections make navigating the site smooth.
provencore.bond – Clean interface, site communicates reliability with clarity and confidence.
bloomvendor.shop – Such a pleasant browsing experience with lovely selections available.
engine insights – Easy navigation and well-laid-out pages improve the user experience.
Online chocolate shop – Clear sections and easy navigation create a pleasant experience.
Official Daisy Crate – The product assortment is solid, and placing orders is straightforward.
Visit Captain’s Closet – Shopping here feels seamless, with stylish finds available throughout.
Basket Wharf Outlet – The interface is simple, and browsing feels fast and smooth.
Stock Stack Products – Organized interface and fast, easy-to-read content.
showcase homepage – A nicely coordinated project with an easy-to-follow structure.
Shop Aurora Bend Online – The site feels polished and moving between sections is simple.
Meal Prep Storefront – Simple and clear design allows fast access to all content.
Check Out Products – Shopping feels easy and the site layout is clear and reliable.
tidalthimble boutique – Clean interface and navigating the catalog is easy.
retail destination – The interface feels friendly, and moving through the pages is effortless.
trustvector.bond – Organized visuals, messaging reinforces confidence and transparency.
Official Cherry Checkout Store – Navigation is intuitive and the checkout works seamlessly.
Prairie Vendor Direct – The clean design makes browsing simple and fast across the site.
Shop Merniva – A few items looked interesting, and the price points seem good.
Official Saucier Studio – The site showcases artistic and one-of-a-kind items beautifully.
Curated Online Market – Everything feels quick and the bargains are appealing.
visit this platform – Browsing is seamless, with easy-to-understand menus.
Workbench Wonder Collection – Practical items and descriptions are well-organized and informative.
Your Online Cart – Browsing feels effortless and the site is reliable and simple to navigate.
Amber Bazaar Deals – Found interesting products and pricing feels right.
product hub – Modern layout and well-structured pages make it enjoyable to explore.
jointventure.bond – Polished layout, content emphasizes alignment and collaborative problem solving.
Official Cherry Crate Store – Product photos are clear, and it’s easy to find what I need.
Lark Vendor Online – Found interesting items with clear guidance in their descriptions.
Zipp Aisle Boutique – Ordering items was hassle-free and very efficient.
workbenchwonder marketplace online – Products feel practical and all details are easy to understand.
Shop Trending Items – Browsing is effortless and descriptions help understand features and benefits.
calmcart.shop – Shopping is simple, convenient, and navigating the site feels effortless.
Formula Forest Products – The assortment appears carefully chosen, and transactions wrap up fast.
brisklet.shop – Navigation works perfectly and content is clear to read.
Shop Amber Outpost – Checkout went smoothly and pages open almost instantly.
trustline.bond – Well-organized interface, pages reinforce stability and professional communication.
this web store – Clean interface and well-organized sections make the experience effortless.
Winter Vendor Shop Now – I love how intuitive and fast navigation is across the website.
layoutlagoon – Really enjoyed browsing, the site feels well organized.
Your Go-To Shop – Browsing is easy, pages respond fast, and navigating the site feels intuitive.
Aurora Vendor Marketplace – Lots of options and finalizing purchases is easy.
Shop Calm Cart Online – Navigation is simple, and shopping overall is convenient and pleasant.
Varnika Deals – Categories are easy to follow and the layout feels intuitive.
Visit Silver Stride – Navigation is effortless and looking through items is enjoyable.
official storefront – The design is clean, and navigation feels intuitive.
linecrest.bond – Clean interface, content emphasizes reliability and a sense of modernity.
Amber Wharf Specials – Appreciate the clear interface and logically grouped product categories.
official sheetsierra site – Plenty of options and the checkout worked smoothly.
elmvendor.shop – The selection is high-quality and the prices feel fair at the moment.
Your Go-To Shop – Pages load fast and navigation is seamless and easy.
Visit Calm Cart – Overall experience is smooth, reliable, and easy to move through.
Xenonest Shop Now – Nice vibe overall and product descriptions make shopping easier.
Explore the Collection – New products appear regularly, and it’s enjoyable to browse everything available.
anchorbase.bond – Smooth navigation, content is approachable and emphasizes trust and security.
Inventory Ivy Specials – Each page offers descriptive content that supports smart buying.
shopping page – The site is structured clearly, and locating information is effortless.
wellnesswilds essentials – Soothing visuals and site browsing is simple.
apricotaisle.shop – Browsing is smooth and the product descriptions are very useful.
their shop page – Browsing is easy, and the design is intuitive and user-friendly.
Official Bay Crate Store – Quality products and clearly organized categories make shopping enjoyable.
Official Rooftop Vendor – Customer service was responsive and addressed my concerns expertly.
Explore Popular Products – Browsing is intuitive, convenient, and the shopping process feels seamless.
Soft Parcel Experience – Fast, smooth page loads make exploring the site effortless.
steadfastbond.bond – Professional interface, messaging conveys trust and a grounded user experience.
Discover Best Deals – Layout is easy to understand and the experience feels dependable overall.
Sample Sunrise Collection – Creative layout and content feels organized and approachable.
online retail site – The design is crisp and exploring the site feels natural.
Network Nectar Hub – Moving through the site feels natural and very fast.
Official Apricot Crate – The products look excellent and ordering is hassle-free.
Curated Collections – Navigation is effortless and products are easy to locate.
Your Online Cart – Browsing feels effortless and the site is reliable and simple to navigate.
Shop Cherry Vendor – Frequent updates make browsing the latest arrivals a pleasure.
Fetch Bay Online Shop – Ordering is quick and the clean interface makes browsing pleasant.
runroute – The design is clean and locating items is fast and easy.
solidbase.bond – Smooth layout, pages feel grounded and content is approachable and reliable.
jolvix.shop – Simple design but it definitely gets the job done.
shopping page – The layout flows well and browsing feels natural.
Network Nectar Experience Hub – The site layout is intuitive and every page loads without noticeable delay.
Your Go-To Shop – Easy to move around, reliable site, and overall shopping is stress-free.
Premium Online Store – Customer service is approachable and responds fast.
Shop the Collection – Moving between sections is seamless and responsive.
Tally Cove Online Shop – Smooth and easy-to-use layout makes every visit enjoyable.
Order Grove Shop Now – Product range is impressive and searching for items works effortlessly.
tagtides corner – Great branding and navigation feels effortless.
tobiasinthepark curated shop – The atmosphere is lovely, every detail seems carefully thought out.
reliablesource.bond – Clean interface, messaging emphasizes steadfastness and professional presentation.
Feather Crate Store – The layout is clean and navigating through products feels easy.
Dew Dock Store – Smooth navigation and tidy presentation made it easy to check items.
ecommerce site – It’s simple to navigate, and the presentation is pleasing to use.
fireflymarket deals – Well-organized sections make it easy to locate products quickly.
best of frostdock – Clear structure with smooth browsing makes shopping easy.
Find Exclusive Items – Smooth navigation and a convenient layout make shopping effortless.
Jade Aisle Online Shop – The range is attractive and prices feel balanced for quality.
calmcrate.shop – The site has a clean layout and I could find products without any hassle.
Official Maple Vendor – The product assortment is solid and photos are detailed and helpful.
Supply Symphony Collection – Nice variety overall and navigation is user-friendly.
Acorn Crate Boutique – Smooth performance and clear navigation make using the site enjoyable.
Visit Ash Wharf – There’s plenty to choose from and the site feels warm and friendly.
gladegoods collection – User-friendly design makes navigating the site straightforward.
browse harborwharf – Organized sections allow for smooth product browsing.
bridgecapital.bond – Clean and approachable, messaging emphasizes trust and easy navigation.
furkidsboutique outlet – The items are charming and browsing felt smooth and enjoyable.
online library – Scanned the pages and the content is easy to digest and well-organized.
featherfind online shop – Easy-to-use layout and smooth page transitions make exploring quick.
fireflyvendor featured – Well-structured layout and fast-loading pages make browsing easy.
driftaisle marketplace – Neat structure and accessible design make it easy to check products.
Your Online Cart – Browsing feels effortless and the site is reliable and simple to navigate.
Discover Best Deals – I enjoy browsing the newest products and seeing updates posted frequently.
frostgalleria store – Smooth interface and clean design make exploring items easy.
Harbor Lark Boutique – Browsing is quick and smooth on phones and tablets alike.
Alpine Aisle Experience – Every visit is simple, pleasant, and reliably smooth.
glimmercrate treasures – Easy-to-use design makes finding items a breeze.
Shop at BloomVendor – Whenever there’s an issue, the team reacts in a reassuring and professional way.
harborwharf store – Clean interface and easy navigation make browsing enjoyable.
Trending Items Hub – I enjoyed reviewing the options and spotting something different.
coralmarket online – Found several great options and checkout moved along fast.
feathervendor outlet – Tidy pages and intuitive navigation make browsing easy.
Flake Crate Online – Well-organized layout makes browsing effortless.
official garnetcrate – Browsing is effortless, and products are clearly presented.
driftcrate featured picks – Well-laid-out pages and straightforward navigation make finding items simple.
glowgalleria picks – Smooth experience, with all categories clearly arranged for browsing.
Check Out Products – Wide variety with simple navigation makes finding items effortless.
harborwharf selections – Simple design and logical layout make exploring quick.
Gold Vendor Deals – The brand image feels trustworthy while still being inviting.
cottoncounter fashion picks – Everything was arranged logically and moving around the site was quick.
<Top Picks Online – Browsing feels secure and pleasantly simple.
flakefind outlet – Simple structure and neat sections make shopping effortless.
fernaisle web store – Easy-to-use design and clear structure make shopping pleasant.
garnetgoods finds – Neat pages and clear presentation make finding items simple.
shop goldenvendor – Items are well organized and the site is simple to navigate.
online jaspervendor – Came across this page, looks like a tidy and simple site for browsing.
iciclemarket – Just discovered this store today, products look interesting and worth checking.
driftwharf style store – The showcase feels well planned and the descriptions are informative.
harborwharf market – Neat structure and clear visuals make finding items effortless.
Discover Best Deals – Fast and helpful customer service made the whole experience smooth.
lemonloft page – Website feels clean and smooth, user-friendly for browsing.
this resource – Just discovered this site and moving through it feels easy and clear.
browse this page – Came across this site, the structure feels clear and accessible.
cottoncrate homepage – Straightforward browsing helped me get what I came for.
flintcrate online shop – Clean design and well-laid-out pages make browsing easy.
browse this page – Came across this website, everything feels tidy and well-structured.
fernfinds deals page – Everything loads quickly and the layout is intuitive.
graingalleria picks – Easy to navigate and items are clearly displayed.
garnetmarket finds – Fast-loading pages and clear presentation simplify browsing.
jewel marketplace – Appears to be a clean and simple platform for exploring products.
discount corner – Appears to be a page where deal hunters could find something useful.
harborwharf browse – Fast-loading pages and structured layout make shopping simple.
visit duneaisle – Easy-to-navigate design and neat layout make finding products smooth.
take a look – Discovered this site earlier, browsing through it feels effortless.
linencrate – Came across this earlier while browsing and it actually looks pretty practical.
useful link – I ran into this site today, navigating items feels simple and fast.
interesting spot – Just visited this website, interface feels clean and user-friendly.
Explore the Collection – Navigation is simple and finding items feels quick and easy.
cottonvendor outlet – Products look sturdy and the text explains features clearly.
Flint Folio Online – Everything is neatly displayed, making it easy to find what you need.
grainmarket hub – Organized structure ensures browsing is effortless.
useful link – I ran into this website today, layout is organized and easy to follow.
fernvendor web store – Everything feels organized and navigating pages is straightforward.
gildaisle essentials – Smooth pages and straightforward shopping experience.
look at this store – Found this platform today and browsing products feels easy.
harborwharf essentials – Clear structure and tidy presentation simplify exploring products.
visit indigohub – The page feels simple and smooth to navigate today.
see this website – Came across this site today, seems like a good and stable platform.
see this site – Happened to run into this and the layout feels straightforward.
recommended page – Found this link today, navigation is smooth and layout is clean.
simple shop – Found this site today and the browsing experience feels straightforward.
Flora Finds Online – Well-organized pages and smooth browsing improve the experience.
granitecrate online – Clean presentation and logical layout make shopping convenient.
official covecrate site – The theme stands out and the items look carefully chosen.
fernvendor style store – Neat structure and clear product listings make browsing effortless.
juniper deals hub – Navigation feels simple thanks to the tidy layout.
Find Top Products – Categories are tidy and product details are informative and helpful.
check this site – Found this link today, exploring items seems smooth and straightforward.
gildcorner finds – Smooth browsing with clear layouts for all items.
check this vendor site – Ran into this website while searching around and it looks interesting.
harborwharf online shop – Smooth interface with organized content makes browsing enjoyable.
take a peek – I discovered this link today, the layout feels clear and easy to explore.
this resource – Discovered this platform, navigation seems simple and browsing items is quick.
interesting website – Just found this link, the site is easy to navigate and user-friendly.
link worth seeing – Came across this website and the clean layout stands out.
floravendor hub – Clean design and easy navigation enhance the overall experience.
granitegoods online – Everything is neatly arranged, making shopping simple and enjoyable.
creekcart featured picks – The site is responsive and content shows up fast.
juno crate corner – Looks like a clean layout and easy to browse.
fieldfind collection – Well-arranged layout makes browsing products easy.
gingergoods hub – Fast-loading content and tidy layout improve the shopping experience.
recommended page – Found this link today, layout is clean and browsing feels simple.
easy crate store – The page layout feels organized and user friendly.
harborwharf hub shop – Logical navigation and clear visuals make exploring products effortless.
cool platform – Came across this store, the browsing experience feels smooth and organized.
quick browse – I discovered this page earlier, the layout makes browsing easy and convenient.
harborbundle store – Clean presentation and well-structured pages make shopping easy.
forestaisle – Enjoyed checking out the items, everything feels thoughtfully arranged.
this site – I came across this earlier and the simple design feels easy on the eyes.
check juno hub – Stumbled on this page, seems like a straightforward website.
creekcrate collection – Easy-to-use design helps me quickly spot the products I want.
finchmarket deals page – Clean pages and fast loading make it simple to browse.
ivory market shop – Everything on the page seems neatly arranged and easy to check out.
take a peek – Discovered this link today, browsing items is convenient and easy.
visit gingervendor – Well-laid-out pages make finding items simple and stress-free.
harborwharf essentials – Clear structure and tidy presentation simplify exploring products.
visit here – Ran into this website recently, navigating items is straightforward and convenient.
see this shop – Came across this website, navigation seems simple and exploring products is quick.
harborwharf outlet – Easy-to-follow structure makes finding products fast and simple.
online store – Noticed this site today, layout is minimal and items are easy to find.
forestvendor showcase – Organized pages and smooth interface create a pleasant shopping experience.
quick juno shop – The site feels organized, making it easy to browse through products.
this page here – Spotted this website earlier and the layout feels easy to follow.
jade crate store – This place looks like it might have a few unique things to check out.
this platform – I noticed this site while searching and everything looks well arranged.
creekvendor style store – Positive first impression, very structured and easy to navigate.
fireflyfind deals page – Organized sections and simple navigation make browsing quick and easy.
gladecrate showcase – Smooth scrolling and clear product layout make exploration simple.
harborwharf online finds – Organized layout with fast navigation makes browsing easy.
this platform – I noticed this page while searching, layout is clean and browsing is easy.
check this site – Found this link today, navigation feels smooth and practical.
online kettlecrate hub – The page appears organized and pleasant to navigate.
jadevendor – Nice little website, seems easy to browse through the products today.
take a look – I discovered this page earlier, browsing through it feels effortless.
this resource – Discovered this link earlier and the site feels comfortable to explore.
recommended page – Found this link today, layout is organized and browsing items feels simple.
quick shop – Came across this site, layout looks clean and browsing items feels simple.
check this site – Found this link today, the layout seems tidy and user-friendly.
link worth checking – Stumbled on this page today, layout feels simple and well-structured.
jasperjunction hub – Found this website earlier, looks like a solid site for shopping online.
take a look – Discovered this online and it seems like a good site to browse.
tinytill.shop – I’ll be saving this site to revisit for upcoming purchases.
visit tundrarack – Found this store today and the items seem organized and easy to explore.
this platform – I noticed this site while searching, the interface is clean and accessible.
this resource – Ran into this page, it feels organized and easy to move through.
jasper market corner – Seems like a neat site for browsing multiple product options.
wickercrate – Just came across this shop earlier and the items seem quite interesting.
browse here – Found this site while browsing and it seems easy and intuitive.
Evoraa Specials – Website runs well and product pages are simple to understand.
quick shop – Came across this site, interface feels organized and exploring products is effortless.
visit here – Ran into this page recently, navigation feels effortless and straightforward.
open the vendor hub – I discovered this page today and the navigation felt really straightforward.
wickervault – I stumbled onto this site earlier and the layout feels clean and simple.
cool platform – Found this while browsing and the layout feels organized and simple.
Click for VioletVend – Navigation is straightforward and products are eye-catching.
take a look here – Stumbled on this marketplace today and navigating the catalog is smooth.
Honey Corner Online – Clear design and browsing pages was straightforward.
Rain Bazaar Hubspot – Organized layout, moving around the site is easy.
Meadow Finds Hub – Neatly arranged pages, navigating the site is effortless.
apricotvendor – Just discovered this site and the pages load quickly with a clean layout.
visit the shop – Stumbled on this website earlier and it appeared to be a decent place for sourcing items.
Discover this platform – A thoughtful website designed to spark curiosity and encourage fresh inspiration.
rubyvendor – Found this site earlier, layout seems organized and easy to navigate.
Vendor House Rain – Well-structured design, moving through sections feels effortless.
Icicle Storefront – Neatly structured pages make browsing simple.
Mint Marketplace – Pages are neat and organized, exploring the site feels natural.
this crate website – I checked this site earlier and the design looks clean and minimal.
valetrade – Came across this platform today, browsing feels straightforward and intuitive overall.
marketplace here – Stumbled on this website while looking around and it seems solid.
kindlemart.shop – Great range of items and the site loads incredibly fast.
Raven Lane Picks – Clean and organized layout, browsing the website is simple.
Mint Market Hub Studio – Layout feels tidy, moving through sections is natural.
take a peek here – Found this website while exploring and the clean layout makes navigating easy.
Icicle Selection – Pages are neat and moving around is very simple.
Open this shop – A small but pleasant store where the layout keeps everything easy to locate.
sagecorner shop – Found this site, navigation is smooth and exploring products is straightforward.
Browse AisleGlow – Well-arranged categories and a user-friendly navigation system.
supply warehouse – I browsed it briefly and everything loaded nicely on my phone.
River Outlet Studio – Friendly and neat layout, navigating through the site is smooth.
Go to Valleyvendor – Discovered this website and it seems well arranged and easy to move around.
bazaar hub online – Just landed on this page and everything feels easy to explore.
Moon Hub Corner – Pages are tidy, exploring the site is effortless.
Ivory Bazaar Hub – Very tidy layout, browsing the site feels effortless.
Discover the thrill of real-money live casino action at [url=https://maxispin-au.com/]live casino welcome offer[/url], where you can enjoy live dealers, top software providers, and exclusive promotions.
Helpful guides and clear menus minimize friction when users search for content.
Explore Ulvika – Product explanations are helpful and the site feels intuitive.
inventory vault – I opened the site today and it appears neatly organized.
Rose Vendor Market – Well-arranged sections, navigation is intuitive and quick.
See the Velvetvendor page – Noticed this platform; navigation is clear and convenient.
this vendor hub – Found this site today and moving around the pages is really easy.
sage crate online – Just visited this site, layout is tidy and browsing feels effortless.
Moss Central – Organized pages make exploring smooth.
Vendor Outlet Ivory – Well-structured pages make browsing straightforward.
IrisVendor Online – Smooth loading experience and products seem durable and refined.
Rose Studio Picks – Well-arranged sections, exploring the site feels effortless.
inventory crate – I visited the site briefly and the categories appear well arranged.
Browse the market – Recently found this website and the interface keeps navigation easy.
vendor marketplace – Just noticed this page and the navigation is smooth and clear.
Moss Picks House – Smooth interface, moving between sections is easy.
OliveOrder Deals – Everything is well organized and navigation runs smoothly.
Vendor Studio Jasper – Pages are well-arranged, browsing sections is simple.
Ruby Studio Hub – Neat and organized layout, moving across pages is smooth.
Browse this vendor – Recently came across it; the interface is organized and smooth to use.
shop satinrack – Just checked this site, interface looks tidy and navigating products is simple.
warehouse link – Stopped by the page today and everything loaded quickly.
go to this vendor hub – Stumbled upon this site and everything loads smoothly with a clear structure.
Night World Market – Clear organization, moving through pages is natural.
Elnesta Specials – Website functions well and ordering was fast and simple.
violetmarket – Came across this store, navigation looks clean and intuitive overall today.
Sage Studio Hub – Friendly interface, browsing sections is easy.
Jewel Shop Online – Smooth pages, browsing content is comfortable.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.com/zh-TC/register-person?ref=DCKLL1YD
visit the vendor page – Found this site by chance and browsing feels smooth and clear.
crate store link – The website is tidy and flipping through pages feels easy.
Opravdovalekarna.cz – kde se kvalita nepotkava s vysokou cenou
https://opravdovalekarna.cz
TinyTill Online – Saving this for later, I’ll shop here again.
Oak World Outlet – Clear structure, moving through the website is easy.
Sage Hub House – Clean and simple design, moving around feels effortless.
check out this site – I noticed this page today and the design appears organized and smooth to explore.
Jewel Finds – Smooth pages, exploring the site feels effortless.
browse coral aisle hub – Found this page earlier and the structure makes exploring effortless.
this vault site – Discovered this today, and the details provided seem helpful.
this page – Everything is organized clearly and clicking through feels smooth.
Olive Hub – Tidy structure, navigating the site is straightforward.
browse coral crate hub – Found this page earlier and everything seems organized and easy to explore.
Juniper Stop – Clean pages, navigating through sections is easy.
online vendor store – Just spotted this page and the shop layout seems tidy and organized.
Olive Stop Studio – Simple and clear pages, exploring content is smooth.
check it out – Just explored it and the page design looks quite clear.
cotton hub online – Found this site and moving around it feels simple and natural.
Kettle Marketplace – Pages are organized neatly, moving between sections is easy.
vault info page – Clean design and logical arrangement of content throughout.
Opal Depot – Clear navigation, moving through sections is natural.
check this site – Clean design overall and moving through sections is effortless.
browse this vendor platform – Came across this page earlier and the structure is simple and practical.
Lantern Hub Online – Well-arranged sections make navigating easy.
see this shop – Just discovered this site and it seems nicely arranged for checking items.
market resource page – Stumbled upon this online, looks like a good source of information.
crystalvendorcorner – Just visited this site and browsing feels smooth with a polished layout.
Opal Market Hub Vault – Cleanly structured pages, browsing the site is comfortable.
silvervendorstudio – Stumbled upon this site, and navigating through pages is smooth and simple.
Vendor Outlet Lantern – Well-organized structure, moving between sections is smooth.
woodwarehouse – Found this online today, and it seems like a trustworthy site.
open this vendor hub – Came across this website today and navigating it feels natural and simple.
Orchard Treasure Hub – Clean design, browsing feels effortless.
view the shop – The site feels organized and moving between sections is quick.
seashopper online shop – Just discovered this store and the design feels tidy and easy to check out.
Lavender Studio Hub – Well-structured pages, navigating sections is simple.
online warehouse hub – Quick loading times and a clean interface make browsing easy.
marketplace online – Just noticed this page and browsing feels smooth and straightforward.
Pearl Vendor Corner – Well-organized design, browsing the site feels comfortable.
look at keystonecrate – Seems organized and user-friendly for visitors.
online bazaar – The site feels organized and navigating through pages is simple.
browse zephyr vendor – Discovered this page, seems promising and well-organized.
dunevendorstore – Just visited this site and the layout is tidy with easy-to-follow navigation.
quick browse – I discovered this site earlier, interface is practical and items are simple to find.
keystonehub – Just exploring this site now, feels easy to navigate.
online market link – I noticed this site recently, and browsing items seems simple and smooth.
Pebble Mart – Well-organized pages, navigating the site is easy.
visit online – The pages feel tidy and moving through them is seamless.
Lemon Finds – Simple interface, exploring content is easy.
this online vendor hub – Ran into this page today and navigating it feels calm and effortless.
online spot – Just found this page, navigation is effortless and products are easy to browse.
Pine Hub – Tidy structure, navigation feels straightforward.
check the vendor – The interface is clear and the pages feel easy to navigate.
Linen Depot – Pages are tidy, moving through content feels smooth.
vendor marketplace online – Just noticed this page and moving through it is simple and convenient.
see this store – I checked this website recently and the interface seems simple and convenient.
quick browse – I found this website earlier, interface is clear and products are simple to find.
velvet marketplace studio – Enjoyed scrolling through, everything looks neat and accessible
check the vendor collective – The platform feels approachable with clear navigation
echoharborvendorplace.shop – Nice little marketplace, pages load quickly and feel easy today
see the platform – Found this site, pages load quickly and everything is easy to follow
Plum Vendor Picks – Clear structure, exploring the site is easy.
see the site – Clear structure and fast loading make browsing enjoyable.
Maple Market Hub – Layout feels tidy, navigating sections is easy.
visit ember market lane – Came across this page today and navigating feels smooth and effortless.
official shop page – Looked around the marketplace and the layout appears pretty polished
visit here – Noticed this page recently, everything seems tidy and convenient to explore.
birch sellers district – The marketplace looks organized and easy to explore
browse the violet bazaar – The pages load nicely and the interface is welcoming
discover this marketplace – Navigation works nicely, layout is simple to understand
check this page – Stumbled upon this site, sections are clear and pages are organized
official page – Came across this page, layout looks clean and easy to follow
TrailEmporiumDeals – Took a quick peek, already seeing some sections that stand out.
check seavendoremporium – User-friendly platform with clearly arranged sections
Quartz Hub – Nice simple layout, moving through the pages feels easy.
Maple Outlet – Tidy design, navigating pages is comfortable.
take a look here – Found this store today, and navigating the sections seems simple and intuitive.
view their products – The pages load smoothly and the navigation feels natural
visit the crate – The design is minimal and navigating feels smooth.
vendor portal link – Layout is clear, moving between sections is simple
this vendor place page – Browsed the site and everything feels organized and easy to follow
site I found – Just discovered this platform, navigating products feels simple and smooth.
open this vendor marketplace – Overall design is neat and moving through the site is easy
shop homepage link – Content is accessible, pages load fast, and browsing is effortless
explore platform – Noticed this site, structure is well arranged and browsing is effortless
UplandMarketSpotlight – Skimmed through, the interface feels practical and easy to navigate.
quick link – Found this platform, browsing is smooth and intuitive throughout
take a look – Everything loads nicely and the layout is user-friendly.
glassvendorworkshop.shop – Pleasant browsing experience, pages load fast and design feels neat
browse here – Came across this platform recently, exploring items is quick and intuitive.
wild marketplace hub – The site is creative, tidy, and easy to explore
quick shop access – Interface is simple, and navigation is smooth
UplandRiverPortal – Browsed casually, the pages feel simple and easy to navigate.
embermarketstudio.shop – Really enjoyable site, design is neat and navigation works well
silvermarket store – Ran into this website today, and navigating it seems smooth and straightforward.
visit this marketplace – Explored for a few minutes and the layout is really clean and easy to use
Marble Hub Online – Well-structured pages make moving through content smooth.
official vendor emporium link – Enjoyed a quick look, everything feels accessible and clear
purevalueoutlet – Inspiring and interactive site, perfect for learning and creating new ideas
Meadow Quick Depot – Simple interface, browsing between pages is comfortable.
explore silk vendor pages – Simple design, everything feels logical and clear
wood vendor marketplace – Quick loading pages make browsing simple and enjoyable
browse vendor listings – Navigation feels intuitive, and content is well organized
this resource – Ran into this page earlier, navigation is smooth and browsing feels convenient.
VendorFinderValeBrook – Took a peek, the platform feels organized and approachable.
browse today – Checked this platform, layout feels organized and user-friendly
discover this shop – Layout is simple, and finding items is quick and easy
browse today – Found this platform, navigation is smooth and content is clearly arranged
brimstone vendor hub – Quick navigation with clearly separated categories
vendor studio homepage – First time here and the layout looks simple to navigate
HubMarketplaceVale – Checked some pages, the site feels clean and well-laid-out.
discover products online – Sections are structured well, making browsing effortless
silverbrookvendorhub.shop – Nice website here, definitely planning to explore more later
check this out – Found this platform today, navigating products feels smooth and intuitive.
this silvershopper store – Stumbled upon this site and the interface feels tidy and easy to explore.
official page – Browsed this marketplace, structure is clean and navigation is smooth
browse today – Ran into this platform, navigation feels effortless and intuitive
quick shop access – Just checked it out, layout is simple and intuitive
this vendor hub page – Browsed through the site, everything is neat and organized
VelvetMarketplace – Skimmed some sections, the layout is tidy and intuitive.
official vendor workshop page – Gave it a quick visit and scrolling around on my phone works fine
see items online – Pleasant browsing experience, sections feel clear
this resource – Ran into this page recently, navigation is simple and browsing feels effortless.
granitevendoremporium.shop – Interesting marketplace, sections are easy to navigate and look organized
silvergrovevendorhouse.shop – Everything looks organized well, browsing through posts feels smooth
view their products – Pages are clear, and moving between categories is straightforward
explore studio – Found this platform, navigation feels smooth and sections are organized
this vendor collective page – Browsed around, everything is organized and user-friendly
HubMarketplaceVelvet – Checked some pages, everything feels clean and user-friendly.
seller place link – Checked several parts of the site and it’s easy to move around
explore the shop – Very user-friendly interface and everything feels intuitive
quick browse – Just discovered this page, interface is clean and browsing items feels effortless.
harborcratecollective.shop – First impression good, site design feels friendly and user oriented
skycrate website – I checked this store earlier, and moving through sections is straightforward.
woodvendor emporium online – Clean layout and easy to navigate, worth a visit.
product catalog link – Layout is clean, and moving between pages is simple
flintvendorworkshop.shop – Good browsing experience, layout is clean and simple to navigate
VioletDealsHub – Browsed lightly, sections are easy to find and clear.
discover yelvora hub – Interesting shop name, looking forward to checking products.
seller studio link – Pages are clear and moving around is straightforward
silvervendor online pages – Enjoying the content, everything is well organized
see carameldock shop – Pleasant design, navigation is simple and user-friendly.
raincrestvendorplace.shop – Just browsing casually, but already noticing some useful information here
alpine vendor hub store – Looks like a neat shop and the page layout is organized
learn more here – Checked this hub, pages load fast and structure is very user-friendly
browse here – Found this page recently, interface is organized and exploring items is simple.
VendorFinderViolet – Looked around, the platform is well-structured and intuitive.
direct shop access – Layout is tidy, and the site feels well structured overall
explore zenbrook marketplace – Took a brief look, vendors look promising and interesting.
tap here – Found this page, everything is well arranged and easy to browse
explore cedarvendor shop – Straightforward interface, browsing was hassle-free.
kestrelcrate.shop – Cool name for a shop, curious what products appear soon.
open the vendor workshop – Sections are clean and moving around is smooth
visit rain vendor – Layout is clean and easy to navigate through
hazelvendorcollective.shop – Good platform, browsing feels effortless and everything looks neat today
amberstone marketplace studio – The site appears to offer helpful insights
skyridge vendor pages portal – Layout is user-friendly, very easy to browse
go to slatecrate – Ran into this site today, and the layout appears clean and effortless to browse.
this resource – Just checked this page, layout is clear and navigating items is easy.
VendorPlaceWalnutCrest – Took a quick look, everything seems organized and approachable.
marketplace homepage – Navigation is effortless and the site looks neat and inviting
discover cedarwharf hub – Unique branding, definitely stands out among other stores.
discover here – Came across this vendor hub, pages are logical and simple to browse
zenvendorcollective.shop – Nice marketplace concept, looking forward to seeing more sellers join.
hiveloft portal shop – Easy to navigate, browsing experience was seamless and quick.
discover now – Found this platform, pages are clean and easy to navigate
visit ravensage collective – Nice design, navigation feels effortless and smooth
open the vendor place – Layout is logical and finding items is simple
open reedmarket shop – Simple and tidy, navigation feels smooth.
visit amber vendor collective – Took a look and the items are easy to browse through
Pure Value Market – Smooth navigation, learning and exploring was effortless.
sky vendor online hub – Information is clear, design feels simple and neat
WalnutMarketplace – Skimmed a few sections, the layout is tidy and simple to navigate.
cool marketplace – Found this platform recently, navigation feels straightforward and browsing items is simple.
check this marketplace – First impression excellent, pages are easy to navigate and well arranged
discover cherryaisle online – Playful branding, the store looks welcoming and easy to navigate.
visit the hub – Came across this site, design looks tidy and navigation feels smooth
explore platform – Noticed this site, layout is clean and browsing is effortless
raven platform – Pages are intuitive and content is easy to browse
browse seldrin online – Short and catchy, makes remembering the shop effortless.
see the vendor collective site – Smooth browsing and well-laid-out pages make navigation pleasant
digitalbuyingexperience.click – Pages load quickly and the layout makes moving around the site effortless.
apricotstone sellers house – Found this site by chance and it seems worth checking
open reedmart online – Sleek design, categories are easy to browse.
WaveVendorSpotlight – Browsed a bit, sections are tidy and readable.
Summit Collections – Organized layout, navigating sections was effortless.
check clovervendor marketplace – Nice concept, could become a favorite for buyers.
shopping portal link – Looked around quickly, interface is simple, modern, and user-friendly
explore here – Noticed this marketplace, content is clear and sections are tidy
snow crest online collective – Overall a solid platform, very easy to browse
riverstone vendor shop – Browsing is simple and design looks professional
online collective – Browsed this site, design is minimal yet intuitive
this queltaa site – Creative branding, eager to see upcoming additions.
visit this vendor shop – The page design is clear and comfortable to read
chestnut sellers hub – Layout is tidy and moving around feels intuitive
check ridgecrate store – Tidy layout, made finding items quick and straightforward.
visit digital buying experience – The site runs smoothly and it’s very easy to navigate through.
a href=”https://wavevendoremporium.shop/” />VendorHubWave – Took a glance, the content is clear and structured.
go to site – Noticed this hub, layout is modern and navigation is effortless
visit coastcrate store – Clean structure, categories are simple to explore.
see their products – Navigation is intuitive, and the site looks polished and organized
Sun Corner – Clean design, moving between pages felt seamless.
check river emporium – User-friendly design, everything is simple to access
snow vendor studio – Simple navigation and well-presented information
check this page – Came across this platform, pages load quickly and layout is clean
aurorabrook vendor platform – Opened a few pages and they load very quickly
browse harbor pick – Layout is clear, moving through pages is effortless.
chestnut vendor center – Browsing is smooth and categories are easy to follow
WheatVendorCenter – Checked some pages, everything is well-arranged and readable.
check ridgemart hub – Clean and approachable, shopping felt smooth and easy.
see smart consumer hub – Looks useful for browsing products, planning to return soon.
quick link – Checked this hub, pages load quickly and design is user friendly
check coppermarket marketplace – Friendly and approachable name, encourages exploring further.
visit the vendor hub – Took a quick look, sections are organized and easy to navigate
Teal Finds – Simple and attractive, exploring products was easy.
rose vendor online – Pleasant experience, reading and browsing is easy
open this vendor marketplace – Everything seems nicely grouped and simple to navigate
explore vendor lane – Came across this platform, everything is logically arranged and easy to follow
HubVendorWheatOnline – Checked some sections, everything looks organized and readable.
open uplandvendor hub – Good marketplace idea, planning to revisit soon.
this online cloudbrook hub – Navigation feels natural and browsing is pleasant
solar vendor studio portal – Very practical site, browsing feels effortless and organized
explore riverretail – Clean layout, browsing items felt smooth and effortless.
browse daisyaisle portal – Cheerful store presentation, makes finding products simple.
quick link – Came across this marketplace, layout feels simple and intuitive
see this global store – Surprisingly simple layout considering the big name.
quick shop link – Just visited, interface is neat and browsing feels intuitive
check rose collective – Well-structured platform, reading and navigation are intuitive
WildSelections – Took a glance, the layout is clear and intuitive.
Teal Gems Hub – Clean and approachable, browsing items was convenient.
autumn crate vendor page – The exchange style makes the platform stand out
explore vendor hub – Came across this platform, everything is structured and intuitive
discover blossom crate – Friendly and inviting name, feels very approachable.
vendor collective homepage – Sections are easy to find and navigating is smooth
check daisycargo hub – Smooth and tidy layout, browsing the store was simple.
Crate Corner – Playful twist, makes it easy to recall.
quick explore – Browsed this marketplace, content feels well structured and user-friendly
direct shop access – Layout is tidy, and the site is simple to navigate overall
stone vendor collective – Nice and neat layout, makes finding information easy
explore zenvendor marketplace – Interesting vendor hub, curious how it will grow with more sellers.
explore rubyridge studio – Nice design, content is structured clearly
WildVendorFinderOnline – Skimmed lightly, the layout is simple and easy to follow.
open this vendor marketplace – The site has a warm presentation style
discover hazelmarket portal – Well-structured pages, browsing is effortless.
Terra Gems – Minimalist interface, navigating sections was fast.
browse today – Stumbled upon this platform, layout is logical and pages are easy to follow
see blossomstore online – Charming branding, looking forward to checking new arrivals.
check the site – Found this marketplace, design is modern and sections are easy to follow
vendor hub homepage – Organized pages make it easy to find products
The Rack Hub – User-friendly interface, makes the marketplace intuitive.
marketplace homepage – Navigation is smooth, layout feels neat and browsing is intuitive
WindSelections – Took a glance, the layout is clear and straightforward.
visit zen vendor collective – Interesting platform idea, hopefully more vendors come onboard soon.
rubyvendorworkshop.shop – Smooth navigation and clear structure, makes reading posts enjoyable here
stone vendor pages hub – Very user-friendly, everything is structured logically
see the vendor studio site – Checked a few pages and they seem nicely structured
dawnbundle.shop – Neat name, browsing categories felt smooth and intuitive today.
check it out – Noticed this page, sections are well organized and intuitive
browse branchcrate online – Store idea looks appealing, categories sorted neatly for browsing.
shop collection – Found this outlet, layout is clean and easy to browse
Terra Gems – Catchy and modern, very easy to recall later.
open the clover marketplace – Layout is neat and sections are well organized
Vendor Collections – Organized interface, shopping is straightforward.
see their products – Navigation feels intuitive and the site looks well structured
WindShopSpot – Looked around casually, content is neat and approachable.
browse sagecrest hub – Navigation is simple and reading content is enjoyable
this online vendor workshop – Checked a few pages and they work nicely on mobile
online shopping hub – Took a peek today and it looks like a fresh store building up its catalog.
discover dawnmarket online – Tidy layout, pages load quickly and browsing is simple.
take a look – Browsed this page, sections are tidy and design feels modern
breezevendor.shop – Smooth browsing experience today, pages loaded really fast.
sunridge vendor hub – Really like how clear and easy-to-navigate this site is
Thistle Ventures – Clean and memorable, navigating categories was smooth.
browse coastridge hub – Navigation is intuitive and overall experience is pleasant
shopping portal link – Looked around quickly, interface is clean, modern, and user-friendly
Rooftop Treasures – Clear layout, exploring different sections was effortless.
WoodVendorPortal – Browsed casually, pages feel simple and well-laid-out.
sage vendor hub – Very straightforward layout, everything is easy to navigate
explore now – Warm, classic, and easy to remember for users.
browse deltacrate store – Smooth design, items are easy to locate and pages load quickly.
berrycrest trading place – Site feels well organized and moving around is effortless
interesting store – This name showed up today and it sounds pretty original.
ember shop link – The store name really has a distinctive charm.
Glade Meadow Corner – Cozy and approachable, giving the outlet a friendly vibe.
explore exchange – Came across this platform, everything is organized and browsing is smooth
willowlane – Clean, approachable visuals make the marketplace feel both cozy and professional.
discover bronzebasket shop – Eye-catching name, stands out nicely in searches.
quick shop link – Just visited, interface is neat and browsing is straightforward
open this vendor marketplace – Neat structure and smooth navigation make browsing simple
Scarlet Picks Hub – Friendly yet bold, leaves a strong impression.
SunnyDealsOnline – Browsing around, already seeing some highlights.
Thistle Treasures – Distinct and neat, browsing items felt effortless.
see the store – The wording is smooth and surprisingly memorable.
seastonevendor links – Enjoyable experience, content is clearly presented
explore the shop – Unique and carefully crafted, leaves a positive vibe.
see dewcrate marketplace – Smooth browsing experience with cleanly structured pages.
discover this store – The branding seems simple yet carefully planned.
explore teapot shop online – Branding feels quirky and fun, drew me in fast.
learn more here – Found this marketplace, navigation flows easily and pages are structured
MapleAndMain – This branding gives a cozy yet stylish impression for visitors.
browse the bronzecrate store – Appealing concept, marketplace shows good potential.
Glass Ridge Boutique – Feels sophisticated and exclusive while remaining welcoming.
Silk Isle Collection Spot – Refined and easy to remember, elegant brand identity.
browse the courtyard – Memorable and approachable, stands out nicely.
browse eastcrate portal – Organized sections, navigation feels simple and effective.
VendorTealFinds – Took a peek around, the design feels simple and uncluttered.
Tide Finds – Memorable and friendly, perfect for browsing new items.